Abstract
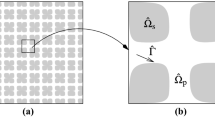
This paper is devoted to the computation of effective equations for the transport of a solute in a chromatograph. We focus our attention on models that retain dispersion effects. A chromatograph is a biporous periodic heterogeneous medium, made up of macropores, and of small porous adsorbing crystals that have a retention effect on the solute. We use the method of multiple scales expansions. Various macroscopic behaviours appear, according to the respective orders of magnitude of the dimensionless characteristic parameters: Peclet number in the macropores, ratio of the characteristic time of diffusion in the macropores to the characteristic time of diffusion in the crystals, adsorption coefficient. Dispersion occurs for a Peclet number of order ε−1. We then discuss the effective behaviour of the solute, with respect to the orders of magnitude of the other characteristic parameters. To our knowledge, most of the models are new. Our modelling is not restricted to chromatographs. It applies to various situations of physic and chemical engineering: fixed bed reactors, catalytic cracking, ground water for instance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire, G.: Homogenization and two scale-convergence, SIAM J. Math. An. 23(26) (1992), 1482–1518.
Amaral Souto, H. P.: diffusion–dispersion en milieu poreux: étude numérique du tenseur de dispersion pour quelques arrangements périodiques bidimensionnels “ordonnés” et “désordonn és”, thèse de l'Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine, 1993.
Aris, R.: On the dispersion of a solute in a fluid flowing through a tube, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 235 (1956), 67–77.
Auriault, J. L.: Heterogeneous medium. Is an equivalent macroscopic description possible? Int. J. Engng Sci. 29(7) (1991), 785–795.
Auriault, J. L. and Adler, P. M.: Taylor dispersion in porous media: analysis by multiple scale expansions, Adv. Water Res. 18(4) (1995) 217–226.
Auriault, J. L., Lewandowska, J.: Macroscopic modelling of pollutant transport in porous media, Arch. Mech. 45(I) (1993) 51–64.
Auriault, J. L. and Lewandowska, J.: Modelling of pollutant migration in porous media with interfacial transfer: local equilibrium/non-equilibrium, Mechanics of Cohesive-Frictional Materials 2 (1997), 205–221.
Bear, J.: Hydrodynamic Dispersions in Flow Through Porous Media, In: (R. de Wiest (ed.), Academic Press, New York, 1969.
Brenner, H.: Dispersion resulting from flow through spatially periodic porous media, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. 297 (1980), 81–133.
Carbonell, R. G. and Whitaker, S.: Dispersion in pulsed systems II, theoretical developments for passive dispersion in porous media, Chem. Engng Sci. 38 (1983), 1795–1802.
Dagan, G.: Flow and Transport in Porous Formations, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1989.
De Josselin de Jong, G.: Longitudinal and transverse diffusion in granular deposits, Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 39(1) (1958), 67–74.
Frankel, I. and Brenner, H.: Dispersion resulting from flow through spatially periodic porous media, J. Fluid Mech. 204 (1989), 97–191.
Golay, M. J. E.: Theory of Chromatography in Open and Coated Tubular Columns with Round and Rectangular Cross-sections, In: D. H. Desty (ed.), Butterworths, London, 1958, pp. 36–55.
Mei, C. C.: Method of homogenization applied to dispersion in porous media, Transport in Porous Media 9 (1992), 261–274.
Rubinstein, J. and Mauri, R.: Dispersion and convection in periodic porous media, SIAM, J. Appl. Math. 46(6) (1986), 1019–1023.
Saffman, P. G.: A theory of dispersion in porous medium, J. Fluid Mech. 6 (1959), 321–349.
Sanchez-Palencia, E.: Non-homogeneous Media and Vibration Theory, Lecture Notes in Physics N 127, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1980.
Scheidegger, A. E.: A general theory of dispersion in porous media, J. Geophys. Res. 66(10) (1961), 3273–3278.
Taylor, G. I.: Dispersion of soluble matter in solvent flowing slowly through a tube, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 223 (1954).
Valentin, P.: Chromatographie en phase gazeuse, thèse d'état, université de Paris VI, 1971.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canon, É., Bensmina, H. & Valentin, P. On the Modelling of Generalized Taylor–Aris Dispersion in Chromatographs via Multiple Scales Expansions. Transport in Porous Media 36, 307–339 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006654621514
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006654621514