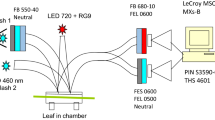
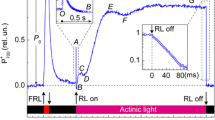
Abstract
Chlorophyll a fluorescence induction measured by a fluorometer with a high temperature stressed plant material shows a new K step which is a clear peak due to fast fluorescence rise and subsequent decrease of fluorescence intensity. We focused on an explanation of the decrease of fluorescence after the K step using artificial electron acceptors and donors to photosystem 2 (PS2). Addition of the artificial electron acceptors or donors suppressed the decrease of fluorescence after the K step. We suggest that the decrease mainly reflects (by more than 81 %) an energy loss process in the reaction centre of PS2 which is most probably a nonradiative charge recombination between P680+ (oxidised primary electron donor in PS2) and a negative charge stored on either Pheo− or QA − (reduced primary electron acceptor of PS2 and reduced primary quinone electron acceptor of PS2, respectively). We suggest that the energy loss process is only possible when the inhibition of both the donor and the acceptor sides of PS2 occurs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barthélemy, X., Popovic, R., Franck, F.: Studies on the O-J-I-P transient of chlorophyll fluorescence in relation to photosystem II assembly and heterogeneity in plastids of greening barley.-J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 39: 213-218, 1997.
Briantais, J.-M., Dacosta, J., Goulas, Y., Ducruet, J.-M., Moya, I.: Heat stress induces in leaves an increase of the minimum level of chlorophyll fluorescence, F0: A time-resolved analysis.-Photosynth. Res. 48: 189-196, 1996.
Bukhov, N.G., Sabat, S.C., Mohanty, P.: Analysis of chlorophyll a fluorescence changes in weak light in heat treated Amaranthus chloroplasts.-Photosynth. Res. 23: 81-87, 1990.
Butler, W.L.: On the primary nature of fluorescence yield changes associated with photosynthesis.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 69: 3420-3422, 1972.
Cao, J., Govindjee: Chlorophyll a fluorescence transient as an indicator of active and inactive photosystem II in thylakoid membranes.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 1015: 180-188, 1990.
Cramer, W.A., Whitmarsh, J., Low, P.S.: Differential scanning calorimetry of chloroplast membranes: identification of an endothermic transition associated with the water-splitting complex of photosystem II.-Biochemistry 20: 157-162, 1981.
Dau, H.: Molecular mechanisms and quantitative models of variable photosystem II fluorescence.-Photochem. Photobiol. 60: 1-23, 1994.
Delosme, R.: Étude de l'induction de fluorescence des algues vertes et des chloroplastes au début d'une illumination intense.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 143: 108-128, 1967.
Deprez, J., Dobek, A., Geacintov, N.E., Paillotin, G., Breton, J.: Probing fluorescence induction in chloroplast on a nanosecond time scale utilizing picosecond laser pulse pairs.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 725: 444-454, 1983.
Ducruet, J.-M., Lemoine, Y.: Increased heat sensitivity of the photosynthetic apparatus in triazine-resistant biotypes from different plant species.-Plant Cell Physiol. 26: 419-429, 1985.
Goltsev, V., Yordanov, I., Tsonev, T.: Evaluation of relative contribution of initial and variable chlorophyll fluorescence measured at different temperatures.-Photosynthetica 30: 629-643, 1994.
Guissé, B., Srivastava, A., Strasser, R.J.: Effects of high temperature and water stress on the polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient of potato leaves.-In: Mathis, P. (ed.): Photosynthesis: From Light to Biosphere. Vol. IV. Pp. 913-916. Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht-Boston-London 1995a.
Guissé, B., Srivastava, A., Strasser, R.J.: The polyphasic rise of the chlorophyll a fluorescence (O-K-J-I-P) in heat-stressed leaves.-Arch. Sci. Genève 48: 147-160, 1995b.
Havaux, M.: Characterization of thermal damage to the photosynthetic electron transport system in potato leaves.-Plant Sci. 94: 19-33, 1993.
