Abstract
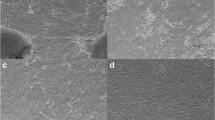
A cell line, PHL, has been successfully established from newly hatched herring larvae. The cells are maintained in growth medium consisting of Leibovitz's L-15 supplemented with 15% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and have been cryopreserved and maintain viability after thawing. These cells retain a diploid karotype after 65 population doublings. PHL are susceptible to infection by the North American strain of viral hemorrhagic septicemia (VHS) virus, and are sensitive to the cytotoxic effects of naphthalene, a common environmental contaminant. Naphthalene is a component of crude and refined oil, and may be found in the marine environment following acute events such as oil spills. In addition, chronic sources of naphthalene contamination include offshore drilling and petroleum contamination from areas such as docks and marinas that have creosote-treated docks and pilings and also receive constant small inputs of petroleum products. This cell line should be useful for investigations of the toxicity of naphthalene and other petroleum components to juvenile herring. In addition, studies of the VHS virus will be facilitated by the availability of a susceptible cell line from an alternative species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babich H, Borenfreund E. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity assays with cultured fish cells: a review. Toxicol in Vitro. 1991;5:91–100.
Bols NC, Lee LEJ. Technology and uses of cell cultures from the tissues and organs of bony fish. Cytotechnology. 1991;6:163–87.
Bols NC, Ganassin RC, Tom DJ, Lee LEJ. Growth of fish cell lines in glutamine-free medium. Cytotechnology. 1994;16:159–66.
Bols NC, Schirmer K, Joyce EM, Dixon DG, Greenberg BM, Whyte JJ. Ability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to induce 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activity in a trout liver cell line. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. 1999;44:118–28.
Brezden CB, Rauth AM. Differential cell death in immortalized and non-immortalized cells at confluency. Oncogene. 1996;12:201–6.
Chen TR. In situ detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by Hoechst 33258 stain. Exp Cell Res. 1977;104:255–62.
Cobb JP, Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE, Buchman TG. Mechanisms of cell injury and death. Br J Anaesth. 1996;77:3–10.
Collodi P, Kamei Y, Ernst T, Miranda C, Buhler DR, Barnes DW. Culture of cells from zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio) embryo and adult tissues. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1992;8:43–61.
Freshney RI. Characterization. In: Culture of animal cells, a manual of basic technique, 3rd edn. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1994a:197–217.
Freshney RI. The culture environment. In: Culture of animal cells, a manual of basic technique, 3rd edn. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1994b:71–103.
Fryer JL, Lannan CN. Three decades of fish cell culture: a current listing of cell lines derived from fishes. J Tiss Cult Methods. 1994;1:87–94.
Ganassin RC, Bols NC. Culture of cells from poikilotherms. In: Griffiths JB, Doyle A, Newell DG, eds. Cell and tissue culture: laboratory procedures. Chichester: Wiley; 1997:23:A1.1–1.9.
Hahn ME, Woodward BL, Stegemen JJ, Kennedy, SW. Rapid assessment of induced cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A1) protein and catalytic activity in fish hepatoma cells grown in multi-well plates. Environ Toxicol Chem. 1996;15:582–91.
Hammond DK, Strobel HW. Ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase activity in intact human cells. Toxicol in Vitro. 1992;6:41–6.
Hart JL. Pacific fishes of Canada. Fisheries Research Board of Canada; 1973;96.100; Bulletin 180.
Hayasaka K, Sato M, Mitani H, Shima A. Transfection of cultured fish cells RBCF-1 with exogenous oncogene and their resistance to malignant transformation. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1990;96B:349–54.
Kocan RM, Hose JE, Brown ED, Baker TT. Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi) embryo sensitivity to Prudhoe Bay petroleum hydrocarbons: laboratory evaluation and in situ exposure at oiled and unoiled sites in Prince William Sound. Can J Fish Aquat Sci. 1996;53:2366–75.
