Abstract
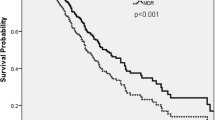
Two hundred and twenty-four episodes of Pseudomonas spp. complications that occurred in 179 consecutive patients with HIV infection were retrospectively reviewed. Pseudomonas spp. organisms were responsible for 11.6% of 1933 episodes of non-mycobacterial bacterial diseases (5.4% of 1072 episodes of sepsis), observed over an 8-year period; 20.7% of patients experienced disease relapses (45 episodes). These complications mostly involved lower airways (66 cases), urinary tract (53 episodes), and blood (34 cases), with Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated in 161 episodes, and other Pseudomonas spp. in the remaining 63 cases. An advanced HIV disease was frequently present (as expressed by a prior diagnosis of AIDS, a low CD4+ lymphocyte count, and leukopenia–neutropenia). Indwelling intravascular and urinary catheters were often associated with bacteremia and urinary tract involvement, respectively. More than 60% of patients were given antibiotics and/or cotrimoxazole in the month preceding the onset of Pseudomonas spp. disease. Bacterial strains isolated from our HIV-infected patients showed a favorable sensitivity to piperacillin, ceftazidime, imipenem, amikacin, tobramycin, and ciprofloxacin. An adequate antimicrobial treatment led to clinical and microbiological cure in 73.2% of patients at the first episode, and in 22.3% more subjects after one or more relapses. A lethal outcome occurred in only eight patients of 179 (4.5%), suffering from a far advanced HIV disease; P. aeruginosa infection directly contributed to death in four cases (sepsis, and/or pneumonia). Nosocomial disease occurred in 46.4% of the 224 episodes, and was significantly related to a previous diagnosis of AIDS, concurrent neutropenia, the occurrence of sepsis or urinary tract infection, disease relapses, the involvement of non-aeruginosa Pseudomonas spp., and a lethal outcome, compared with community-acquired infection. Our experience (the largest reported to date) confirms that Pseudomonas spp. (including non-aeruginosa Pseudomonas spp. organisms) is responsible for remarkable morbidity and mortality among patients with HIV infection, and may pose relevant problems to clinicians and microbiologists involved in the care of HIV-infected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burack JH, Hahn JA, Saint Maurice D, Jacobson MA. Microbiology of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia in persons with and at risk for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Arch Intern Med 1994; 154: 2589–2596.
Hirschtick RE, Glassroth J, Jordan MC, et al. Bacterial pneumonia in persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 845–851.
Furman AC, Jacobs J, Sepkowitz KA. Lung abscess in patients with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis 1996; 22: 81–85.
Johann-Liang R, Cervia JS, Noel GJ. Characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus-infected children at the time of death: An experience in the 1990s. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1997; 16: 1145–1150.
Bernard E, Carles M, Pradier C, Ozouf N, Dellamonica P. Septicé mies communautaires et nosocomiales chez le patient infecté par le virus de l'immunodéficience humaine. Presse Med 1996; 25: 746–750.
Brettle RP. Bacterial infections in HIV: the extent and nature of the problem. Int J STD AIDS 1997; 8: 5–15.
Frank U, Daschner FD, Schulgen G, Mills J. Incidence and epidemiology of nosocomial infections in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 25: 318–320.
Berger BJ, Hussain F, Roistacher K. Bacterial infections in HIV-infected patients. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1994; 8: 449–465.
DeMarais PL, Gertzen J, Weinstein RA. Nosocomial infections in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in a long-term care setting. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 25: 1230–1232.
Kovacs A, Leaf HL, Simberkoff MS. Management of the HIV-infected patient. Bacterial infections. Med Clin North Am 1997; 81: 319–343.
Fichtenbaum CJ, Dunagan WC, Powderly WG. Bacteremia in hospitalized patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus: A case-control study of risk factors and outcome. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 1995; 8: 51–57.
Tumbarello M, Tacconelli E, Caponera S, Cauda R, Ortona L. The impact of bacteraemia on HIV infection. Nine years experience in a large Italian university hospital. J Infect 1995; 31: 123–131.
Goetz AM, Squier C, Wagener MM, Muder RR. Nosocomial infections in the human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient: A two-year survey. Am J Infect Control 1994; 23: 334–339.
