Abstract
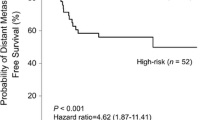
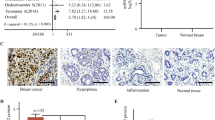
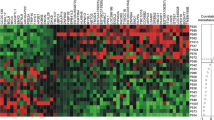
In the present study, mdr1 gene expression was investigated by a sensitive reverse transcriptase-PCR assay in advanced breast cancer and in corresponding adjacent normal tissues obtained before and after treatment with primary chemotherapy. Comparatively to normal tissues, a significant induction of mdr1 expression was observed in untreated tumors (p=0.0222). Similarly, a significant induction of mdr1 expression was revealed when treated samples were compared to untreated counterparts (p=0.0222), but no differences were detected between tumor and normal samples (p=0.3199). Noteworthy, a significant induction of mdr1 gene expression occurred in treated normal samples comparatively to untreated ones (p=0.0037), and this induction was even more important in normal than in tumoral tissue (p=0.0627). However, neither the basal expression nor the induction of mdr1 were correlated with subsequent response to chemotherapy or with survival. Thus, in agreement with previous reports, our data show that chemotherapy induce mdr1 gene expression in breast cancer cells, but they also indicate that a similar phenomenon occurs in adjacent normal tissues. Therefore, our results strongly suggest that mdr1 gene overexpression is not a characteristic of breast malignant cells, but rather constitutes a general phenomenon occurring both in normal and tumor cells which could explain at least in part the absence of relationship between mdr1 expression and the clinical outcome of breast cancer patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris JR, Morrow M, Bonadonna G: Cancer of the breast. In: DeVita VT Jr, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA (eds) Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. Lippincott, Philadelphia, 1993, pp 1264–1332
Goldstein LJ: MDR1 gene expression in solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 32A: 1039–1050, 1996
Gros P, Croop J, Housman D: Mammalian multidrugresistance gene: complete sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell 47: 371–374, 1986
Luker GD, Nilsson KR, Covey DF, Piwnica-Worms D: Multidrug resistance (MDR1) P-glycoprotein enhances esterification of plasma membrane cholesterol. J Biol Chem 274: 6979–6991, 1999
Radvin PM: Anthracycline resistance in breast cancer: clinical applications of current knowledge. Eur J Cancer 31A: S11–S14, 1995
Ling V:Multidrug resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 40 suppl: S3–8, 1997
Madden MJ, Morrow CS, Nakagawa M, Goldsmith ME, Fairchild CR, Cowan KH: Identification of 50 and 30 sequences involved in the regulation of transcription of the human mdr1 gene in vivo. J Biol Chem 268: 8290–8297, 1993
Bradshaw DM, Arceci RJ: Clinical relevance of transmembrane drug efflux as a mechanism of multidrug resistance. J Clin Oncol 16: 3674–3690, 1998
Salmon SE, Grogan TM, Miller T, Scheper R, Dalton WS: Prediction of doxorubicin resistance in vitro in myeloma, lymphoma, and breast cancer by p-glycoprotein staining. J Natl Cancer Inst 81: 696–701, 1989
Warner E, Hedley D, Andrulis I, Myers R, Trudeau M, Warr D, Pritchard KI, Blackstein M, Goss PE, Franssen E, Roche K, Knight S, Webster S, Fraser RA, Oldfied SS, Hill W, Kates R: Phase II study of dexverapamil plus anthracycline in patients with metastatic breast cancer who have progressed on the same anthracycline regimen. Clin Cancer Res 4: 1451–1457, 1998
Chevillard S, Pouillart P, Beljord C, Asselain B, Beuzeboc P, Magdelénat H, Vielh P: Sequential assessment of multidrug resistance phenotype and measurement of S-phase fraction as predictive markers of breast cancer response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer 77: 292–300, 1996
Wang CS, LaRue H, Fortin A, Gariepy G, Tetu B: mdr1 mRNA expression by RT-PCR in patients with primary breast cancer submitted to neoadjuvant therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 45: 63–74, 1997
Punyammlee B, Manoromana S, Purisa W, Chariyalertsak S, Rerkamnuaychok B: Association of mdr1 gene expression with other prognostic factors and clinical outcome in human breast cancer. J Med Assoc Thai 80S1: S162–S173, 1997
Kaye SB: Multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Is the jury in yet? J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 902–903, 1997
