Abstract
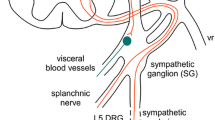
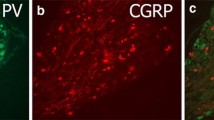
Tyrosine hydroxylase immunocytochemistry was used to reveal the sympathetic postganglionic axons that sprout to form basket-like skeins around the somata of some primary sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia (DRGs) following sciatic nerve injury. Ultrastructural observations in rats revealed that these sprouts grow on the surface of glial lamellae that form on the neurons. Sciatic nerve injury triggers glial cell proliferation in the DRG, and the formation of multilamellar pericellular onion bulb sheaths, primarily around large diameter DRG neurons. We infer that these glia participate in the sprouting process by releasing neurotrophins and expressing growth supportive cell surface molecules. Many DRG cell somata, and their axons in intact nerves and nerve end neuromas, express α2A adrenoreceptors intracytoplasmically and on their membrane surface. However, sympathetic axons never make direct contacts with the soma membrane. The functional coupling known to occur between sympathetic efferents and DRG neurons must therefore be mediated by the diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules in the extracellular space. Sympathetic basket-skeins were observed in DRGs removed from human neuropathic pain patients, but the possibility of a functional relation between these structures and sensory symptoms remains speculative.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulla, F. A. & Smith, P. A. (1997) Ectopic a2 adrenoreceptors couple to N-type Ca2+ channels in axotomized rat sensory neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 1633-1641.
Ali, Z., Ringkamp, M., Hartke T. V., Chien, H. F., Flavahan, N. A., Campbell, J. N. & Meyer, R. A. (1999) Uninjured cutaneous C-fiber nociceptors develop spontaneous activity and alpha adrenergic sensitivity following L6 spinal nerve ligation in the monkey. Journal of Neurophysiology 81, 455-466.
Amir, R. & Devor, M. (1996) Chemically-mediated crossexcitation in rat dorsal root ganglia. Journal of Neuroscience 16, 4733-4741.
Amir, R., Michaelis, M. & Devor, M. (1999) Membrane potential oscillations in dorsal root ganglion neurons: role in normal electrogenesis and in neuropathic pain. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 8589-8596.
Belenky, M. & Devor, M. (1997) Association of postganglionic sympathetic neurons with primary afferents in sympathetic-sensory co-cultures. Journal of Neurocytology 26, 715-731.
Birder, L. A. & Perl, E. R. (1999) Expression of a2-adrenergic receptors in rat primary afferent neurons after peripheral nerve injury or inflammation. Journal of Physiology (London) 515, 533-542.
Bossut, D. F. & Perl, E. R. (1995) Effects of nerve injury on sympathetic excitation of Adelta mechanical nociceptors. Journal of Neurophysiology 73, 1721-1723.
Burchiel, K. (1984) Spontaneous impulse generation in normal and denervated dorsal root ganglia: sensitivity to alpha-adrenergic stimulation and hypoxia. Experimental Neurology 85, 257-272.
Chen, Y., Michaelis, M., Janig, W. & Devor, M. (1996) Adrenoreceptor sub-type mediating sympatheticsensory coupling in injured sensory neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology 76, 3721-3730.
Cho, H.-J., Kim, D.-S., Lee, N.-H., Lee, K.-M., Han, K.-S., Kang, Y.-N. & Kim, K.-J. (1997) Changes in the a2-adrenergic receptor subtypes gene expression in rat dorsal root ganglion in an experimental model of neuropathic pain. NeuroReport 8, 3119-3122.
Chung, K., Kim, H.J., Na, H. S., Park, M. J. & Chung, J. M. (1993) Abnormalities of sympathetic innervation in the area of an injured peripheral nerve in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience Letters 162, 85-88.
Chung, K., Lee, B. H., Yoon, Y. W. & Chung, J.M. (1996) Sympathetic sprouting in the dorsal root ganglia of the injured peripheral nerve in a rat neuropathic pain model. Journal of Comparative Neurology 376, 1-12.
Chung, K., Yoon, Y. W. & Chung, J. M. (1997) Sprouting sympathetic fibers form synaptic varicosities in the dorsal root ganglion of the rat with neuropathic injury. Brain Research 751, 275-280.
Davar, G., Fareed, M., Lee, D. H., Noh, H. R. & Chung, J. M. (1996) Identification and increased expression of a novel alpha 2-adrenoreceptor mRNA in dorsal root ganglia in a rat model of experimental painful neuropathy. In Abstr.8th World Congress on Pain, p. 29. Seattle: IASP Press.