Flores G, Stavola JJ, Noel GJ. Bacteremia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in children with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis 1993; 16: 706–708.
Dropulic LK, Leslie JM, Eldred LJ, Zenilman J, Sears CL. Clinical manifestations and risk factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis 1995; 171: 930–937.
Fichtenbaum CJ, Woeltje KF, Powderly WG. Serious Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: A case-control study. Clin Infect Dis 1994; 19: 417–422.
Shepp DH, Tang ITL, Ramundo MB, Kaplan MH. Serious Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1994; 7: 823–831.
Kirkpatrick BL, Glover SC, Reeves DS, MacGowan AP. Microbiologically proven bacterial infections in AIDS. Postgrad Med J 1997; 73: 565–570.
Moore DA, Gazzard BG, Nelson MR. Central venous line infections in AIDS. J Infect 1997; 34: 35–40.
Manfredi R, Nanetti A, Ferri M, Coronado OV, Mastroianni A, Chiodo F. Profile and trend of antimicrobial resistance of non-opportunistic bacterial pathogens isolated from patients with HIV infection. J Antimicrob Chemother 1996; 38: 910–913.
Manfredi R, Nanetti A, Ferri M, Chiodo F. Xanthomonas maltophilia: an emerging pathogen in patients with HIV disease. Int J STD AIDS 1998; 9: 201–207.
Manfredi R, Nanetti A, Ferri M, Chiodo F. Bacteremia and respiratory involvement by Alcaligenes xylosoxidans in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1997; 16: 933–938.
Bonadio M, Gigli C, Maccanti O, Longo B, Smorfa A. Bloodstream infections in HIV-positive patients: A review of sixty-eight episodes. J Chemother 1998; 10: 243–247.
Gilks CF, Brindle RJ, Otieno LS, et al. Life-threatening bacteraemia in HIV-1 seropositive adults admitted to hospital in Nairobi, Kenya. Lancet 1990; 336: 545–549.
Vugia DJ, Kielbauch JA, Yeboue K, et al. Pathogens and predictors of fatal septicemia associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection in Ivory Coast, West Africa. J Infect Dis 1993; 168: 564–570.
Nathoo KJ, Chigonde S, Nhembe M, Ali MH, Mason PR. Community-acquired bacteremia in human immundeficiency virus-infected children in Harare, Zimbabwe. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1996; 15: 1092–1097.
Grant AD, Djomand G, Smets P, et al. Profound immuno-suppression across the spectrum of opportunistic disease among hospitalized HIV-infected adults in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire. AIDS 1997; 11: 1357–1364.
Krumholz HM, Sande MA, Lo B. Community-acquired bacteremia in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: clinical presentation, bacteriology, and outcome. Am J Med 1989; 86: 776–779.
Meyer CN, Skinhoj P, Prag J. Bacteremia in HIV-positive and AIDS patients: Incidence, species distribution, risk factors, outcome, and influence of long-term prophylactic antibiotic treatment. Scand J Infect Dis 1994; 26: 635–642.
Shanson DC. Septicaemia in patients with AIDS. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1990; 84 (Suppl. 1): 14–16.
Manfredi R, Costigliola P, Ricchi E, Chiodo F. Sepsis-bacteraemia and other infections due to non-opportunistic bacterial pathogens in a consecutive series of 788 patients hospitalized for HIV infection. Clin Ter 1993; 143: 279–290.
Ruiz Contreras J, Ramos JT, Hernandez Sampelayo T, et al. Sepsis in children with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1995; 14: 522–526.
Roilides E, Marshall D, Venzon D, Butler K, Husson R, Pizzo PA. Bacterial infections in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected children: The impact of central venous catheters and antiretroviral agents. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1991; 10: 813–819.
Andiman WA, Mezger JA, Shapiro E. Invasive bacterial infections in children born to women infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Pediatr 1994; 124: 846–852.
Krasinski H, Borkowsky W, Bonk S, Lawrence R, Chandwani S. Bacterial infections in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1988; 7: 323–328.
Roilides E, Butler KM, Husson RN, Mueller BU, Lewis LL, Pizzo PA. Pseudomonas infections in children with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 1992; 11: 547–553.