Kocan RM, Bradley M, Elder N, Meyers T, Batts W, Winton J. North American strain of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus is highly pathogenic for laboratory-reared Pacific herring. J Aquat Anim Health. 1997;9:279–90.
Lee LEJ, Clemons JH, Bechtel DG et al. Development and characterization of a rainbow trout liver cell line expressing cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenase activity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1993;9:279–94.
Mackay D, Shiu WY, Ma KC. Illustrated handbook of physical-chemical properties and environmental fate for organic chemicals (2). Chelsea, MI: Lewis Publishers; 1992.
Marty GD, Freiberg EF, Meyers TR, Wilcock J, Farver TB, Hinton DE. Viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus, Ichthyophonus hoferi, and other causes of morbidity in Pacific herring Clupea pallasi spawning in Prince William Sound, Alaska, USA. Dis Aquat Organisms 1998;26:15–40.
Meyers TR, Short S, Lipson K et al. Association of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus with epizootic hemorrhages of the skin in Pacific herring Clupea harengus pallasi from Prince William Sound and Kodiak Island, Alaska, USA. Dis Aquat Organisms. 1994;19:27–37.
Middaugh DP, Shelton ME, McKenney CL Jr, Chapman PJ, Courtney LA. Preliminary observations on responses of embryonic and larval Pacific herring, Clupea pallasi, to neutral fraction biodegeneration products of weathered Alaska North Slope oil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1998;34:188–96.
National Research Council. Oil in the sea: inputs, fates and effects. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1985: 601 p.
Ohno S, Wolf U, Atkin NB. Evolution from fish to mammals by gene duplication. Hereditas. 1968;59:169–87.
Saeki K, You A, Kato M, Miyazono K, Yazaki Y, Takaku F. Cell density-dependent apoptosis in HL-60 cells, which is mediated by an unknown soluble factor, is inhibited by TGF-β and overexpression of bcl-2. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:20003–10.
Schaeffer WI. Terminology associated with cell, tissue, and organ culture, molecular biology, and molecular genetics. Tissue Culture Association Terminology Committee. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990;26:97–101.
Schirmer K, Chan AGJ, Greenberg BM, Dixon DG, Bols NC. Methodology for demonstrating and measuring the photocytotoxicity of fluoranthene to fish cells in culture. Toxicol in Vitro. 1997;11:107–19.
Schirmer K, Dixon DG, Greenberg BM, Bols NC. Ability of 16 priority PAHs to be directly cytotoxic to a cell line from the rainbow trout gill. Toxicology. 1998;15:129–41.
Schirmer K, Herbrick JS, Greenberg BM, Dixon DG, Bols NC. Use of fish gill cells in culture to evaluate the cytotoxicity and photocytotoxicity of intact and photomodified creosote. Environ Toxicol Chem. 1999;6:1277–88.
Short JW, Nelson BD, Heintz RA et al. Mussel tissue and sediment hydrocarbon data synthesis, 1989–1995. Auke Bay Laboratory, AK: NOAA, NMFS; 1996. State/Federal natural resource damage assessment final report, subtidal study number 8.
Sikkema J, de Bont JAM, Poolman B. Interactions of cyclic hydrocarbons with biological membranes. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:8022–8.
Varanasi U, Brown DW, Hom T et al. Survey of Alaskan subsistence fish, marine mammal, and invertebrate samples collected 1989–91 for exposure to oil spilled from the Exxon Valdez. US Department of Commerce; 1993. NOAA Tech Memo. NMFS-NWFSC-12.
Wolf K. Fish viruses and fish viral diseases. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press; 1988.
Yasaka T, Ichisaka S, Katsumoto T et al. Apoptosis involved in density-dependent regulation of rat fibroblastic 3Y1 cell culture. Cell Struct Funct. 1996;21:483–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganassin, R., Sanders, S., Kennedy, C. et al. Development and characterization of a cell line from Pacific herring, Clupea harengus pallasi, sensitive to both naphthalene cytotoxicity and infection by viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus. Cell Biol Toxicol 15, 299–309 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007615818427
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007615818427