Davies, A. M., Bandtlow, C., Heumann, R., Korsching, S., Rohrer, H. & Thoenen, H. (1987) Timing and site of nerve growth factor synthesis in developing skin in relation to innervation and expression of the receptor. Nature 326, 353-358.
Davis, B. M., Albers, K. M., Seroogy, K. B. & Katz, D. M. (1994) Overexpression of nerve growth factor in transgenic mice induces novel sympathetic projections to primary sensory neurons. Journal of Comparative Neurology 349, 464-474.
Devor, M. (1983) Nerve pathophysiology and mechanisms of pain in causalgia. Journal of Autonomic Nervous System 7, 371-384.
Devor, M. (1999) Unexplained peculiarities of the dorsal root ganglion. Pain (Supplement 6), S27-S35.
Devor, M., Govrin-lippmann, R., Frank, I. & Raber, P. (1985) Proliferation of primary sensory neurons in adult rat dorsal root ganglion and the kinetics of retrograde cell loss after sciatic nerve section. Somatosensory Research 3, 139-167.
Devor, M. & Janig, W. (1981) Activation of myelinated afferents ending in a neuroma by stimulation of the sympathetic supply in the rat. Neuroscience Letters 24, 43-47.
Devor, M., Janig, W. & Michaelis, M. (1994) Modulation of activity in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons by sympathetic activation in nerve-injured rats. Journal of Neurophysiology 71, 38-47.
Devor, M. & Seltzer, Z. (1999) Pathophysiology of damaged nerves in relation to chronic pain. In Textbook of Pain, 4th ed. (edited by Wall, P. D. & Melzack, R.), pp. 129-164. London: Churchill Livingstone.
Fried, K., Govrin-lippmann, R. & Devor, M. (1993) Close apposition among neighbouring axonal endings in a neuroma. Journal of Neurocytology 22, 663-681.
Fried, K., Govrin-lippmann, R., Rosenthal, F., Ellisman, M. H. & Devor, M. (1991) Ultrastructure of afferent axon endings in a neuroma. Journal of Neurocytology 20, 682-701.
Gold, M. S., Dastmalchi, S. & Levine, J. D. (1997) a2-Adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat dorsal root and superior cervical ganglion neurons. Pain 69, 179-190.
Habler, H., Liu, X., Eschenfelder, S. & Janig, W. (1998) Responses of axotomized afferents to blockade of nitric oxide synthesis after spinal nerve lesion in the rat. Neuroscience Letters 254, 33-36.
Hammarberg, H., Piehl, F., Cullheim, S., Fjell, J., Hokfelt, T. & Fried, K. (1996) GDNF mRNA in Schwann cells andDRGsatellite cells after chronic sciatic nerve injury. NeuroReport 7, 857-860.
Haycock, J. W. (1987) Stimulation-dependent phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat corpus striatum. Brain Research Bulletin 19, 619-622.
Herzberg, U., Eliav, E., Dorsey, J. M., Gracely, R. H. & Kopin, I. J. (1997) NGF involvement in pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the rat sciatic nerve. NeuroReport 8, 1613-1618.
Heumann, R., Lindholm, D., Bandtlow, C., Meyer, M., Radeke, M. J., Misko, T. P., Shooter, E. & Thoenen, H. (1987) Differential regulation of mRNA encoding nerve growth factor and its receptor in rat sciatic nerve during development, degeneration and regeneration: role of macrophages. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 84, 8735-8739.
Humberston, A. E., Zimmerman, E. & Leedy, M. (1969) A chronological study of mitotic activity in satellite cell hyperplasia associated with chromatolytic neurons. Zeitschrift fur Zellfoschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 100, 507-515.
Janig, W. & Koltzenburg, M. (1991) What is the interaction between the sympathetic terminal and the primary afferent fiber? In Towards a New Pharmacotherapy of Pain, Dahlem Workshop Reports (edited by Basbaum, A. & Besson, J.-M. ), pp. 331-352. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.
Janig, W. & Stanton-Hicks, M. D. (eds.) (1997) Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy: a Reappraisal; Progress in Pain Research and Management, Vol. 6. Seattle: IASP Press.
Jones, M. G., Munson, J. B. & Thompson, S. W. N. (1999) A role for nerve growth factor in sympathetic sprouting in rat dorsal root ganglia. Pain 79, 21-29.