Henrysson, T., Sundby, C.: Characterization of photosystem II in stroma thylakoid membranes.-Photosynth. Res. 25: 107-117, 1990.
Johnson, G.N., Rutherford, A.W., Krieger, A.: A change in the midpoint potential of the quinone QA in Photosystem II associated with photoactivation of oxygen evolution.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 1229: 202-207, 1995.
Krause, G.H., Weis, E.: Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: The basis.-Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant mol. Biol. 42: 313-349, 1991.
Laible, P.D., Zipfel, W., Owens, T.G.: Excited state dynamics in chlorophyll-based antennae: The role of transfer equilibrium.-Biophys. J. 66: 844-860, 1994.
Lavergne J., Trissl H.-W.: Theory of fluorescence induction in Photosystem II: Derivation of analytical expressions in a model including exciton-radical-pair equilibrium and restricted energy transfer between photosynthetic units.-Biophys. J. 68: 2474-2492, 1995.
Lazár, D.: Chlorophyll a fluorescence induction.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 1412: 1-28, 1999.
Lazár, D., Brokeš, M., Nauš, J., Dvořák, L.: Mathematical modeling of 3-(3′,4′-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea action in plant leaves.-J. theor. Biol. 191: 79-86, 1998.
Lazár, D., Ilík, P.: High-temperature induced chlorophyll fluorescence changes in barley leaves. Comparison of the critical temperatures determined from fluorescence induction and from fluorescence temperature curve.-Plant Sci. 124: 159-164, 1997.
Lazár, D., Ilík, P., Nauš, J.: An appearance of K-peak in fluorescence induction depends on the acclimation of barley leaves to higher temperatures.-J. Lumin. 72–74: 595-596, 1997b.
Lazár, D., Nauš, J., Matoušková, M., Flašarová, M.: Mathematical modeling of changes in chlorophyll fluorescence induction caused by herbicides.-Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 57: 200-210, 1997a.
Lazár, D., Pospíšil, P.: Mathematical simulation of chlorophyll a fluorescence rise measured with 3-(3′,4′-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea-treated barley leaves at room and high temperatures.-Eur. Biophys. J. 28: 468-477, 1999.
Lichtenthaler, H.K.: Chlorophylls and carotenoids — pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes.-In: Colowick, S.P., Kaplan, N.O. (ed.): Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 148. Pp. 350-382. Academic Press, San Diego-New York-Berkeley-Boston-London-Sydney-Tokyo-Toronto 1987.
Masamoto, K., Nishimura, M.: Effects of ethanol on the interaction of photosynthetic processes in spinach chloroplasts.-Plant Cell Physiol. 19: 1543-1552, 1978.
Mauzerall D.: Light-induced fluorescence changes in Chlorella, and the primary photoreactions for the production of oxygen.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 69: 1358-1362, 1972.
Munday, J.C., Jr., Govindjee: Light induced changes in the fluorescence yield of chlorophyll a in vivo. III. The dip and the peak in the fluorescence transient of Chlorella pyrenoidosa.-Biophys. J. 9: 1-21, 1969.
Nedbal, L., Samson, G., Whitmarsh, J.: Redox state of a one-electron component controls the rate of photoinhibition of photosystem II.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 7929-7933, 1992.
Neubauer, C., Schreiber, U.: The polyphasic rise of chlorophyll fluorescence upon onset of strong continuous illumination: I. Saturation characteristics and partial control by the photosystem II acceptor side.-Z. Naturforsch. 42c: 1246-1254, 1987.
Owens, T.G.: Processing of excitation energy by antenna pigments.-In: Baker, N.R. (ed.): Photosynthesis and the Environment. Pp. 1-23. Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht-Boston-London 1996.
Pospíšil, P.: Mechanisms of non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching in higher plants.-Photosynthetica 34: 343-355, 1997.
Renger, G., Kayed, A.: Fluorescence decline as a function of redox potential and actinic light intensity in spinach thylakoids.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 894: 261-269, 1987.
