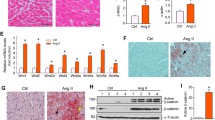
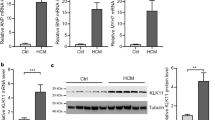
Abstract
The involvement of the Renin Angiotensin System (RAS) and the role of its primary effector, angiotensin II (Ang II), in etiology of myocardial hypertrophy and ischemia is well documented. In several animal models, the RAS is activated in cardiac cell types that express the receptor AT1, and/or AT2, through which the Ang II mediated effects are promoted. In this article, we briefly review recent experimental evidence on the critical role of a prominent signaling pathway, the Jak/Stat pathway in activation and maintenance of the local RAS in cardiac hypertrophy and ischemia. Recent studies in our laboratory document that the promoter of the prohormone angiotensinogen (Ang) gene serves as the target site for STAT proteins, thereby linking the Jak/Stat pathway to activation of heart tissue autocrine Ang II loop. Stat5A and Stat6, are selectively activated when the heart is subjected to ischemic injury, whereas activation of Stat3 and Stat5A is involved in myocardial hypertrophy. Blockage of RAS activation by treatment with specific inhibitor promotes a remarkable recovery in functional hemodynamics of the myocardium. Thus, activation of selective sets of Stat proteins constitutes the primary signaling event in the pathogenesis of myocardial hypertrophy and ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeunemaitre X, Soubrier F, Kotelevtsev YV, Lifton RP, Williams CS, Charru A, Hunt SC, Hopkins PN, Williams RR, Lalouel JM, Corvol P: Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell 71: 169–180, 1992
Kimura S, Mullins JJ, Bunnemann B, Metzger R, Hilgenfeldt U, Zimmermann F, Jacob H, Fuxe K, Ganten D, Kaling M: High blood pressure in transgenic mice carrying the rat angiotensinogen gene. EMBO J 11: 821–827, 1992
Pfeffer JM, Pfeffer MA, Mirsky I, Braunwald E: Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy and prevention of left ventricular dysfunction by captopril in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 3310–3314, 1982
DiBona GF, Jones SY, Brooks VL: Ang II receptor blockade and artrial baroreflex regulation of renal nerve activity in cardiac failure. Am J Phys 269: R1189–R1196, 1995
Reid JL, MacFadyen RJ, Squire IB, Lees KR: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in heart failure: Blood pressure changes after the first dose. Am Heart J 126: 794–797, 1993
Waeber B, Brunner HR: Cardiovascular hypertrophy: Role of angiotensin II and bradykinin. J Cardiol Pharm 27(suppl 2): S36–S40, 1996
Bulpitt CJ: Quality of life with ACE inhibitors in chronic heart failure. J Cardiol Pharm 27(suppl 2): S31–S35, 1996
Eberhardt RT, Kevak RM, Kang PM, Frishman WH: Angiotensin II receptor blockade: an innovative approach to cardiovascular pharmacotherapy. J Clin Pharm 33: 1023–1038, 1993
Sadoshima J, Izumo S: Molecular characterization of angiotensin II induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes and hyperplasia of cardiac fibroblasts. Critical role of the AT1 receptor subtype. Circ Res 73: 413–423, 1993
Duff JL, Marrero M, Paxton W, Schieffer B, Bernstein KE, Berk BC: Angiotensin II signal transduction and the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway. Cardiovasc Res 30: 511–517, 1995
Booz GW, Baker KM: Molecular signalling mechanisms controlling growth and function of the cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res 30: 537–543, 1995
Schieffer B, Paxton W, Marrero M, Bernstein K: Importance of tyrosine phosphorylation in Angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling. Hypertension 27: 476–480, 1996
Bernstein K, Marrero M: The importance of tyrosine phosphorylation in angiotensin II signaling. Trends Cardiovasc Med 6: 179–187, 1996
Ihle JN: Stats: Signal transducers and activators of transcription. Cell 84: 331–334, 1996
Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE Jr: STAT3: A STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 264: 95–98, 1994
Durbin JE, Hackenmiller R, Simon MC, Levy DE: Targeted disruption of the mouse STAT1 gene results compromised innate immunity to viral diseases. Cell 84: 443–450, 1996
Meraz MA, White JM, Sheeba KC, Bach EA, Rodig SJ, Dighe AS, Kaplan DH, Schreiber RD: Targeted disruption of the STAT1 gene in mice reveals unexpected physiologic specificity in the Jak/STAT signaling pathway. Cell 84: 431–442, 1996