Edge MD, Rimland D. Community-acquired bacteremia in HIV-positive patients: Protective benefit of co-trimoxazole. AIDS 1996; 10: 1635–1639.
Schuster MG, Norris AH. Community-acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia in patients with HIV infection. AIDS 1994; 8: 1437–1441.
Witt DJ, Craven DE, McCabe WR. Bacterial infections in adult patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. Am J Med 1987; 82: 900–906.
Tumbarello M, Tacconelli E, Cauda R, Ortona L. Role of trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in preventing HIV-associated bacteraemia. AIDS 1997; 11: 1070–1071.
Nelson MR, Shanson DC, Barter GJ, Hawkins DA, Gazzard BG. Pseudomonas septicaemia associated with HIV. AIDS 1991; 5: 761–763.
Skoutelis AT, Murphy RL, MacDonell KB, Von Roenn JH, Sterkel CD, Phair JP. Indwelling central venous catheter infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1990; 3: 335–342.
Eng RHK, Bishburg E, Smith SM, Geller H, Kapila R. Bacteremia and fungemia in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol 1986; 86: 105–107.
Kielhofner M, Atmar RL, Hammill RJ, et al. Life-threatening Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in patients with human immunedeficiency virus infection. Clin Infect Dis 1992; 14: 403–411.
Franzetti F, Cernuschi M, Esposito R, Moroni M. Pseudomonas infections in patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. J Intern Med 1992; 231: 437–443.
Baron AD, Hollander H. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bronchopulmonary infection in late human immunodeficiency virus disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 1993; 148: 992–996.
O'Reagan S, Russo P, Lapointe N, Rousseau E. AIDS and urinary tract. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1990; 3: 244–250.
Traill ZC, Miller RF, Ali N, Shaw PJ. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bronchopulmonary infection in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus disease. Br J Radiol 1996; 69: 1099–1103.
Milgrim LM, Rubin JS, Rosenstreich DL, Small CB. Sinusitis in human immunodeficiency virus infection: Typical and atypical organisms. J Otolaryngol 1994; 23: 450–453.
Nash E, Livingston P, Margo CE. Orbital cellulitis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol 1997; 115: 677–678.
Roca B, Vilar C, Perez EV, Saez Royuela A, Simon E. Breast abscess with lethal septicemia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a patient with AIDS. Presse Med 1996; 25: 803–804.
Von Wichmann MA, Castiella A, Rodriguez Arrondo F, Iribarren JA, Arrizabalaga J, Lopez P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa cholangitis in a HIV patient. Am J Gastroenterol 1998; 93: 483–484.
Roig P, Orti A, Navarro V. Meningitis due to Pseudomonas stutzeri in a patient infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis 1996; 22: 587–588.
Tumaliuan JA, Stambouly JJ, Schiff RJ, Pahwa SG, Bakshi SS. Pseudomonas pericarditis and tamponade in an infant with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1997; 151: 207–208.
Raviglione MC, Battan R, Pablos Mendez A, Aceves Casillas P, Mullen MP, Taranta A. Infections associated with Hickman catheters in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.Am J Med 1989; 86: 780–786.
Caperna J, Barber RE, Toerner JG, Mathews WC. Estimation of the effect of neutropenia on rates of clinical bacteraemia in HIV-infected patients. Epidemiol Infect 1998; 120: 71–80.
Keiser P, Higgs E, Smith J. Neutropenia is associated with bacteremia in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Am J Med Sci 1996; 312: 118–122.
Domingo P, Ferre A, Baraldes MA, Ris J, Sanchez F. Remission of relapsing Pseudomonas aeruginosa bronchopulmonary infection following antiretroviral therapy. Arch Intern Med 1998; 158: 929–930.
Nichols L, Balogh K, Silverman M. Bacterial infections in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clinico-pathologic correlations in a series of autopsy cases. Am J Clin Pathol 1989; 92: 787–790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manfredi, R., Nanetti, A., Ferri, M. et al. Pseudomonas spp. complications in patients with HIV disease: An eight-year clinical and microbiological survey. Eur J Epidemiol 16, 111–118 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007626410724
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007626410724