Trock BJ, Leonessa F, Clarke R: Multidrug resistance in breast cancer: a meta-analysis of MDR1/gp170 expression and its possible functional significance. J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 917–931, 1997
Linn SC, Pinedo HM, Van Ark-Otte J, Van der Valk P, Hoekman K, Honkoop AH, Vermorken JB, Giaccone G: Expression of drug resistance proteins in breast cancer, in relation to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer 71: 787–795, 1997
Mechetner E, Kyshtoobayeva A, Zonis S, Kim H, Stroup R, Garcia R, Parker RJ, Fruchaud JP: Levels of multidrug resistance (MDR1) p-glycoprotein expression by human breast cancer correlate with in vitro resistance to taxol and doxorubicin. Clin Cancer Res 4: 389–398, 1998
Hegewisch-Becker S, Staib F, Löning T, Pichlmeier U, Kröger N, Reymann A, Hossfeld DK: No evidence of significant activity of the multidrug resistance gene product in primary human breast cancer. Ann Oncol 9: 85–93, 1998
Gause WC, Adamovicz J: Use of PCR to quantitate relative differences on gene expression. In: Dieffenbach CW, Dveksler GS (eds) PCR Primer, A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1995, pp 293–311
Riedy MC, Timm EA, Jr, Stewart CC: Quantitative RT-PCR for measuring gene expression. In: Siebert P (ed) The PCR Technique: RT-PCR. Eaton Publishing, 1998, pp 169–177
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N: Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Annal Biochem 162: 156–159, 1987
Giaccone G, Linn SC, Pinedo HM: Multidrug resistance in breast cancer: mechanisms, strategies. Eur J Cancer 31A (Suppl. 7): S15–S17, 1995
Dexter DW, Reddy RK, Geles KG, Bansal S, Myint MA, Rogakto A, Leighton, JC, Goldstein LJ: Qantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction measured expression of MDR1 and MRP in primary breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 4: 1533–1542, 1998
Yang X, Uziely B, Groshen S, Lukas J, Israel V, Russell C, Dunnington G, Formenti S, Muggia F, Press MF: MDR1 gene expression in primary and advanced breast cancer. Lab Invest 79: 271–280, 1999
Baas F, Jongsma APM, Broxterman HJ, Arceci RJ, Housman D, Scheffer GL, Riethorst A, van Groenigen M, Nieuwint AWM, Joenje H: Non-P-glycoprotein mediated mechanism for miltidrug resistance precedes P-glycoprotein expression 20 M Arnal et al. during in vitro selection for doxorubicin resistance in a human lung cancer cell line. Cancer Res 50: 5392–5398, 1990
Ohga T, Koike K, Ono M, Makino Y, Itagati Y, Tanimoto M, Kuwano M, Kohno K: Role of the human Y box-binding protein YB-1 in cellular sensitivity to the DNA-damaging agents cicplatin, mitomycin C, and ultraviolet light. Cancer Res 56: 4224–4228, 1996
Goldsmith ME, Madden MJ, Morrow CS, Cowan KH: A Ybox consensus sequence is required for basal expression of the human multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene. J Biol Chem 268: 5856–5860, 1993
Combates NJ, Rzepka RW, Chen YNP, Cohen D: NF-IL6, a member of the C/EBP family of transcription factors, binds and trans-activates the human MDR1 gene promoter. J Biol Chem 269: 29715–29719, 1994
Kono K, Tanimura H, Sato S, Nakayama Y, Makino Y, Wada M, Fojo AT, Kuwano M: Cellular control of human multidrug resistance 1 (mdr-1) gene expression in absence and presence of gene amplification in human cancer cells. J Biol Chem 269: 20503–20508, 1994
Ohga T, Uchiumi T, Makino Y, Koike K, Wada M, Kuwano M, Kohno K: Direct involvement of the Y-box binding protein YB-1 in genotoxic stress-induced activation of the human multidrug resistance 1 gene. J Biol Chem 273: 5997–6000, 1998
Ladomery M, Sommerville J: A role for Y-box proteins in cell plofieration. Bio Essays 17: 9–11, 1995
Bargou RC, Jurchott K, Wagener C, Bergmann S, Metzner S, Bommert K, Mapara MY, Winzer KJ, Dietel M, Dorken B, Royer HD: Nuclear localization and increased levels of transcription factor YB-1 in primary human breast cancers are associated with intrinsic MDR1 gene expression. Nature Med 3: 447–450, 1997
Ogretmen B, Safa AR: Negative regulation of MDR1 promoter activity in MCF-7, but not in multidrug resistant MCF-7/Adr, cells by cross-coupled NF-kB/p65 and c-Fos transcription factors and their intraction with CAAT region. Biochemistry 38: 2189–2199, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arnal, M., Franco, N., Fargeot, P. et al. Enhancement of mdr1 gene expression in normal tissue adjacent to advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 61, 13–20 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006449931921
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006449931921