Kaplan MH, Sun YL, Hoey T, Grusby MJ: Impaired IL-12 responses and enhanced development of Th2 cells in STAT4-deficient mice. Nature 382: 174–177, 1996
Kaplan MH, Schindler U, Smiley ST, Grusby MJ: STAT6 is required for mediating responses to IL-4 and for development of Th2 cells. Immunity 4: 313–319, 1996
Liu X, Robinson GW, Wagner KU, Garret L, Wynshaw-Boris A, Hennighausen L: STAT5A is mandatory for adult mammary gland development and lactogenesis. Genes Dev 11: 179–186, 1997
Wood TJ, Sliva D, Lobie PE, Pircher TJ, Gouilleux F, Wakao H, Gustafsson JA, Groner B, Norstedt G, Haldosen LA: Mediation of growth hormone-dependent transcriptional activation by mammary gland factor/STAT 5. J Biol Chem 270: 9448–9453, 1995
Gouilleux F, Pallard C, Dusanter-Fourt I, Wakao H, Haldosen LA, Norstedt G, Levy D, Groner B: Prolactin, growth hormone, erythropoietin and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor induce MGF-STAT5 DNA binding activity. EMBO J 14: 2005–2013, 1995
Novak U, Mui A, Miyajima A, Paradiso L: Formation of STAT5-containing DNA binding complexes in response to colony-stimulating factor-1 and platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem 271: 18350–18354, 1996
Leaman DW, Pisharody S, Flickinger TW, Commane MA, Schlessinger J, Kerr IM, Levy DE, Stark GR: Roles of JAKs in activation of STATs and stimulation of c-fos gene expression by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol 16: 369–375, 1996
Gouilleux F, Wakao H, Mundt M, Groner B: Prolactin induces phosphorylation of Tyr694 of STAT5 (MGF), a prerequisite for DNA binding and induction of transcription. EMBO J 13: 4361–4369, 1994
Ghilardi N, Ziegler S, Wiestner A, Stoffel R, Heim MH, Skoda RC: Defective STAT signaling by the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 6231–6235, 1996
Baumann H, Morella KK, White DW, Dembski M, Bailon PS, Kim H, Lai CF, Tartaglia LA: The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 8374–8378, 1996
Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Paxton WG, Heerdt L, Berk BC, Delafontaine P, Bernstein KE: Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature 375: 247–250, 1995
Bhat GJ, Thekkumkara TJ, Thomas WG, Conrad KM, Baker KM: Angiotensin II stimulates sis-inducing factor-like DNA binding activity. Evidence that the AT1A receptor activates transcription factor-STAT91 and/or a related protein. J Biol Chem 269: 31443–31449, 1994
Mascareno E, Dhar M, Siddiqui MAQ: Signal Transduction and Activator of Transcription (STAT) protein-dependent activation of angiotensinogen promoter: A cellular signal for hypertrophy in cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 5590–5594, 1998
Xu X, Sun YL, Hoey T: Cooperative DNA binding and sequence-selective recognition conferred by the STAT amino-terminal domain. Science 273: 794–797, 1996
Horvath CM, Wen Z, Darnell JE Jr: A STAT protein domain that determines DNA sequence recognition suggests a novel DNA-binding domain Genes Dev 9: 984–994, 1995
Hemmann U, Gerhartz C, Heesel B, Sasse J, Kurapkat G, Grotzinger J, Wollmer A, Zhong Z, Darnell JE Jr, Graeve L, Heinrich PC, Horn F: Differential activation of acute phase response factor/STAT3 and STAT1 via the cytoplasmic domain of the interleukin 6 signal transducer gp130. II. Src homology SH2 domains define the specificity of STAT factor activation. J Biol Chem 271: 12999–13007, 1996
Karin M: Signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus through the phosphorylation of transcription factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6: 415–424, 1994
Gotoh A, Takahira H, Mantel C, Litz-Jackson S, Boswell HS, Broxmeyer HE: Steel factor induces serine phosphorylation of STAT3 in human growth factor-dependent myeloid cell lines. Blood 88: 138–145, 1996
David M, Petricoin E III, Benjamin C, Pine R, Weber MJ, Larner AC: Requirement for MAP kinase (ERK2) activity in interferon alpha-and interferon beta-stimulated gene expression through STAT proteins. Science 269: 1721–1723, 1995
Zhong Z, Wen Z, Darnell JE Jr: STAT3: A STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science 264: 95–98, 1994