Karhunen, T., Ulmanen, I. & Panula, P. (1996) Catechol-o-methyltransferase in rat sensory ganglia and spinal cord. Neuroscience 73, 267-276.
Katz, D., Markey, K., Goldstein, M. & Black, I. B. (1983) Expression of catecholaminergic characteristics by primary sensory neurons in the normal adult rat in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA) 80, 3526-3530.
Kim, H. J., Na, H. S., Nam, H. J., Park, K. A., Hong, S. K. & Kang, B. S. (1996) Sprouting of sympathetic nerve fibers into the dorsal root ganglion following peripheral nerve injury depends on the injury site. Neuroscience Letters 212, 191-194.
Lee, S., Shen, H., Taglialatela, G., Chung, J. M. & Chung, K. (1998) Expression of nerve growth factor in the dorsal root ganglion after peripheral nerve injury. Brain Research 796, 99-106.
Levine, J., Taiwo, Y., Collins, S. & Tam, J. K. (1986) Noradrenaline hyperalgesia is mediated through interaction with sympathetic postganglionic neurone terminals rather than activation of primary afferent nociceptors. Nature 323, 158-160.
Lieberman, A. R. (1976) Sensory ganglia. In The Peripheral Nerve (edited by Landon, D. N.), pp. 188-278. London: Chapman & Hall.
Lu, X. & Richardson, P. (1993) Responses of macrophages in rat dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury. Journal of Neurocytology 22, 334-341.
McLachlan, E., Janig, W., Devor, M. & Michaelis, M. (1993) Peripheral nerve injury triggers noradrenergic sprouting within dorsal root ganglia. Nature 363, 543-546.
Merskey, H. & Bogduk, N. (1994) Classification of Chronic Pain.Descriptions of Chronic Pain Syndromes and Definitions of Pain Terms, pp. 40-43. Seattle: IASP Press.
Mesulam, M.-M. (1978) Tetramethylbenzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurochemistry; a noncarcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neuronal afferents and efferents. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 26, 106-17.
Michaelis, M., Devor, M. & Janig, W. (1996) Sympathetic modulation of activity in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons changes over time following peripheral nerve injury. Journal of Neurophysiology 76, 753-763.
Murayama, S., Bouldin, T. W. & Suzuki, K. (1991) Onion bulb formation in the initial complex of neurons in human dorsal root ganglion: their significance Sympathetic-sensory coupling in DRGs 761 and alterations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathologica 82, 462-470.
Nauta, H. J., Wehman, J. C., Koliatsos, V. E., Terrell, M. A. & Chung, K. (1999) Intraventricular infusion of nerve growth factor as the cause of sympathetic fiber sprouting in sensory ganglia. Journal of Neurosurgery 91, 447-453.
Nicholas, A., Pieribone, V. & Hokfelt, T. (1993) Distribution of mRNAs for alpha-2 adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: an in situ hybridization study. Journal of Comparative Neurology 328, 575-594.
Ochoa, J. L. (1970) The structure of developing and adult sural nerve in man and the changes which occur in some diseases. A light and electron microscopic study. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London.
Olucha, F., Martinez-Garica, F. & Lopezgarcia, C. (1985) A new stabilizing agent for the tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) reaction product in the histochemical detection of horseradish peroxidase (HRP). Journal of Neuroscience Methods 13, 1331-1338.
Pannese, E. (1981) The satellite cells of the sensory ganglia. Advances in Anatomy, Embryology and Cell Biology 47, 1-97.
Perll. E. (1994) A reevaluation of mechanisms leading to sympathetically related pain. In Pharmacological Approaches to the Treatment of Chronic Pain: New Concepts and Critical Issues (edited by Fields, H. & Liebeskind, J.), pp. 129-150. Seattle: IASP Press.
Petersen, M., Zhang, J., Zhang, J.-M. & Lamotte, R. H. (1996) Abnormal spontaneous activity and responses to norepinephrine in dissociated dorsal root ganglion cells after chronic nerve constriction. Pain 67, 391-397.
Price, J. M. & Mudge, A. W. (1983) A subpopulation of rat dorsal root ganglion neurones is catecholaminergic. Nature 301, 241-243.
Ramer, M. & Bisby, M. (1997) Rapid sprouting of sympathetic axons in dorsal root ganglia of rats with a chronic constriction injury. Pain 70, 237-244.
Robertson, B. & Grant, G. (1985) A comparison between wheat germ agglutinin-and choleragenoidhorseradish peroxidase as anterogradely transported markers in central branches of primary sensory neurones in the rat with some observations in the cat. Neuroscience 14, 895-905.
