Abstract
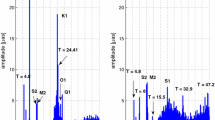
An overview of the abilities of Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) to measure the variable Earth rotation and of the international VLBI collaboration is given. The paper concentrates on the short-period, i.e. subseasonal variations of Earth rotation which can be seen in VLBI measurements of length of day (lod) and polar motion between 1981 and 1999. The wavelet transform allows the time localisation of an irregular quasi-harmonic signal within a given data set. The wavelet analysis of lod series yields in the high-frequency range periods of ∼28 days, ∼14 days down to 6.86 days caused by the lunisolar tides and irregular quasi-periodic variations between 40 and 130 days. These are mainly associated with global zonal wind changes which can be seen when looking on the wavelet cross-scalogram between the lod series and the atmospheric angular momentum (AAM) time series. In polar motion variable periods between two and five months and even down to 7–10 days can be made visible by the wavelet scalograms.Today it is possible by VLBI to determine polar motion and UT1-UTC with a temporal resolution of as short as 3–7 minutes. The results of parallel VLBI sessions which took place since 1998 using two independent VLBI networks were analyzed in the subdiurnal period range and compared by computing the wavelet cross-scalograms, the covariance spectrum and the normed coherency. Periods between 5 and 7 hours can be seen in many of the UT1-UTC data sets besides the well-known diurnal and semi-diurnal periods. The wavelet analyses reveal interesting patterns in the subdiurnal range in polar motion, too.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfa-Kaboodvand, K., Groten, E., Varga, P. and Závoti, J.: 2000, Interpretation of high frequency polar motion and length of day variations, IERS Technical Note No 28, pp. 15–25.
Brosche, P., Seiler, U., Sündermann, J. and Wünsch, J.: 1989, Periodic changes in Earth' rotation due to oceanic tides, Astronomy and Astrophysics 220, 318–320.
Brosche, P., Wünsch, J., Campbell, J. and Schuh, H.: 1991, Ocean tide effects in Universal Time detected by VLBI, Astronomy and Astrophysics 245, 676–682.
Campbell, J. and Schuh, H.: 1986, Short-period variations of Earth rotation determined by VLBI, Proc. of the Xth International Symp. on Earth Tides, Madrid, 1985, ed. by R. Vieira, C.S.I.C., pp. 943–951.
Carter, W.E., Robertson, D.S. and MacKay, J.R.: 1985, Geodetic Radio Interferometric Surveying: Applications and Results, J. Geophys. Res. 90(B6), 4577–4587.
Carter, W.E., Robertson, D.S., Nothnagel, A., Nicolson, G., Schuh, H. and Campbell, J.: 1988, IRISS: Extending Geodetic VLBI Observations to the Southern Hemisphere, J. Geophys. Res. 93, 14947–14953.
Chao, B.F. and Naito, I.: 1995, Wavelet analysis provides a new tool for studying Earth' rotation, EOS Trans. AGU 76, 161–165.
Clark, T.A., Ma, C., Vandenberg, N.R., Gipson, J.M. and Niell, A.E.: 1997, CORE/IVN-Geodetic VLBI for the New Millenium, CSTG Bull. No. 13, Progress Report 1997, ed. by G. Beutler, H. Drewes and H. Hornik, pp. 37–41.
Eubanks, T.M.: 1993, Variations in the orientation of the Earth, In Contributions of Space Geodesy to Geodynamics: Earth Dynamics, Geodynamics Series, AGU 24, 1–54.
Eubanks, T.M., Steppe, J.A., Dickey, J.O., Rosen, R.D. and Salstein, D.A.: 1988, Causes of rapid motions of the Earth' pole, Nature 334, 115–119.
Gambis, D.: 1992, Wavelet transform analysis of the length of the day and the El Niño/Southern Oscillation variations at intraseasonal and interannual time scales, Ann. Geophysicae 10, 429–437.
Gibert, D., Holschneider, M. and Le Mouël, J.L.: 1998, Wavelet Analysis of the Chandler Wobble, J. Geophys. Res. 103(B11), 27069–27089.
Kolaczek, B, Kosek, W. and Schuh, H.: 2000, Short-Period Oscillations of Earth Rotation, Proceedings of the IAU Colloquium 178 Polar motion: Historical and scientific problems, Cagliari, Sept. 1999, ed. by S. Dick, Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series 208, pp. 533–544.
Ma, C.: 1978, Very long baseline interferometry applied to polar motion, relativity and geodesy, Ph.D. Thesis, NASA Technical Memorandum 79582, Greenbelt, USA.
MacMillan D.S., Himwich, W.E., Thomas, C.C., Vandenberg, N.R., Bosworth, J.M., B. Chao, T.A. Clark and C. Ma: CORE: 1999, Continuos, high-accuracy Earth orientation measurements, Proceedings of the 13th Working Meeting on European VLBI for Geodesy and Astrometry, Viechtach, Feb. 12–13, 1999, ed. by W. Schlüter and H. Hase, Bundesamt für Kartographie and Geodäsie, Wettzell, pp. 166–171.