Seidel HM, Milocco LH, Lamb P, Darnell JE, Stein RB, Rosen J: Spacing of palindromic half sites as a determinant of selective STAT (signal transducers and activators of transcription) DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 3041–3045, 1995
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GM: Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264: 1415–1421, 1994
Lew DJ, Decker T, Strehlow I, Darnell JE Jr.: Overlapping elements in the guanylate-binding protein gene promoter mediate transcriptional induction by alpha and gamma interferons. Mol Cell Biol 11: 182–191, 1991
Hill CS, Treisman R: Differential activation of c-fos promoter elements by serum, lysophosphatidic acid, G proteins and polypeptide growth factors. EMBO J 14: 5037–5047, 1995
Kojima H, Nakajima K, Hirano T: IL-6-inducible complexes on an IL-6 response element of the junB promoter contain STAT3 and 36 kDa CRE-like site binding protein(s). Oncogene 12: 547–554, 1996
Zhang D, Sun M, Samols D, Kushner I: STAT3 participates in transcriptional activation of the C-reactive protein gene by interleukin-6. J Biol Chem 271: 9503–9509, 1996
Lavrovsky Y, Drummond GS, Abraham NG: Downregulation of the human heme oxygenase gene by glucocorticoids and identification of 56b regulatory elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 218: 759–765, 1996
Bugno M, Graeve L, Gatsios P, Koj A, Heinrich PC, Travis J, Kordula T: Identification of the interleukin-6/oncostatin M response element in the rat tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) promoter. Nucl Acid Res 23: 5041–5047, 1995
Kordula T, Travis J: The role of STAT and C/EBP transcription factors in the synergistic activation of rat serine protease inhibitor-3 gene by interleukin-6 and dexamethasone. Biochem J 313: 1019–1027, 1996
McWhinney CD, Dostal DE, Baker KM: Angiotensin II activates STAT5 through Jak2 kinase in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 30: 751–761, 1998
Pan J, Fukuda K, Saito M, Matsuzaki J, Kodama H, Sano M, Hori S, Ogawa: Biphasic activation of the Jak/STAT pathway by angiotensin II in rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 84: 1127–1136, 1998
Ihle JN, Kerr IM: Jaks and STATs in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet 11: 69–74, 1995
Heim MH: The Jak-STAT pathway: Specific signal transduction from the cell membrane to the nucleus. Eur J Clin Invest 26: 1–12, 1996
Schindler C, Darnell JE Jr.: Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: The Jak-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 64: 621–651, 1995
Hirota H, Yoshida K, Kishimoto T, Taga T: Continuous activation of gp130, a signal transducing receptor component for interleukin 6 related cytokines, causes myocardial hypertrophy in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 4862–4866, 1995
Pennica D, King KL, Shaw KJ, Luis E, Rullamas J, Luoh SM, Darbonne WC, Knutzon DS, Yen R, Chien KR, Baker JB, Wood W: Expression cloning of cardiotrophin 1, a cytokine that induces cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 1142–1146, 1995
Kodama H, Fukuda K, Pan J, Makino S, Baba A, Hori S, Ogawa S: Leukemia inhibitory factor, a potent cardiac hypertrophic cytokine, activates the Jak/STAT pathway in rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 81: 656–663, 1997
Hirota H, Chen J, Betz U, Rajewsky K, Gu Y, Ross J, Muller W, Chien KR: Loss of a gp130 cardiac muscle cell survival pathway is a critical event in the onset of heart failure during biomechanical stress. Cell 97: 189–198, 1999
Pan J, Fukuda K, Kodama H, Makino H, Makino S, Takahashi T, Sano M, Hori S, Ogawa S: Role of angiotensin II in activation of the Jak/ STAT pathway induced acute pressure overload in the rat heart. Circ Res 81: 611–617, 1997
Takeda K, Kaisho T, Yoshida N, Takeda J, Kishimoto T, Akira S: STAT3 activation is responsible for IL-6 dependent T cell proliferation through preventing apoptosis: Generation and characterization of T cell specific STAT3 deficient mice. J Immunol 161: 4652–4660, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mascareno, E., Siddiqui, M. The role of Jak/STAT signaling in heart tissue renin-angiotensin system. Mol Cell Biochem 212, 171–175 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007157126806
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007157126806