Abstract
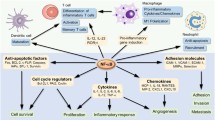
NFκB is a ubiquitous transcription factor involved in the proinflammatory response to cytokines (such as IL-1 or TNF-α) and some particular stresses. The unraveling of the molecular mechanisms involved in its activation is quite recent, particularly in the case of IL-1-stimulated cells, but the identification of the molecules involved in this pathway opens new prospects in both pharmacological and toxicological research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeuerle PA. Pro-inflammatory signalling: last pieces in the NF-κB puzzle? Curr Biol. 1998;8:R19-R22.
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–79.
Bonizzi G, Piette J, Schoonbroodt S et al. Reactive oxygen intermediate-dependent NF-kappaB activation by interleukin-1beta requires 5-lipoxygenase or NADPH oxidase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:1950–60.
Fujihara SM, Nadler SG. Modulation of nuclear protein import: a novel means of regulating gene expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;56:157–61.
Gosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappaB and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:225–60.
Hu Y, Baud V, Delhase M, Zhang P et al. Abnormal morphogenesis but intact IKK activation in mice lacking the IKKalpha subunit of IkappaB kinase. Science. 1999;284: 316–20.
Jobin C, Bradham CA, Russo MP et al. Curcumin blocks cytokine-mediated NF-kappa B activation and pro-inflammatory gene expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-kappa B kinase activity. J Immunol. 1999;163:3474–83.
Kopp E, Ghosh S. Inhibition of NF-kB by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science. 1994;265:956–9.
Kumar A, Dhawan S, Aggarwal BB. Emodin (3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation, IkappaB degradation, and expression of cell surface adhesion proteins in human vascular endothelial cells. Oncogene. 1998;17:913–18.
Li N, Karin M. Is NF-kB the sensor of oxidative stress? FASEB J. 1999;13:1137–43.
Li Q, Lu Q, Hwang JY et al. IKK1-deficient mice exhibit abnormal development of skin and skeleton. Genes Dev. 1999a;13:1322–8.
Li Q, Van Antwerp D, Mercurio F, Lee KF, Verma IM. Severe liver degeneration in mice lacking the IkappaB kinase 2 gene. Science. 1999b;284:321–5.
Lum RT, Kerwar SS, Meyer SM et al. A new structural class of proteasome inhibitors that prevent NF-kappa B activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55:1391–7.
Mercurio F, Manning AM. Multiple signals converging on NF-kappaB. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:226–32.
Milligan SA, Owens MW, Grisham MB. Differential regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B signal transduction pathways by hydrogen peroxide and tumor necrosis factor. Arch Biochem Biophys 1998;352:255–62.
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM et al. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene. 1999;18:6013–20.
Raes M, Renard P, Bosmans E, Delaive E, Remacle J. Effects of antioxidants on IL-6 secretion induced by IL-1 in human cultured lung fibroblasts. Involvement of NFκB. In: Pasquier C, Auclair C, Packer L. eds. Oxidative stress, cell activation and viral infection. Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag. 1994; 77–90.
Renard P, Zachary M-D, Bougelet C et al. Effects of antioxidant enzyme modulations on interleukin-1-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997;53: 149–60.
Rothwarf DM, Zandi E, Natoli G, Karin M. IKK-gamma is an essential regulatory subunit of the IkappaB kinase complex. Nature. 1998;395:297–300.
Schreck R, Albermann K, Baeuerle PA. Nuclear factor κB: an oxidative stress responsive transcription factor of eukaryotic cells (a review). Free Radic Res Commun. 1992a;17:221–37.
Schreck R, Meier B, Männel DN, Dröge W, Baeuerle PA. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kB activation in intact cells. J Exp Med. 1992b;175:1181–94.
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:405–55.
Singh S, Aggarwal BB. Activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB is suppressed by curcumin (diferulomethane). J Biol Chem. 1995;270:24995–5000.
Tanaka M, Fuentes ME, Yamaguchi K et al. Embryonic lethality, liver degeneration, and impaired NF-kappa B activation in IKK-beta-deficient mice. Immunity. 1999;10:421–9.
Tsai SH, Liang YC, Lin-Shiau SY, Lin JK. Suppression of TNFalpha-mediated NFkappaB activity by myricetin and other flavonoids through downregulating the activiy of IKK in ECV304 cells. J Cell Biochem. 1999;74:606–15.
Yin MJ, Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature. 1998;396:77–80.
Zhao Q, Lee FS. Mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinases 2 and 3 activate nuclear factor-kappaB through IkappaB kinase-alpha and IkappaB kinase-beta. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:8355–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Renard, P., Raes, M. The proinflammatory transcription factor NFκB: a potential target for novel therapeutical strategies. Cell Biol Toxicol 15, 341–344 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007652414175
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007652414175