Rogers, K. E., Dõandrea, M. R. & Oaklander, A. L. (1999) Catecholaminergic neurons are increased in dorsal root ganglia from pain patients. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 25, 1941.
Rosin, D. L., Zeng, D., Stornetta, R. L., Norton, F. R., Riley, T., Okusa, M. D., Guyenet, P. G. & Lynch, K. R. (1993) Immunohistochemical location of a2A adrenergic receptors in catecholaminergic and other brainstem neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 56, 139-155.
Rubin, G., Kaspi, T., Rappaport, Z. H., Cohen, S., Ravikovitch, M., Lomazov, P. & Devor, M. (1997) Adrenosensitivity of injured afferent neurons does not require the presence of postganglionic sympathetic terminals. Pain 72, 183-191.
Sato, J. & Perl, E. (1991) Adrenergic excitation of cutaneous pain receptors induced by peripheral nerve injury. Science 251, 1608-1610.
Schachner, M. (1991) Cell surface recognition and neuron-glia interactions. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 633, 105-112.
Sebert, M. E. & Shooter, E. M. (1993) Expression of mRNA for neurotrophic factors and their receptors in the rat dorsal root ganglion and sciatic nerve following nerve injury. Journal of Neuroscience Research 36, 357-367.
Shen, H., Chung, J. M. & Chung, K. (1999) Expression of neurotrophin mRNAs in the dorsal root ganglion after spinal nerve injury. Molecular Brain Research 64, 186-192.
Shinder, V. & Devor, M. (1994) Structural basis of neuron-to-neuron cross-excitation in dorsal root ganglia. Journal of Neurocytology 23, 515-531.
Small, J. R., Scadding, J. W. & Landon, D. N. (1996) Ultrastructural localization of sympathetic axons in experimental rat sciatic nerve neuromas. Journal of Neurocytology 25, 573-582.
Stephenson, J. L. & Byers, M. R. (1995) GFAP immunoreactivity in trigeminal ganglion satellite cells after tooth injury in rats. Experimental Neurology 131, 11-22.
Stevens, R. T., Hodge, C. J. J. & Apkarian, A. V. (1983) Catecholamine varicosities in cat dorsal root ganglion and spinal ventral roots. Brain Research 261, 151-154.
Talley, E. M., Rosin, D. L., Lee, A., Guyenet, P. G. & Lynch, K. R. (1996) Distribution of alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Journal of Comparative Neurology 372, 111-134.
Thompson, S. W. & Majithia, A. A. (1998) Leukemia inhibitory factor induces sympathetic sprouting in intact dorsal root ganglia in the adult rat in vivo. Journal of Physiology (London), 809-816.
Uno, T., Hisa, Y., Tadaki, N., Okamura, H. & Ibata, Y. (1996) Tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive cells in the nodose ganglion for the canine larynx. NeuroReport 7, 1373-1376.
Wall, P. D. & Gutnick, M. (1974) Ongoing activity in peripheral nerves: the physiology and pharmacology of impulses originating from a neuroma. Experimental Neurology 43, 580-593.
Wells, M. R., Vaidya, U. & Schwartz, J. P. (1994) Bilateral phasic increases in dorsal root ganglia nerve growth factor synthesis after unilateral sciatic nerve crush. Experimental Brain Research 101, 53-58.
Woodham, P., Anderson, P. N., Nadim, W. & Turmaine, M (1989) Satellite cells surrounding axotomised rat dorsal root ganglion cells increase expression of a GFAP-like protein. Neuroscience Letters 98, 8-12.
Xie, Y., Zhang, J. & Petersen, M. & Lamotte, R. H. (1995) Functional changes in dorsal root ganglion cells after chronic nerve constriction in the rat. Journal of Neurophysiology 73, 1811-1820, 93-94.
Zhou, X. F., Deng, Y. S., Chie, E., Xue, Q., Zhong, J. H., Mclachlan, E. M., Rush, R. A. & Xian, C. J. (1999) Satellite-cell-derived nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3 are involved in noradrenergic sprouting in the dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury in the rat. European Journal of Neuroscience 11, 1711-1722.
Zimmermann, M. (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16, 109-110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinder, V., Govrin-Lippmann, R., Cohen, S. et al. Structural basis of sympathetic-sensory coupling in rat and human dorsal root ganglia following peripheral nerve injury. J Neurocytol 28, 743–761 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007090105840
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007090105840