Nothnagel, A., Nicolson, G.D., Campbell, J. and Schuh, H.: 1992, Radiointerferometric polar motion observations with high temporal resolution, Bull. Géod. 66, 346–354.
Popinski, W. and Kosek, W.: 1994, Wavelet transform and its application for short period Earth rotation analysis, Planetary Geodesy 22, 29 (2), 75–86.
Praveen, K.: 1997, Wavelet analysis for geophysical applications, Reviews of Geophysics 35(4), 385–412.
Robertson, D.S., Carter, W.E., Campbell, J. and Schuh, H.: 1985, Daily Earth rotation determinations from IRIS very long baseline interferometry, Nature 316, 424–427.
Rothacher, M., Beutler, G., Weber, R. and Hefty, J.: 2000, High-frequency Earth rotation variations from three years of global positioning system data, submitted to J. Geophys. Res.
Schmidt M.: 2000, Wavelet analysis of stochastic signals, IERS Technical Note No 28, pp. 65–71.
Schmidt, M. and Schuh, H.: 2000, Abilities of wavelet analysis for investigating short-period variations of Earth rotation, IERS Technical Note No 28, pp. 73–80.
Schmitz-Hübsch, H. and Schuh, H.: 1999, Seasonal and short-period fluctuations of Earth rotation investigated by wavelet analysis, Festschrift for E. W. Grafarend, ed. by F. Krumm and V.S. Schwarze, Technical Reports Dep. of Geodesy and Geoinformatics, Nr. 1999.6-2, pp. 421–431.
Schuh, H.: 1999, The rotation of the Earth observed by VLBI, Acta Geod. Geoph. Hung. 34(4), 421–432.
Schuh, H. and Campbell, J.: 1994, VLBI in geodynamical investigations, Acta Geod. Geophys. Hung. 29(3–4), 397–420.
Schuh, H. and Titov, O.: 1999, Short-period variations of the Earth rotation parameters as seen by VLBI, Proc. of the 13th Working Meeting on European VLBI for Geodesy and Astrometry, Viechtach, Feb. 1999, ed. by W. Schlüter and H. Hase, pp. 172–177.
Sovers, O.J.: 1991, Observation model and parameter partials for the JPL VLBI parameter estimation software ‘MODEST’ – 1991, JPL Publication 83-39, Rev. 4.
Sovers, O.J., Fanselow, J.L. and Jacobs, C.S.: 1998, Astrometry and geodesy with radio interferometry: experiments, models, results, Rev. of Modern Physics 70(4), 1393–1454.
Tesmer, V. and Schuh, H.: 2000, Comparison of the results obtained by different VLBI networks within CORE, Proc. of the 14th Working Meeting on European VLBI for Geodesy and Astrometry, Bologna, Sept. 2000, ed. by P. Tomasi, F. Mantovani, M.A. Perez-Torres, pp. 7–12.
Titov, O.: 2000, Least squares collocation method for space geodetic data analysis, Proc. of the IAG Symposium Towards an Integrated Global Geodetic Observing System (IGGOS), Munich, Oct. 1998, IAG Symposia Series 120, ed. by R. Rummel, H. Drewes, W. Bosch, H. Hornik, pp. 238–240.
Titov, O. and Zarraoa, N.: 1997, OCCAM 3.4 user' guide, Communications of the Institute for Applied Astronomy (IAA), St. Petersburg, No. 69.
Weber, R. and Rothacher, M.: 2000, The quality of subdaily polar motion estimates based on GPS observations, Proceedings of the IAU Colloquium 178 Polar motion: Historical and scientific problems, Cagliari, Sept. 1999, ed. by S. Dick, Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series 208, pp. 527–532.
Wünsch, J.: 2000, Oceanic influence on the annual polar motion, J. of Geodynamics 30, 389–399.
Yoder, C.E., Williams, J.G. and Parke, M.E.: 1981, Tidal variations of Earth rotation, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 881–891.
IERS Conventions (1996): 1996, ed. by D. D. McCarthy, IERS Technical Note 21, Observatoire de Paris.
IERS Technical Note No. 28: 2000, High frequency oscillations of Earth rotation, ed. by B. Kolaczek, H. Schuh and D. Gambis, Observatoire de Paris.
International VLBI Service for Geodesy and Astrometry (IVS): 1999, Annual Report, 1999, ed. by N.R. Vandenberg, NASA /TP-1999-209243. (also on the IVS web site: http://ivscc.gsfc.nasa.gov/publications/ar1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuh, H., Schmitz-Hübsch, H. Short Period Variations In Earth Rotation As Seen By VLBI. Surveys in Geophysics 21, 499–520 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006769727728
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006769727728