Abstract
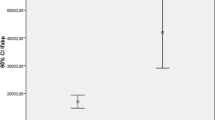
A novel calcium-binding protein regucalcin has been shown to be specifically expressed in the liver of various specifies including human. Regucalcin concentration in the serum of patients with chronic liver injury was estimated by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay (ELISA) with rabbit-anti-regucalcin IgG. Serum samples were obtained from 42 persons who were diagnosed as liver disorder. Serum regucalcin concentration in all patients was in the range of 3.7-69.6 ng/ml, although regucalcin was not entirely seen in the serum of normal subjects (10 persons) without hepatitis. Meanwhile, in 18 patients with liver injury, serum glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) activities were normal value (less than 40 I.U./l). Serum GOT and GPT activities from 24 patients showed a comparatively higher level (50-234 I.U./l). The present results demonstrate the potential sensitivity of regucalcin as a marker of chronic liver injury. (Mol Cell Biochem 167: 187-190, 1997)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williamson JR, Cooper RK, Hoek JB: Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 243–295, 1981
Reinhart PH, Taylor WM, Bygrave FL: The role of calcium ions in the mechanisms of action of α-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Biochem J 223: 1–13, 1984
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 19–27, 1980
Nishizuka Y: Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science 233: 305–312, 1986
Yamaguchi M: A novel Ca2+-binding protein regucalcin and calcium inhibition: Regulatory role in liver cell function. In: K Kohama (ed). Calcium Inhibition. Japan Sci Soc Press, Tokyo and CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1992, pp 19–41
Mori S, Yamaguchi M: Hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin decreases Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity in rat liver cytosol. Chem Pharm Bull 38: 2216–2218, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Tai H: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodi-esterase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 106: 25–30, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on protein kinase C activity in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Med Metab Biol 43: 140–146, 1990
Shimokawa N, Matsuda Y, Yamaguchi M: Genomic cloning and chro-mosomal assignment of rat regucalcin gene. Mol Cell Biochem 151: 157–163, 1995
Shimokawa N, Isogai M, Yamaguchi M: Specific species and tissue differences for the gene expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin. Mol Cell Biochem 143: 67–71, 1995
Yamaguchi M, Isogai M: Tissue concentration of calcium binding protein regucalcin in rats by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem 122: 65–68, 1993
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration stimulates the expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver. FEBS Lett 305: 151–154, 1992
Yamaguchi M, Kanayama Y, Shimokawa N: Expression of calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA in rat liver is stimulated by calcitonin: the hormonal effect is mediated through calcium. Mol Cell Biochem 136: 43–48, 1994
Yamaguchi M, Oishi K, Isogai M: Expression of hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin mRNA is elevated by refeeding of fasted rats: Involvement of glucose, insulin and calcium as stimulating factors. Mol Cell Biochem 142: 35–41, 1995
Isogai M, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration increases calcium-binding protein regucalcin concentration in the liver of rats. Mol Cell Biochem 143: 53–58, 1995
Isogai M, Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Hepatic calciumbinding protein regucalcin is released into the serum of rats administered orally carbon tetrachloride. Mol Cell Biochem 131: 173–179, 1994
Isogai M, Oishi K, Yamaguchi M: Serum release of hepatic calcium-binding protein regucalcin by liver injury with galactosamine administration in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 136: 85–90, 1994
Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto T: Purification of calcium binding substance from soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 26: 1915–1918, 1978
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall E: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–273, 1951
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, M., Isogai, M. & Shimada, N. Potential sensitivity of hepatic specific protein regucalcin as a marker of chronic liver injury. Mol Cell Biochem 167, 187–190 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006859121897
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006859121897