Abstract
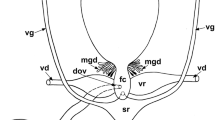
The process of egg formation in the body cavity of a phytoseiid mite, Phytoseiulus persimilis, was observed to examine fertilization of male eggs. After insemination, one of the ova at the periphery of the ovary began to expand, taking up yolk. Two pronuclei appeared in the expanded egg, located dorsally in the ovary, and yolk granules were formed gradually. After the egg became filled with yolk granules the two pronuclei fused. The egg moved via the narrow entrance at the ventral region into the oviduct, where the eggshell was formed. When the eggshell was complete, and while embryogenesis proceeded, the egg was deposited. In the meantime some ova began to expand sequentially and two joining pronuclei appeared in expanding eggs. The joining pronuclei in the first egg proved male diploidy. This is additional evidence of pseudo-arrhenotoky in this phytoseiid mite species, since the first eggs developed into males.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti, G. 1988. Genital system of gamasida and its bearing on phylogeny. In: Progress in acarology, G.P. ChannaBasavanna and C.A. Viraktamath (eds), Vol. 1, pp. 479–490. Ellis Horwood, Chichester.
Alberti, G. and Hänel, H. 1986. Fine structure of the genital system in the bee parasite, Varroa jacobsoni (Gamasida: Dermanyssina) with remarks on spermiogenesis, spermatozoa and capacitation. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2: 63–104.
Amano, H. and Chant, D.A. 1978. Mating behavior and reproductive mechanisms of two species of predacious mites, Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot and Amblyseius andersoni (Chant) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Acarologia 20: 196–213.
Blommers-Schlosser, R. and Blommers, L. 1975. Karyotypes of eight species of phytoseiid mites (Acarina: Mesostigmata) from Madagascar. Genetica 45: 145–148.
De Jong, J.H., Lobbes, P.V. and Bolland, H.R. 1981. Karyotypes and sex determination in two species of laelapid mites (Acari: Gamasida). Genetica 55: 187–190.
Hansell, R.I., Mollison, M.M. and Putman, W.L. 1964. A cytological demonstration of arrhenotoky in three mites of the family Phytoseiidae. Chromosoma 15: 562–567.
Helle, W., Bolland, H.R., van Arendonk, R.V., De Boer, R., Schulten, G.G.M. and Russell, V.M. 1978. Genetic evidence for biparental males in haplo-diploid predator mites (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Genetica 49: 165–171.
Hoy, M.A. 1979. Parahaploidy of the "arrhenotokous" predator, Metaseiulus occidentalis (Nesbitt) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Chromosoma 77: 263–276.
Michael, A.D. 1892. On the variations in the internal anatomy of the Gamasina especially in that of the genital organs, and their mode of coition. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond. (Zool.) 5: 281–317.
Nelson-Rees, W.A., Hoy, M.A. and Roush, R.T. 1980. Heterochromatinization, chromatin elimination and haploidization in the parahaploid mite Metaseiulus occidentalis (Nesbitt) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Chromosoma 77: 263–276.
Norton, R.A., Kethley, J.B., Johnston, D.E. and Oconnor, B.M. 1993. Phylogenetic perspectives on genetic systems and reproductive modes of mites. In: Evolution and Diversity of Sex Ratio in Insects and Mites, D.L. Wrensch and M.A. Ebbert (eds), pp. 8–99. Chapman & Hall, New York.
Oliver, J.H., Jr. 1977. Cytogenetics of mites and ticks. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 22: 407–429.
Romoser, W.S. and Stoffolano, J.G., Jr. 1998. The Science of Entomology. McGraw-Hill, Singapore, 4th ed., 605 pp.
Schulten, G.G.M. 1985. Pseudo-arrhenotoky. In: World Crop Pests: Spider Mites, Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, W. Helle and M.W. Sabelis (eds), Vol. 1B, pp. 67–71. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Schulten, G.G.M., van Arendonk, R.C.M., Russell, V.M. and Roorda, F.A. 1978. Copulation, egg production and sex-ratio in Phytoseiulus persimilis and Amblyseius bibens (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 24: 145–153.
Toyoshima, S. and Amano, H. 1998. Effect of prey density on sex ratio of two predacious mites, Phytoseiulus persimilis and Amblyseius womersleyi (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 22: 709–723.
Went, D.F. and Krause, K. 1973. Normal development of mechanically activated, unlaid eggs of an endoparasitic hymenopteran. Nature 244: 454–455.
White, M.J.D. 1973. Animal Cytology and Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 3rd ed., 961 pp.
Wysoki, M. 1973. Further studies on karyotypes and sex determination of phytoseiid mites (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Genetica 44: 139–145.
Wysoki, M. 1985. Karyotyping. In: World Crop Pests: Spider Mites, Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, W. Helle and M.W. Sabelis (eds), Vol. 1B, pp. 191–196. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Wysoki, M. and Bolland, R. 1983. Chromosome studies of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Gamasida). Intern. J. Acarol. 9: 91–99.
Wysoki, M. and McMurtry, J.A. 1977. Karyotypes of eight species of phytoseiid mites of the genus Amblyseius Berlese (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Genetica 47: 237–239.
Wysoki, M. and Swirski, E. 1968. Karyotypes and sex determination of ten species of phytoseiid mites (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Genetica 39: 220–228.
Yastrebtsov, A.V. 1992. Embryonic development of gamasid mites (Parasitiformes: Gamasida). Intern. J. Acarol. 18: 121–141.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toyoshima, S., Nakamura, M., Nagahama, Y. et al. Process of Egg Formation in the Female Body Cavity and Fertilization in Male Eggs of Phytoseiulus Persimilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 24, 441–451 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006484621449
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006484621449