Abstract
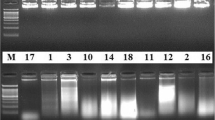
A simple procedure for DNA isolation from processed dried commercial samples of tea is described. The method involves a modified CTAB procedure employing extensive washing, use of 1% PVP to remove polyphenolics and a single phenol:chloroform extraction step. The average yield ranges from 164–494 μg/g tea sample for various market samples. The DNA obtained from 11 different brands of tea using this procedure were consistently amplifiable (using both RAPD primers as well as defined sequences as primers) and digestible with restriction endonucleases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox AV, Bennett MD and Dyer TA (1992) Use of the PCR to detect spacer size heterogeneity in plant 5 s rRNA gene clusters and to locate such clusters in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Theor Appl Genet 83: 684–690.
John ME (1992) An efficient method for isolation of RNA and DNA from plants containing polyphenolics. Nuc Acids Res 20: 2381.
Kim CS, Lee CH, Shin JS, Chung YS and Hyung NI (1997) A simple and rapid method for isolation of high quality genomic DNA from fruit trees and conifers using PVP. Nuc Acids Res 25: 1085–1086.
Matsumoto S, Takeuchi A, Hayatsu M and Kondo S (1994) Molecular cloning of phenyle alanine ammonia lyase cDNA and classification of varieties and cultivars of tea plants using the tea PAL cDNA as a probe. Theor Appl Genet 89: 671–675.
Rogers SU and Bendich AJ (1988) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5: 69–76.
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KA, Jorgenson RA and Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer length polymorphism in Barley: Mendalian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA). 8: 8014–18.
Tai TH and Tanksley SD (1990) A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue. Plant Mol Biol Reptr 8: 297–303.
Takeuchi A, Matsumoto S, Hayatsu M(1994) Chalcone synthase from C. sinensis: isolation of cDNA and the organ specific and sugar responsive expression of genes. Plant Cell Physiol 35: 1011–18.
Wachira FN, Waugh R, Hackett CA and Powell W(1995) Detection of genetic diversity in tea using RAPD markers. Genome 38: 201–210.
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA and Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nuc Acids Res 18: 6531–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M., Bandana & Ahuja, P. Isolation and PCR Amplification of Genomic DNA from Market Samples of Dry Tea. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 17, 171–178 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007562802361
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007562802361