Abstract
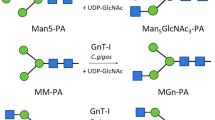
UDP-GlcNAc : α-3-D-mannoside β-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I (GnT I, EC 2.4.1.101) plays an essential role in the conversion of oligomannose to complex and hybrid N-glycans. Rabbit GnTI is 447 residues long and has a short four-residue N-terminal cytoplasmic tail, a 25-residue putative signal–anchor hydrophobic domain, a stem region of undetermined length and a large C-terminal catalytic domain, a structure typical of all glycosyltransferases cloned to date. Comparison of the amino acid sequences for human, rabbit, mouse, rat, chicken, frog and Caenorhabditis elegans GnT I was used to obtain a secondary structure prediction for the enzyme which suggested that the location of the junction between the stem and the catalytic domain was at about residue 106. To test this hypothesis, several hybrid constructs containing GnT I with N- and C-terminal truncations fused to a mellitin signal sequence were inserted into the genome of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV), Sf 9 insect cells were infected with the recombinant baculovirus and supernatants were assayed for GnT I activity. Removal of 29, 84 and 106 N-terminal amino acids had no effect on GnT I activity; however, removal of a further 14 amino acids resulted in complete loss of activity. Western blot analysis showed strong protein bands for all truncated enzymes except for the construct lacking 120 N-terminal residues indicating proteolysis or defective expression or secretion of this protein. The data indicate that the stem is at least 77 residues long.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reglero A, Rodriguez-Aparicio LB, Lueno JM (1993) Int J Bio-chem 25: 1517-27.
Harduin-Lepers A, Recchi MA, Delannoy P (1995) Glycobiol-ogy 5: 741-58.
Livingston BD, Paulson JC (1993) J Biol Chem 268: 11504-7.
Fryer HJL, Hockfield S (1996) Current Opin Neurobiol 6: 113-16.
Coughlan CM, Seckl JR, Fox DJ, Unsworth R, Breen KC (1996) Glycobiology 6: 15-22.
Maguire TM, Breen KC (1995) Dementia 6: 185-90.
Maguire TM, Thakore J, Dinan TG, Hopwood S, Breen KC (1997) Biol Psychiatry: In press.
Hayes FD, Breen KC (1994) Toxic in vitro 8: 407-11.
Munro S (1991) EMBO J 12: 3577-88.
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1993) In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology (Janssen K ed.) New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Breen KC, Regan CM (1986) J Neurochem 47: 1176-80.
Coughlan CM, Seckl JM, Breen KC (1996) Cell Mol Neurobiol 16: 431-6.
Skoza L, Mohos S (1976) Biochem J 159: 457-62.
Martin ML, Breen KC, Regan CM (1988) Tox in vitro 2: 43-8.
Wang XC, O'Hanlon TP, Lau JTY (1989) J Biol Chem 264: 1854-9.
Livingston BD, De Robertis EM, Paulson JC (1990) Glycobiol-ogy 1: 39-44.
Lee EU, Roth J, Paulson JC (1989) J Biol Chem 264: 13848-55.
Nakagawa H, Zheng MZ, Hakomori S, Tsukamoto Y, Kawamura Y, Takahashi N (1996) Eur J Biochem 237: 76-85.
Veiga SS, Chammas R, Cella N, Brentani RR (1995) Int J Cancer 61: 420-4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, M., Pagny, S., Unligil, U. et al. Removal of 106 amino acids from the N-terminus of UDP-GlcNAc :alpha-3-D-mannoside beta-1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I does not inactivate the enzyme. Glycoconj J 15, 193–197 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006928624913
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006928624913
- N-glycan synthesis
- GlcNAc-transferase
- Sf 9 insect cells
- baculovirus
- catalytic domain
- AcMNPV, Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus
- FCS, foetal calf serum
- GnT, N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
- PCR, polymerase chain reaction
- SDS-PAGE sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- Sf9, Spodoptera frugiperda
- UDP-GlcNAc : alpha-3-D-mannoside beta-12-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I, GnT I (EC 241101)