Abstract
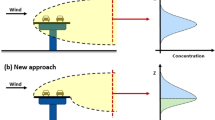
An integrated method for the prediction of the spatial pollution distribution within a street canyon directly from a microscopic traffic simulation model is outlined. The traffic simulation package Paramics is used to model the flow of vehicles in realistic traffic conditions on a real road network. This produces details of the amount of pollutant produced by each vehicle at any given time. The authors calculate the dispersion of the pollutant using a particle tracking diffusion method which is superimposed on a known velocity and turbulence field. This paper shows how these individual components may be integrated to provide a practical street canyon pollution model. The resulting street canyon pollution model provides isoconcentrations of pollutant within the road topography.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison P. S. (1997), EPSRC Grant GR/L3608, 'Investigation of a Separation-Distance Centred Non-Linear Car-Following Model'.
Addison P. S., Qu B., Nisbet A. &; Pender G. (1997), A non-Fickian particletracking diffusion model based on fractional Brownian motion, Int. J. Numerical Methods in Fluids, 25, pp 1373–1384.
Addison P. S., Qu B., Ndumu A. S. and Pyrah I. (1998), A particle tracking model for non-Fickian subsurface diffusion, Math. Geology, 16, pp 127–151.
Addison P.S., McCann J.M., Low D.J. and Currie J.I., (1999) 'An Integrated Approach to Modelling Traffic Pollution in the Urban Environment', Traffic Engineering and Control. (In Press.)
Hotchkiss R. S. &; Harlow. H. (1973), 'Air pollution in street canyons', Rep. EPA-R4-73-029, U.S. Env. Protection Agency, Washington D.C., United States.
Low D. J. &; Addison P. S. (1998a), The Complex Dynamical Behaviour of Congested Road Traffic, 3rd IMA Conf. on Mathematics in Transport Planning and Control, Cardiff Wales, April 1-3.
Low D. J. &; Addison P. S. (1998b), A Nonlinear Temporal Headway Model of Traffic Dynamics, Nonlinear Dynamics, 16, pp 127–151.
Lanzani G. &; Tamponi M. (1995), A microscale Lagrangian particle model for the dispersion of primary pollutants in a street canyon, Atmospheric Environment, 29, (23), pp 3465–3475.
Thomson D. J. (1985), A random walk model of dispersion in turbulent flows and its application to dispersion in a valley, Q.J.R. Met. Soc., 112, pp511–530
Yamarito R. J. &; Wiegand G. (1986), Development and evaluation of simple models for the flow, turbulence and pollutant concentration fields within an urban street canyon, Atmospheric Environment, 20(11), pp 2137–21562
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Addison, P.S., Currie, J.I., Low, D.J. et al. An Integrated Approach to Street Canyon Pollution Modelling. Environ Monit Assess 65, 333–342 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006400406047
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006400406047