Schreiber, U., Bauer, R., Franck, U.F.: Chlorophyll fluorescence induction in green plants at oxygen deficiency.-In: Forti, G., Avron, M., Melandri, A. (ed.): Photosynthesis, Two Centuries After Its Discovery by Joseph Priestley. Vol. 1. Pp. 169-179. Dr W. Junk Publ., The Hague 1972.
Schreiber, U., Neubauer, C.: The polyphasic rise of chlorophyll fluorescence upon onset of strong continuous illumination: II. Partial control by the photosystem II donor side and possible ways of interpretation.-Z. Naturforsch. 42c: 1255-1264, 1987.
Schreiber, U., Neubauer, C.: Correlation between dissipative fluorescence quenching at photosystem II and 50 μs recombination luminescence.-FEBS Lett. 258: 339-342, 1989.
Schreiber, U., Neubauer, C.: O2-dependent electron flow, membrane energization and the mechanism of non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence.-Photosynth. Res. 25: 279-293, 1990.
Shinkarev, V.P., Govindjee: Insight into the relationship of chlorophyll a fluorescence yield to the concentration of its natural quenchers in oxygenic photosynthesis.-Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 7466-7469, 1993.
Sonneveld, A., Rademaker, H., Duysens, L.N.M.: Chlorophyll a fluorescence as a monitor of nanosecond reduction of the photooxidized primary donor P-680+ of Photosystem II.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 548: 536-551, 1979.
Srivastava, A., Guissé, B., Greppin, H., Strasser, R.J.: Regulation of antenna structure and electron transport in Photosystem II of Pisum sativum under elevated temperature probed by the fast polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient: OKJIP.-Biochim. biophys. Acta 1320: 95-106, 1997.
Stirbet, A., Govindjee, Strasser, B.J., Strasser, R.J.: Chlorophyll a fluorescence induction in higher plants: Modelling and numerical simulation.-J. theor. Biol. 193: 131-151, 1998.
Stirbet, A.D., Govindjee, Strasser, B.J., Strasser, R.J.: Numerical simulation of chlorophyll a fluorescence induction in plants.-In: Mathis, P. (ed.): Photosynthesis: from Light to Biosphere. Vol. II. Pp. 919-922. Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht-Boston-London 1995.
Strasser, B.J.: Donor side capacity of Photosystem II probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transients.-Photosynth. Res. 52: 147-155, 1997.
Strasser, R.J., Govindjee: The F0 and the O-J-I-P fluorescence rise in higher plants and algae.-In: Argyroudi-Akoyunoglou, J.H. (ed.): Regulation of Chloroplast Biogenesis. Pp. 423-426. Plenum Press, New York 1991.
Strasser, R.J., Govindjee: On the O-J-I-P fluorescence transient in leaves and D1 mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.-In: Murata, N. (ed.): Research in Photosynthesis. Vol. II. Pp. 29-32. Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht-Boston-London 1992.
Strasser, R.J., Srivastava, A., Govindjee: Polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient in plants and cyanobacteria.-Photochem. Photobiol. 61: 32-42, 1995.
Thompson, L.K., Sturtevant, J.M., Brudvig, G.W.: Differential scanning calorimetric studies of photosystem II: Evidence for a structural role for cytochrome b559 in the oxygen evolving complex.-Biochemistry 25: 6161-6169, 1986.
Vernon, L.P., Shaw, E.R.: Photoreduction of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol by diphenylcarbazide: A photosystem 2 reaction catalyzed by Tris-washed chloroplasts and subchloroplast fragments.-Plant Physiol. 44: 1645-1649, 1969.
Yamashita, T., Butler, W.L.: Photoreduction and photophosphorylation with Tris-washed chloroplasts.-Plant Physiol. 43: 1978-1986, 1968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazár, D., Pospíšil, P. & Nauš, J. Decrease of Fluorescence Intensity After the K Step in Chlorophyll a Fluorescence Induction is Suppressed by Electron Acceptors and Donors to Photosystem 2. Photosynthetica 37, 255–265 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007112222952
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007112222952