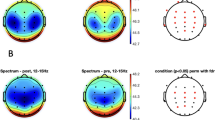
Abstract
Age-related specific features of the regulation of the CNS functional state (relaxation) were studied in adolescents between the ages of 14 and 15 years using 6-Hz rhythmic stimulation. The dynamics of the EEG findings (spectral power density, coherence functions) in the quiet wakefulness–relaxation–initial-state cycle was analyzed. The dynamics of the functional state was controlled by changes in the electrodermal resistance (EDR). The data showed that the studied group of adolescents was heterogeneous by the effectiveness of self-regulation: the majority was characterized by marked shifts whose distribution character was close to normal; the others, by mild EDR changes. It was shown that, with the use of rhythmic stimulation, relaxation shifts were more marked than those induced by common psychotherapeutic techniques. The basic relaxation changes in the EEG parameters are related to changes in the coherence function values, i.e., increases in its values, especially those of distant relations (with the focus) of significant connections in the frontal regions. The rate of the occurrence of relaxation changes in the coherence values is substantially higher in the low-frequency band (5 to 7 Hz) than in the EEG α-band, constituting 20 to 50% in terms of different relations. The revealed specific features of the relaxation dynamics of the EEG parameters are analyzed in the age-related aspect. The influence of higher structures of the CNS and puberty-related rearrangements in the system of neuroendocrine regulation on the effectiveness of the regulatory function is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Everly, J.C. and Rosenfeld, R., Stress (Priroda i lechenie) (Stress (Nature and Treatment)), Moscow: Meditsina, 1985.
Machac, M., Changes in Cortical Level in Saliva Following Relaxation-Activation Autoregulation Intervention, Act. Nerv. Super. 1987, vol. 29, no. 3, p. 159.
Roberts, T.B., Multistate Education: Metacognitive Implication of the Minbody Psychologies, J. Transpersonal Psychol., 1989, vol. 21, no. 1, p. 83.
Burdenyuk, G.M., Ritmopediya v obuchenii inostrannym yazykam (Rhythmopedics in Teaching Foreign Languages), Chisinau, 1985.
Ukhtomskii, A.A., Parametr fizicheskoi labil'nosti i nelineinaya teoriya kolebanii. Izbrannye trudy (The Parameter of Physical Lability and Nonlinear Theory of Oscillations: Selected Works), Leningrad: Nauka, 1978, p. 187.
Fedotchev, A.I., Analysis of Resonance EEG Reactions in the Assessment of the Effectiveness of Sensory Stimuli, Fiziol. Chel., 1997, vol. 23, no. 4, p. 117.
Pervushin, Yu.V., Resonance Mechanisms of Changing Biological States, Biofizika, 1991, vol. 36, no. 3, p. 534.
Gorev, A.S., The Dynamics of EEG Rhythmic Components under Relaxation Conditions in 9–to 10–Year-Old Schoolchildren with Different Learning Achievement, Fiziol. Chel., 1998, vol. 24, no. 6, p. 42.
Gorev, A.S., The Dynamics of EEG α -Band Rhythmic Components of in Children between the Ages of 7 and 8 Years under Relaxation Conditions, Fiziol. Chel., 1998, vol. 24, no. 1, p. 21.
Gorev, A.S., The Dynamics of Evoked Visual Potentials in the Situation of Mobilization Readiness in Children of Different Ages, Fiziol. Chel., 1984, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 538.
Strukturno-funktsional'naya organizatsiya razvivayushchegosya mozga (Structural-Functional Organization of the Developing Brain), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990.
Lukashevich, I.P., Machinskaya, R.I., and Fishman, M.N., The Diagnosis of the Functional State of the Brain in Elementary Schoolchildren with Learning Dif-ficulties, Fiziol. Chel., 1994, vol. 20, no. 5, p. 34.
Gorev, A.S., The Dynamics of the EEG Parameters in Elementary Schoolchildren with a Change in the Functional State (Relaxation) Influenced by Aural Rhythmic Stimulation, Fiziol. Chel., 2000, vol. 26, no. 2, p. 37.
Farber, D.A. and Dubrovinskaya, N.N., The Structural-Functional Maturation of the Child's Brain, in Fiziologiya rosta i razvitiya detei i podrostkov (Physiology of Growth and Development of Children and Adolescents), Baranov, A.A. and Shcheplyagina, L.A., Eds., Moscow: Shchtinnitsa, 2000, p. 5.
Semenova, L.K., Vasil'eva, V.A., and Tsekhmistrenko, T.A., Structural Transformations in the Frontal Region of the Human Cerebral Cortex in Postnatal Ontogenesis, in Strukturno-funktsional'naya organizatsiya razvivayushchegosya mozga (Structural-Functional Organization of the Developing Brain), Leningrad: Nauka, 1990, p. 8.
Farber, D.A., The Ideas of A.A. Ukhtomskii in Studying Cognitive Activity, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2000, vol. 86, no. 8, p. 921.
Livanov, M.N., Prostranstvennaya organizatsiya protsessov golovnogo mozga (Spatial Organization of the Brain Processes), Moscow, 1972.
Sviderskaya, N.E. and Korol'kova, T.A., The Importance of the Concept of Spatial Synchronization of Brain Electrical Processes for Neurophysiological Studies, Usp. Fiziol. Nauk, 1987, vol. 18, no. 3, p. 98.
Mel'nikov, E.V., Dombayan, N.A., and Kiroi, V.N., Analysis of the Field Structure of the Cerebral Cortex Potentials, Fiziol. Chel., 1990, vol. 16, no. 1, p. 5.
Sarmanov, V.Ya., The Ratio of Mental and Neurophysiological Phenomena and Biological Feedback, Fiziol. Chel., 1982, vol. 8, no. 5, p. 846.
Wang, G., Takigawa, M., and Matsushita, T., Correlation of α -Activity between the Frontal and Occipital Cortex, Jpn. J. Physiol., 1982, vol. 42, no. 1, p. 1.
Luriya, A.R., Osnovy neiropsikhologii (The Essentials of Neuropsychology), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1973.
Khomskaya, E.D., Mozg i aktivatsiya (Brain and Activation), Moscow: Mosk. Gos. Univ., 1972.
Suhara, K., Suzuki, H., Katada, A., et al., Cross Spectral Analysis of Phase Relations of Different Frequency Components in Human EEG, EEG Clin. Neurophysiol., 1973, vol. 4, p. 248.
Ozaki, H., Yamazaki, K., Katada, K., et al., Distribution and Interregional Relationship of Alpha Rhythm on Scalp in Man, EEG Clin. Neurophysiol., 1977, vol. 43, p. 541.
Dubrovinskaya, N.N., Specific Features of the Neurophysiological Mechanisms of Attention Organization in Juvenile Schoolchildren, in Fiziologiya shkol'nikov yunosheskogo vozrasta (Physiology of Juvenile Schoolchildren), Moscow, 1988, p. 47.
Farber, D.A. and Vil'davskii, V.Yu., Heterogeneity and the Age-Related Dynamics of the EEG α -Rhythm, Fiziol. Chel., 1996, vol. 22, no. 5, p. 5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorev, A.S. Dynamics of the Adolescent EEG Parameters with Changes in the CNS Functional State (Relaxation) Influenced by Rhythmic Acoustic Stimulation. Human Physiology 27, 31–35 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007151122919
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007151122919