Abstract
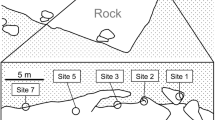
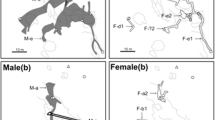
Reproductive ecology and mating system of the gobiid fish, Amblygobius phalaena, were studied on the coral reef at Sesoko Island, Okinawa, Japan. This goby usually lives in pairs, and maintains territories with several burrows for shelter and spawning. Although a few paired individuals changed partners, most pairs remained together over successive rounds of reproduction. Mate guarding by females appeared to prevent males from mating with other females. Spawnings were synchronous with semilunar periods. Several expected spawnings failed to occur (12%). These may have been caused by the delays in spawning preparation of the paired females or by the disturbance caused by a typhoon. A pair spawned in one of the several burrows within their home ranges. Eggs were deposited on the ceiling of the burrow, and were tended by the paired male for 3–4 days until embryos hatched. The males tended eggs at the expense of their feeding. Aggression toward fishes approaching their burrows were exhibited by the males as well as the females. Because of its low frequency in females, this behavior did not limit their ability to feed.
Similar content being viewed by others

References cited
Akihito, Prince 1984. Genus Amblygobius. pp. 245–246. In: H. Masuda, K. Amaoka, C. Araga, T. Uyeno & T. Yoshino (ed.) The Fishes of the Japanese Archipelago, Tokai University Press, Tokyo.
Barlow, G.W. 1984. Patterns of monogamy among teleost fishes. Arch. Fisch Wiss. 35: 75–123.
Barlow, G.W. 1986. A comparison of monogamy among freshwater and coral-reef fishes. pp. 767–775. In: T. Ueno, R. Arai, T. Taniuchi & K. Matsuura (ed.) Indo-Pacific Fish Biology: Proc. Second Internat. Conf. on Indo-Pacific Fishes, Ichthyological Soc. Japan, Tokyo.
Barlow, G.W. 1987. Spawning, eggs and larvae of the longnose filefish, Oxymonacanthus longirostris, a monogamous coralivore. Env. Biol. Fish. 20: 183–194.
Blumer, L.S. 1982. A bibliography and categorization of bony fishes exhibiting parental care. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 76: 1–22.
Breder, C.M. & D.E. Rosen. 1966. Modes of reproduction in fishes. Natural History Press, Garden City. 941 pp.
Gunasekera, R.M., K.F. Shim & T.J. Lam. 1996. Effect of dietary protein level on spawning performance and amino acid composition of eggs of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 146: 121–134.
Hourigan, T.F. 1989. Environmental determinants of butterflyfish social systems. Env. Biol. Fish. 25: 61–78.
van Iersel, J.J.A. 1953. An analysis of parental behaviour of the male three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus L.). Behaviour (Suppl.) 3: 1–159.
Kokita, T. & A. Nakazono. 1998. Plasticity in the mating system of the longnose filefish, Oxymonacanthus longirostris, in relation to mate availability. J. Ethol. 16: 81–89. Lindström, K. & C. Wennström. 1994. Expected future reproductive success and parental behaviour in the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus (Pisces, Gobiidae). J. Fish Biol. 44: 469–477.
Paulson, A.C. 1978. On the commensal habits of Ptereleotris, Acanthurus and Zebrasoma with fossorial Valenciennea and Amblygobius. Copeia 1978: 168–169.
Pressley, P.H. 1981. Pair formation and joint territoriality in a simultaneous hermaphrodite: the coral reef fish Serranus tigrinus. Z. Tierpsychol. 56: 33–46.
Reavis, R.H. 1997. The natural history of a monogamous coral-reef fish, Valenciennea strigata (Gobiidae): 2. Behavior, mate fidelity and reproductive success. Env. Biol. Fish. 49: 247–257.
Reavis, R.H. & G.W. Barlow. 1998. Why is the coral-reef fish Valenciennea strigata (Gobiidae) monogamous? Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 43: 229–237.
Reebs, S.G., F.G. Whoriskey, Jr. & G.J. FitzGerald. 1984. Diel patterns of fanning activity, egg respiration, and the nocturnal behavior of male three-spined sticklebacks, Gasterosteus aculeatus L. (f. trachurus). Can. J. Zool. 62: 329–334.
Robertson, D.R. 1991. The role of adult biology in the timing of spawning of tropical reef fishes. pp. 356–386. In: P.F. Sale (ed.) The Ecology of Fishes on Coral Reefs, Academic Press, San Diego.
Robertson, D.R., N.V.C. Polunin & K. Lieghton. 1979. The behavioral ecology of three Indian Ocean surgeonfishes (Acanthurus lineatus, A. leucosternon and Zebrasoma scopas): their feeding strategies, and social and mating systems. Env. Biol. Fish. 4: 125–170.
Rogers, W. 1988. Parental investment and division of labor in the Midas cichlid (Cichlasoma citrinellum). Ethology 79: 126–142.
Sano, M., M. Shimizu & Y. Nose. 1984. Food habits of teleostean reef fishes in Okinawa Island, southern Japan. Bull. Univ. Mus., Univ. Tokyo, 25: 1–128.
Sevenster, P. 1961. A causal analysis of a displacement activity: fanning in Gasterosteus aculeatus. Behaviour (Suppl.) 9: 1–70.
Takegaki, T. & A. Nakazono. 1999a. Reproductive behavior and mate fidelity in the monogamous goby, Valenciennea longipinnis. Ichthyol. Res. 46: 115–123.
Takegaki, T. & A. Nakazono. 1999b. Division of labor in the monogamous goby, Valenciennea longipinnis, in relation to burrowing behavior. Ichthyol. Res. 46: 125–129.
Takegaki, T. & A. Nakazono. 1999c. Responses of the egg-tending gobiid fish Valenciennea longipinnis to the fluctuation of dissolved oxygen in the burrow. Bull. Mar. Sci. 65: 815–823.
Thresher, R.E. 1984. Reproduction in reef fishes. T.F.H. Publications, Neptune City. 399 pp.
Torricelli, P., M. Lugli & G. Gandolfi. 1985. A quantitative analysis of the fanning activity in the male Padogobius martensi (Pisces: Gobiidae). Behaviour 92: 288–301.
Yanagisawa, Y. 1986. Paternal care in a monogamous mouth-brooding cichlid Xenotilapia flavipinnis in Lake Tanganyika. Japan. J. Ichthyol. 36: 249–261.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takegaki, T. Monogamous Mating System and Spawning Cycle in the Gobiid Fish, Amblygobius phalaena (Gobiidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes 59, 61–67 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007651718465
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007651718465