Abstract
SUMMARY
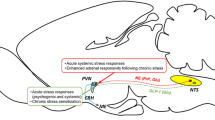
1. The role of α1-adrenergic receptors on CRH mRNA levels in the PVN was studied in control and stressed rats receiving i.c.v. injections of the α1-adrenergic agonist, methoxamine, or the α1- antagonist, prazosin.
2. Plasma ACTH increased significantly 60 min and 4 hr after a single injection of methoxamine (100 μg, i.c.v.). No desensitization of this response was observed after repeated injections every 6 hr for 24 hr. Concomitantly, POMC mRNA in the anterior pituitary increased by 25% at 4 hr after a single injection and by 96% after repeated injections.
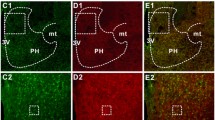
3. CRH mRNA levels in the PVN increased by 131% after repeated injections for 24 hr, but were unchanged 4 hr after a single injection. Central α1-adrenergic blockade with prazosin did not prevent the increases in CRH mRNA following 4 hr of acute stress, but significantly reduced the increases observed 24 hr after an i.c.v. injection of 75 μg of colchicine or after repeated i.p. hypertonic saline injections every 8 hr.
4. These studies demonstrate that while α1-adrenergic receptors contribute to long-term increases of CRH mRNA levels in the PVN during prolonged stress, other factors are likely to be involved in the stimulation of CRH mRNA following acute stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aguilera, G. (1998) Corticotropin-releasing hormone, receptor regulation and the stress response. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 9:329-336.
Aguilera, G., Young, W. S., Kiss, A., and Bathia, A. (1995). Direct regulation of hypothalamic corticotropin releasing hormone neurons by angiotensin II. Neuroendocrinology 61:437-444.
Al-Damluji, S. (1988). Adrenergic mechanisms in the control of corticotropin secretion. J. Endocrinol. 119:5-14.
Al-Damluji, S., (1993). Adrenergic control of the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 7:355-392.
Al-Damluji, S., Thomas, R., White, A., and Besser, M. (1990). Vasopressin mediates α-1-adrenergic stimulation of adrenocorticotropin secretion. Endocrinology 126:1989-1995.
Alonso, G., Szafarczyk, A., Balmefrezol, M., and Assenmacher, I. (1986). Immunohistochemical evidence for a stimulatory control by the ventral noradrenergic bundle on parvocellular corticotropin releasing hormone and vasopressin neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 397:297-307.
Antoni, F. A., (1986). Hypothalamic control of adrenocorticotropin secretion: Advances since the discovery of 41-residue corticotropin-releasing factor. Endocrine Rev. 7:351-378.
Bagdy, G., Calogero, A. E., Murphy, D. L., and Szemeredi, K. (1989). Serotonin agonists causes parallel activation of the sympatho-adrenomedullary system and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis in conscious rats. Endocrinology 125: 664-2669.
Ceccatelli, S., Cortez, R., and Hokfelt, T. (1991). Effect of reserpine and colchicine on neuropeptide mRNA levels in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Mol. Brain. Res. 9:57-69.
Cummings, S., and Seybold, V. (1988). Relationship of alpha-1-and alpha-2 adrenergic binding sites to regions of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus containing corticotropin releasing factor and vasopressin neurons. Neuroendocrinology 47:523-532.
Day, H. E., Campeau, S., Watson, S. J., Jr., and Akil, H. (1999). Expression of alpha(1b) adrenoceptor mRNA in corticotropin-releasing hormone-containing cell of the rat hypothalamus and its regulation by corticosterone. J. Neurosci. 19:10098-10106.
De Goeij, D. C. E., Kvetnansky, R., Whitnall, M. H., Jezova, D., Berkenbosh, F., and Tilders, F. J. H. (1991). Repeated stress-induced activation of corticotropin-releasing factor neurones enhances vasopressin stores and colocalization with corticotropin-releasing factor in the median eminence of rats. Neuroendocrinology 53:150-159.
Gaillet, S., Lachuer, J., Malaval, F., Assenmacher, I., and Szafarczyk, A. (1991). The involvement of noradrenergic ascending pathways in the stress-induced activation of ACTH and corticosterone secretions is dependent on the nature of the stressors. Exp. Brain Res. 87:173-180.
Ganong, W. F., Kramer, N., Salmon, J., Reis, I. A., Lovinger, R., Scapagnini, U., Boryczka, A. T., and Shackelfold, R. (1976). Pharmacological evidence for inhibition of ACTH secretion by central adrenergic system in the dog. Neuroscience 1:167-174.
Grossman, A., Costa, A., Navarra, P., and Tsagarakis, S. (1993). The regulation of hypothalamic corticotropin releasing factor release: in vitro studies. In Chadwick, D., Marsh, J., and Akrill, K. (eds.), Corticotropin Releasing Factor, Wiley, Chichester, U.K., pp. 129-150.
Guillaume, V., Conte-Devolx, B., Szafarczyk, A., Malaval, F., Pares-Herbute, N., Grino, M., Alonso, G., Assenmacher, I., and Oliver, C. (1987). The corticotropin release in rat hypophysial portal blood is mediated by brain catecholamines. Neuroendocrinology 46:143-146.
