Abstract
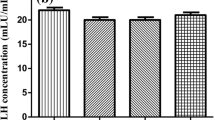
The effect of regucalcin, a Ca2+-bindingf protein isolated from rat livercytosol, on ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis in the nuclei of normal ratliver and of regenerating rat liver was investigated. The liver weight at 1day after partial hepatectomy was increased about 50% of that ofsham-operated (control) rats. Calcium chloride (1.0-20 µM Ca2+ asfinal concentration) was added into the reaction mixture of nuclear RNAsynthesis. RNA synthesis was established by incorporation of [3H]-uridine5'-triphosphate (UTP) into the nuclear RNA. Addition of Ca2+ (5 and 10µM) caused a significant increase of RNA synthesis in the nuclei fromcontrol rat liver. Such effect of Ca2+ was potentiated in the nuclei ofregenerating liver; nuclear RNA synthesis was increased about 2 fold by the1.0 and 2.5 µM Ca2+ addition. The stimulatory effect of Ca2+ wassignificantly inhibited by the presence of a-amanitin (10-8 M), an inhibitorof RNA polymerase II. The presence of regucalcin (0.25 and 0.5 µM)significantly inhibited RNA synthesis in the nuclei from control rat liverand from regenerating rat liver. The inhibitory effect of regucalcin wasremarkable in the presence of EGTA (0.5 mM), and it was weakened by theaddition of Ca2+ (5 µM). Such regucalcin effect was not seen in thepresence of a-amanitin. The presence of anti-regucalcin IgG in the reactionmixture significantly increased RNA synthesis in the nuclei from control ratliver, indicating that the endogenous regucalcin may be involved in nuclearRNA synthesis. The present resuits demonstrate that regucalcin can inhibitnuclear RNA synthesis in rat liver. Regucalcin may have an inhibitory rolein the regulation of liver nuclear RNA synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williamson JR, Cooper RH, Hoek JB: Role of calcium in the hormonal regulation of liver metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 639: 243–295, 1981
Reinhart PH, Taylor WM, Bygrave FL: The role of calcium ions in the mechanisms of action of ?-adrenergic agonists in rat liver. Biochem J 223: 1–13, 1984
Kraus-Friedman N, Feng L: The role of intracellular Ca2+ in the regulation of gluconeogenesis. Metabolism 48: 389–403, 1996
Cruise J, Honck KA, Michalopoulis GK: Induction of DNA synthesis in cultured rat hepatocytes through stimulation of ?-adrenoreceptor by norepinephrine. Nature 227: 749–751, 1985
Bachs O, Carafolli E: Calmodulin and calmodulin-binding proteins in liver cell nuclei. J Biol Chem 262: 10786–10790, 1987
Pujol MJ, Soriano M, Alique R, Carafolli E, Backs O: Effect of ?-adrenergic blockers on calmodulin association with the nuclear matrix of rat liver cells during proliferative activation. J Biol Chem 264: 18863–18865, 1989
Jones DP, McConkey DJ, Nicotera P, Orrenius S: Calcium activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem 264: 6398–6403, 1989
Backs O, Lanini L, Serratosa J, Coll MJ, Bastors R, Alique R, Rius E, Carafolli E: Calmodulin-binding proteins in the nuclei of quiescent and proliferatively activated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem 265: 18595–18600, 1990
Allbritton NL, Oancea E, Kuhn MA, Meyer T: Source of nuclear calcium signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 12458–12462, 1994
Nicotera P, McConkey DJ, Jones DP, Orrenius S: ATP stimulates Ca2+ uptake and increases the free Ca2+ concentration in isolated rat liver nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 453–457, 1989
Yamaguchi M, Oishi K: Characterization of Ca2+-stimulated adenosine 5?-triphosphatase and Ca2+ sequestering in rat liver nuclei. Mol Cell Biochem 125: 43–49, 1993
Humbert J-P, Matter N, Artault J-C, Koppler P, Malviya AN: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor is located to the inner nuclear membrane vindicating regulation of nuclear calcium signaling by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Discrete distribution of inositol phosphate receptors to inner and outer nuclear membranes. J Biol Chem 271: 478–485, 1996
Cheung WY: Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science 202: 18–27, 1984
Yamaguchi M: A novel Ca2+-binding protein regucalcin and calcium inhibition: Regulatory role in liver cell function. In: K Kohama (ed). Calcium Inhibition. Japan Sci Soc Press, Tokyo and CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1992, pp 19–41
Yamaguchi M, Tai H: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity in rat liver cytosol. Mol Cell Biochem 106: 25–30, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Mori S: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on protein kinase C activity in rat liver cytosol. Biochem Med Metab Biol 43: 140–146, 1990
Yamaguchi M, Sakurai T: Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. FEBS Lett 279: 281–284, 1991
Yamaguchi M, Kanayama Y: Calcium-binding protein regucalcin inhibits deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the nuclei of regenerating rat liver. Mol Cell Biochem 162: 121–126, 1996
Yamaguchi M: Effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on Ca2+ transport system in rat liver nuclei: Stimulation of Ca2+ release. Mol Cell Biochem 113: 63–70, 1992
Higgins GH, Anderson RM: Experimental pathology of the liver. Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol 12: 186–202, 1931
Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto T: Purification of calcium binding substance from soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull 26: 1915–1918, 1978
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall FJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–273, 1951
Burton A: Study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62: 315–323, 1956
Yamaguchi M, Takei Y, Yamamoto T: Effect of thyrocalcitonin in liver of intact and thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology 96: 1004–1008, 1975
Yamaguchi M, Isogai M: Tissue concentration of calcium binding protein regucalcin in rats by enzyme-linked immunoadsorbent assay. Mol Cell Biochem 122: 65–68, 1993
Weiss SB: Enzymatic incorporation of ribonucleoside triphosphates into the interpolynucleotide linkages of ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 46: 1020–1030, 1960
Kanayama Y, Yamaguchi M: Enhancement of nuclear Ca2+-ATPase activity in regenerating rat liver: Involvement of nuclear DNA increase. Mol Cell Biochem 146: 179–186, 1995
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett 327: 251–255, 1993
Shimokawa N, Matsuda Y, Yamaguchi M: Genomic cloning and chromosomal assignment of rat regucalcin gene. Mol Cell Biochem 151: 157–163, 1995
Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M: Expression of hepatic calcium binding protein regucalcin mRNA is mediated through Ca2+/calmodulin in rat liver. FEBS Lett 316: 79–84, 1993
Isogai M, Yamaguchi M: Calcium administration increases calcium binding protein regucalcin concentration in the liver of rats. Mol Cell Biochem 143: 53–58, 1995
Yamaguchi M, Kanayama Y: Enhanced expression of calcium binding protein regucalcin mRNA in regenerating rat liver. J Cell Biochem 57: 185–190, 1995
Pardo JP, Fernandez F: Effect of calcium and calmodulin on RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei from rat liver cells. FEBS Lett 143: 157–160, 1982
Sturges MR, Peck LJ: Calcium-dependent inactivation of RNA polymerase III transcription. J Biol Chem 269: 5712–5719, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, M., Ueoka, S. Inhibitory effect of calcium-binding protein regucalcin on ribonucleic acid synthesis in isolated rat liver nuclei. Mol Cell Biochem 173, 169–175 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006833111236
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006833111236