Abstract
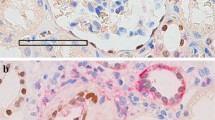
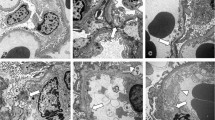
Eighteen renal biopsy specimens from patients with mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis type I (MCGN-I) evaluated by both light and electron microscopy as well as immunofluorescence microscopy and whose full clinical data were available were examined quantitatively. As control 10 biopsy specimens of kidneys removed because of trauma were used. Morphometric investigations were performed by means of a computer image analysis system to evaluate the glomerular expression of α-SMA in MCGN-I, as well as to determine whether this parameter could correlate with quantitatively analysed glomerular cells and mesangial areas. Another purpose of this study was to verify if the expression of α-SMA correlated with the intensity of glomerular leukocyte infiltrates in this glomerulopathy. The morphometric study revealed that mean values of the expression of α-SMA, total glomerular cells per total glomerular area, mesangium (% of total glomerular area), CD 45RB+, CD 43+, CD 20+ and CD 68+ cells were in MCGN-I patients increased in comparison with normal controls. Moreover, in the MCGN-I group, but not in controls, significant positive correlation existed between the glomerular expression of α-SMA and total glomerular cells per total glomerular area, mesangium (% of total glomerular area), as well as CD 45RB+ cells and CD 68+ cells. Significant positive correlation between α-SMA staining and total glomerular cells and mesangial areas suggested that increased α-SMA expression might be in MCGN-I an indicator of mesangial cell activation and mesangial matrix production. The significant positive correlation between the glomerular expression of α-SMA and glomerular CD 68+ cells requires further investigations to elucidate whether monocytes/macrophages play a role in the process of inducing myofibroblast phenotype in mesangial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpers, C. E., Hudkins, K. L., Gown, A. M., Johnson, R. J.: Enhanced expression of ‘muscle specific’ actin in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int., 41, 1134 (1992).
Barbiano di Belgiojoso, G., Tarantino, A., Colasanti, G., Bazzi, C., Guerra, L., Durante, A.: The prognostic value of some clinical and histological parameters in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN). Nephron, 19, 250 (1977).
Cameron, J. S., Turner, D. R., Heaton, J.: Idiopathic mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Comparison of types I and II in children and adults and long-therm prognosis. Am. J. Med., 74, 175 (1983).
Cattran, D. C., Cardella, C. J., Roscoe, J. M.: Results of controlled drug trial in membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int., 27, 436 (1985).
Danilewicz, M., Wągrowska-Danilewicz, M.: Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Comparison of types I, II and III. A quantitative study. J. Nephrol., 7, 284 (1994).
Floege, J., Johnson, R. J., Gordon, K., Iida, H., Pritzl, P., Yoshimura, A., Campbell, C., Alpers, C. E., Couser, W. G.: Increased synthesis of extracellular matrix in mesangialproliferative nephritis. Kidney Int., 40, 477 (1991).
Goumenos, D. S., Brown, C. B., Shortland, J., El Nahs, M.: Myofibroblasts, predictors of progression in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant., 9, 1418 (1994).
Hattori, M., Kim, Y., Steffes, M. W., Mauer, S. M.: Structural-functional relationships in type I mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int., 43, 381 (1993).
Hattori, M., Horita, S., Yoshioka, T., Yamaguchi, Y., Kawaguchi, H., Ito, K.: Mesangial phenotypic changes associated with cellular lesions in primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Am. J. Kidney Dis., 30, 632 (1997).
Imai, E., Arai, M., Isaka, J., Wada, A., Sugiura, T., Akagi, Y., Miyazaki, M., Fujiwara, Y., Ueda, M., Kamada, T.: Phenotypic change of the mesangial cells is induced by over-expression of TGF-β in vivo glomerulus. Am. J. Soc. Nephrol., 5, 782 (1994).
Inaba, S., Tanizawa, T., Igarashi, T.: Long-term follow-up of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type II and pregnancy: a case report. Clin. Nephrol., 32, 10 (1989).
Johnson, R. J., Ida, H., Alpers, C. E.: Expression of smooth muscle cell phenotype by rat mesangial cells in immune complex nephritis. J. Clin. Invest., 87, 847 (1991).
Macpherson, B. R., Leslie, K. O., Lizaso, K. V., Schwarz, J. E.: Contractile cells of the kidney in primary glomerular disorders: an immunohistochemical study using an anti-alpha-smooth muscle actin monoclonal antibody. Hum. Pathol., 24, 710 (1993).
Oba, S., Kimura, K., Suzuki, N., Mise, N., Tojo, A., Miyashita, K., Konno, Y., Hirata, Y., Goto, A., Omata, M.: Relevance of periglomerular myofibroblasts in progression of human glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Kidney Dis., 32, 419 (1998).
Roberts, I. S. D., Burrows, C., Shanks, J. H., Venning, M., McWilliam, L. J.: Interstitial myofibroblasts: predictors of progression in membranous glomerulopathy. J. Clin. Pathol., 50, 123 (1997).
Stephenson, L. A., Haney, L. B., Hussaini, I. M., Karns, L. R., Glass, W. F.: Regulation of smooth muscle alpha-actin expression and hypertrophy in cultured mesangial cells. Kidney Int., 54, 1175 (1998).
Swainson, C. P., Robson, J. S., Thomson, D., MacDonald, M. K.: Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis: A long-term study of 40 cases. J. Pathol., 141, 449 (1983).
Tamimi, N. A., Stevens, P. E., O'Donnell, P. L., Strange, P. G., Muchaneta-Kubara, E. C., El Nahas, A. M.: Expression of cytoskeletal proteins differentiates between progressors and non-progressors in treated idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Exp. Nephrol., 6, 217 (1998).
Wągrowska-Danilewicz, M., Danilewicz, M.: Glomerular and interstitial immune cell populations in idiopathic mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis (MCGN) — a monoclonal antibody study of three morphological subtypes. J. Nephrol., 7, 347 (1994).
Weibel, E. R.: Point counting methods. In: Weibel, E. R., Stereological Methods, vol. 1, Academic Press, London 1979, pp. 101–159.
Yoshiara, S., White, R. H. R., Raafat, F., Smith, N. C., Shah, K. J.: Glomerular morphometry in reflux nephropathy: functional and radiological correlations. Pediatr. Nephrol., 7, 15 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danilewicz, M., Wagrowska-Danilewicz, M. Glomerular Expression of α-Smooth Muscle Actin (α-SMA) in Idiopathic Mesangiocapillary Glomerulonephritis Type I. A Quantitative Study. Int Urol Nephrol 31, 827–838 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007166117916
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007166117916