Harbuz, M. S., Chowdrey, H. S., Jessop, D. S., Biswas, S., and Lightman, S. L. (1991). Role of catecholamines in mediating messenger RNA and hormonal responses to stress. Brain Res. 551:52-57.
Harbuz, M. S., and Lightman, S. L. (1989). Responses of hypothalamic and pituitary mRNA to physical and psychological stress in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 122:705-711.
Hauger, R. L., Millan, M. A., Harwood, J. P., and Aguilera, G. (1988). Corticotropin releasing factor receptors and pituitary-adrenal responses during chronic stress. Endocrinology 123:396-405.
Itoi, K., Suda, T., Tozawa, F., Dobashi, I., Ohmori, N., Sakai, Y., Abe, K., and Demura, H. (1994). Microinjection of norepinephrine into the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus stimulates corticotropin-releasing factor gene expression in conscious rats. Endocrinology 135:2177-2182.
Jessop, D. S., Chowdrey, H. S., Larsen, P. J., and Lightman, S. L. (1992). Substance P: Multifunctional peptide in the hypothalamo-pituitary system? J. Endocrinol. 132:331-337.
Kiss, A., and Aguilera, G. (1992). Participation of α-1 adrenergic receptors in the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone during stress. Neuroendocrinology 56:53-160.
Kiss, J. Z., Mezey, E., and Skirboll, L. (1984). Corticotropin releasing factor immunoreactive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus become arginine-vasopressin positive after adrenalectomy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:6982-6986.
Leibowitz, S. F., Diaz, S., and Temple, D. (1989). Norepinephrine in the paraventricular nucleus stimulates corticosterone release. Brain Res. 496:219-227.
Leibowitz, S. F., Jhanwar-Uniyal, M., Dvorkin, B., and Makman, M. H. (1982). Distribution of alphaadrenergic, beta-adrenergic and dopaminergic receptors in discrete hypothalamic areas of the rat brain. Brain Res. 233:97-114.
Mezey, E., Kiss, J. Z., Skirboll, L. R., Goldstein, M., and Axelrod, J. (1984). Increase of corticotropin-releasing factor staining in rat paraventricular nucleus neurons by depletion of hypothalamic adrenaline. Nature 310:140-142.
Pacak, K., Armando, I., Fukuhara, K., Kvetnansky, R., Palkovits, M., Kopin, I. J., and Goldstein, D. S. (1992). Noradrenergic activation in the paraventricular nucleus during acute and chronic stress in rats: An in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res. 589:1-96.
Plotsky, P. M. (1987). Facilitation of immunoreactive corticotropin-releasing factor secretion into the hypophysial portal circulation after activation of catecholaminergic pathways or central norepinephrine injection. Endocrinology 121:924-930.
Plotsky, P. M., Cunningham, E. T., Jr., and Widmaier, E. P. (1989). Catecholaminergic modulation of corticotropin-releasing factor and adrenocorticotropin secretion. Endocrine Rev. 10:437-458.
Sands, S. A., and Morilak, D. A. (1999). Expression of alpha1D adrenergic receptor messenger RNA in oxytocin-and corticotropin-releasing hormone-synthesizing neurons in the rat paraventricular nucleus. Neuroscience 91:639-649.
Sumimoto, T., Suda, T., Nakano, Y., Tozawa, F., Yamada, M., and Demura, H. (1991). Angiotensin II increases the corticotropin releasing factor messenger ribonucleic acid level in the rat hypothalamus. Endocrinology 128:2248-2252.
Swanson, L. W., Sawchenko, P. E., Rivier, J., Vale, W. W. (1983). The organization of ovine corticotropin releasing factor (CRH)-immunoreactive cells and fibers in the rat brain: An immunohistochemical study. Neuroendocrinology 36:165-186.
Szafarczyk, A., Malaval, F., Laurent, A., Gibaud, R., and Assenmacher, I. (1987). Further evidence for a central stimulatory action of catecholamines on adrenocorticotropin release in the rat. Endocrinology 121:883-892.
Vale, W., Rivier, C., Brown, M. R., Spiess, J., Koob, G., Swanson, L., Bilezikjian, L., Bloom, F., and Rivier, J. (1983). Chemical and biological characterization of corticotropin-releasing factor. Rec. Progr. Hormone Res. 39:245-270.
Whitnall, M. H. (1989). Stress selectively activates the vasopressin-containing subset of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Neuroendocrinology 50:702-707.
Whitnall, M. H., Kiss, A., and Aguilera, G. (1993). Contrasting effects of central alpha-1-adrenoreceptor activation on stress responsive and non-responsive subpopulations of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurosecretory cells. Neuroendocrinology 58:42-48.
Whitnall, M. H., Smyth, D., and Gainer, H. (1987). Vasopressin coexists in half of the corticotropin-releasing factor axons present in the external zone of the median eminence in normal rats. Neuroendocrinology 45:420-424.
Windle, R. J., Brady, M., Kunanandam, T., DaCosta, A. P. C., Wilson, B. C., Harbuz M., Lightman, S. L., and Ingram, C. D. (1997). Reduced response of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis to alpha-1 agonist stimulation during lactation. Endocrinology 138:3741-3748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiss, A., Aguilera, G. Role of Alpha-1-Adrenergic Receptors in the Regulation of Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone mRNA in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus During Stress. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 683–694 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007098724683
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007098724683