Abstract
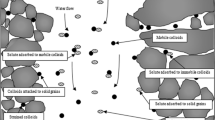
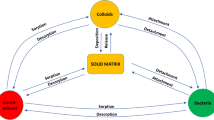
The presence of colloidal particles in groundwater can enhance contaminant transport by reducing retardation effects and carrying them to distances further than predicted by a conventional advective/dispersive equation with normal retardation values. When colloids exist in porous media and affect contaminant migration, the system can best be simulated as a three-phase medium. Mechanisms of mass transfer from one phase to another by colloids and contaminants can be kinetic or equilibrium-based, depending on the sorption–desorption reaction rate between the aqueous and solid phases. When the rate of sorption between the water phase and the solid phase(s) is not much greater than the rate of change in contaminant concentration in the water phase, kinetic sorption models may better describe the phenomenon. In some cases of modeling one or more mass transfer processes, a useful simplification may be to introduce the local equilibrium assumption. In this study, the local equilibrium assumption for sorption processes on colloidal surfaces (hybrid equilibrium model) was compared with kinetic-based models. Sensitivity analyses were conducted to deduce the effect of major parameters on contaminant transport. The results obtained from the hybrid equilibrium model in predicting the transport of colloid-facilitated groundwater contaminant are very similar to those of the kinetic model, when the point of interest is not at contaminant and colloid source vicinities and the time of interest is sufficiently long for imposed sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atinger, R., Kienzler, B., Schubler W. and Kim, J. I.: 1998, Effects of humic substances on the 214Am migration in a sandy aquifer: Column experiments with Gorleben groundwater/sediment systems, J. Contam. Hydrol. 35, 261–275.
Bahr, J. M.: 1990, Kinetically-influenced terms for solute transport affected by heterogeneous and homogeneous classical reactions, Water Resour. Res. 26, 21–34.
Bahr, J. M. and Rubin, J.: 1987, Direct comparison of kinetic and local equilibrium formulations for solute transport affected by surface reaction, Water Resour. Res. 23, 438–452.
Brusseau, M. L. and Rao, P. S. C.: 1989, Sorption nonideality during organic contaminant transport in porous media, CRC Crit. Rev. Envir. Control 19, 22–99.
Corapcioglu, M. Y. and Jiang, S.: 1993, Colloid-facilitated groundwater contaminant transport, Water Resour. Res. 29, 2215–2226.
Corapcioglu, M. Y. and Jiang, S.: 1996, Dimensional analysis of colloid-facilitated groundwater contaminant transport, J. Hydrologic Engng, ASCE 1, 139–143.
Domenico, P. A. and Schwartz, F.W.: 1990, Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, Wiley, New York, P. 477.
Jardine, P. M., Dunnivant, F. M., Selim and McCarthy, J. F.: 1992, Comparison of models for describing the transport of dissolved organic carbon in aquifer columns, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 56, 393–401.
Jennings, A. A. and Kirkner, D. J.: 1984, Instantaneous equilibrium approximation analysis, J. Hydraulic Engng, ASCE 110(2), 1700–1717.
Jiang, S. and Corapcioglu, M. Y.: 1993, A hybrid-equilibrium model of solute transport in porous media in the presence of colloids, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 73, 275–286.
Kim, S. and Corapcioglu, M. Y.: 1996, A kinetic approach to modeling mobile bacteria-facilitated groundwater contaminant transport, Water Resour. Res. 32, 321–331.
McCarthy, J. F. and Zachara, M. M.: 1989, Subsurface transport of contaminants, Envir. Sci. Technol. 23(5), 496–502.
Rubin, J.: 1983, Transport of reacting solutes in porous media: Relation between mathematical nature of problem formulation and chemical nature of reactions, Water Resour. Res. 19, 1231–1252.
Travis, C.C. and Etnier, E. L.: 1981, A survey of sorption relationships for reactive solutes in soil, J. Environ. Qual. 10, 8–17.
Valocchi, A. J.: 1985, Validity of the local equilibrium assumption for modeling sorbing solute transport through homogeneous soil, Water Resour. Res. 21, 808–820.
Weber, W. J., McGinley, P. M. and Katz, L. E.: 1991, Sorption phenomena in subsurface systems: Concepts, models and effects on contaminant fate and transport, Water Res. 25, 499–528.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corapcioglu, M.Y., Jiang, S. & Kim, Sh. Comparison of Kinetic and Hybrid-Equilibrium Models Simulating Colloid-Facilitated Contaminant Transport in Porous Media. Transport in Porous Media 36, 373–390 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006683030354
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006683030354