Abstract
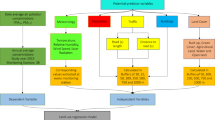
Air quality monitoring is currently ensured by captors measuring few physicochemical parameters, then they cannot evaluate unforeseen compounds and the interaction effects of pollutants. On the contrary, the use of bioindicators can answer these problems. Among them, plants are used in two ways:
1) Passive bioindicators: trees, lichens and mosses are used to determine the distribution and even the contaminants long-term effects on vast zones and, possibly, the concentrations of pollutants to which they were exposed.
2) Active bioindicators: tobacco and mosses make available the defective zones in plants and enable determination of deposition fluxes.
Moreover, techniques based on biomarkers identification should increase the answer's sensitivity. However, the plants present the disadvantage of being unable to provide a response in a time lapse comparable with that of the on-line analysers. Lastly, the development of tools using animal cells should allow, in the near future, to measure the total polluting load under conditions close to those of the routine techniques. Then, the real impact of the contaminant on public health could be approached.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADEME: 1997, ‘La qualité de l'air en France 1994–1995. Zones urbaines industrielles, rurales’, Technical Report, ADEME, Paris, France, 150 p.
ADEME and INRET: 1995, ‘La pollution automobile et ses effets sur la santé: Interrogations et propositions’, Technical Report, ADEME, Paris, France, 45 p.
Aerts, C., Tonnel, A. B., Dutriez, N. and Voisin, C.: 1979, ‘Sensibilité in vitro des macrophages alvéolaires aux composants gazeux de la fumée de tabac’, Les colloques de l'INSERM, INSERM (Ed.), 84, 177–186.
Asta, J.: 1996, ‘Les lichens bioindicateurs de pollution atmosphérique: exemples de cas étudiés en milieux perturbés dans les Alpes’, in L'écotoxicologie du Compartiment Aérien, Congress, Rouen, France, Société d'Ecotoxicologie Fondammentale et Appliquée, pp. 191–196.
Beckett, P. J., Boileau, L. J. R., Padovan, D. and Richardson, D. H. S.: 1982, ‘Lichens and mosses as monitors of industrial activity associated with uranium mining in northern Ontario, Canada’, Environ. Pollut. 4, 91–107.
Becker, M. and Levy, G. D.: 1982, ‘Le dépérissement du chêne en forêt de Tronçais. Les causes écologiques’, Ann. Sci. For. 39, 439–444
Becker, M. and Levy, G. D.: 1988, ‘A propos du dépérissement des forêts: Climat, sylviculture et vitalité de la sapinière vosgienne’, Revue forestière française XL, 345–357.
Belandria, G., Asta, J. and Garrec, J. P.: 1986, ‘Diminution of fluorine contents in lichens due to a regression of pollution in an alpine valley (Maurienne, Savoie, France) from 1975 to 1985’, Rev. Ecol. Alp. 1, 45–58.
Belandria, G. and Asta, J.: 1987, ‘Les lichens bioaccumulateurs: Régression de la pollution fluorée dans la vallée de la Romanche (Isère, France)’, Bull. Ecol. 18, 117–126.
Berg, T., Røyset, O. and Steinnes, E.: 1995, ‘Moss (Hylocomium plendens) used as biomonitor of atmospheric trace element deposition: estimation of uptake efficiencies’, Atm. Env. 29, 353–360.
Bytnerowicz, A., Manning, W. J., Grosjean, D., Chmielewski, W., Dmuchowski, W., Grodzinska, K. and Godzik, B.: 1993, ‘Detecting ozone and demonstrating its phytotoxicity in forested areas of Poland-A pilot study, Environ. Pollut. 80, 301–305.
Bonneau, M. and Landamann, G.: 1988, ‘De quoi la forêt est-elle malade?’, La recherche 205, 1543–1553.
Bonte, J.: 1995, ‘Les effets des polluants sur la végétation’, Technical Report, CDERE, Pau, France, 36 p.
Bouvarel, P.: 1984, ‘Le dépérissement des forêts attribué aux dépôts atmosphériques acides’, Revue forestière française. XXXVI, 173–180.
Brown, D. H. and Brumelis, G.: 1996, ‘A biomonitoring method using the cellular distribution of metal in moss’, Sci. Total Environ. 187, 153–161.
Brown, D. H. and Beckett, R. P.: 1983, ‘Differential sensitivity of lichens to heavy metals’, Ann. of Bot. 52, 51–57.
Castillo, F. and Greppin, H.: 1986, ‘Balance between anionic and cationic extracellular peroxidase activities of Sedum album leaves after ozone exposure. Analysis by high-performence liquid chromatography’, Physiol. Plant. 68, 201–208.
Chiment, F. F., Alscher, R. and Hughes, P. R.: 1986, ‘Glutathione as an indicator of SO2-induced stress in soybean root’, Environ. Exp. Bot. 26, 147–152.
Chiron, M., Quenel, P. and Zmirou, D.: 1997, ‘La pollution d'origine automobile et la santé publique’, Pollution atmosphérique, 153, 41–55.
Cuny, D.: 1997, ‘Bioindication et Bioaccumulation Lichénique sur l'Autoroute du Nord’, in Les Bioindicateurs de la Qualité de l'Air, Congress, Rouen, France, Association Française des Ingénieurs Ecologues, pp. 59–67.
De Backker, A. J.: 1989, ‘Effects of ammonia emission on epiphitic lichen vegetation’, Acta Botonica Neerlandica 38, 337–342.
De Bruin, M. and Hackenitz, E.: 1986, ‘Trace element concentrations in epiphytic lichens and bark substrate’, Environ. Pollut. 11, 153–160.
Deruelle, S.: 1978, ‘Etude comparée de la sensibilité de trois méthodes d'estimation de la pollution atmosphérique, en utilisant les lichens comme indicateurs biologiques, dans la région de Nantes (Yvelines)’, Rev. Bryol. Lichénol. 44, 429–441.
Deruelle, S.: 1984, ‘L'utilisation des lichens pour la détection et l'estimation de la pollution par le plomb’, Bull. Ecol. 15, 1–6.
Deruelle, S.: 1992, ‘Accumulation du plomb par les lichens’, Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 139, 99–109.
Deruelle, S. and Lallemand, R.: 1983, Les lichens témoins de la pollution, Thème Vuibert Université, Vuibert Editeur, 108 p.
Dobson, F.: 1992, Lichens-An Illustrated Guide’, Richmond Publishing, 3rd Ed., 410 p.
Elstner, E. F., Wagner, E. F. and Schutz, W.: 1988, ‘Activated oxygen in green plants in relation to stress situations’, Curr. Topics Plant Biochem. Physiol. 7, 159–187.
European Environment Agency: 1997, ‘Rapport CORINAIR 94’, Technical Report, Summary Report 1, European Environment Agency, Copenhagen, Denmark, 115 p.
Feder, W. A.: 1978, ‘Plants as bioassay systems for monitoring atmospheric pollutants’, Environ. Health Persp. 27, 139–147.
Garrec, J.-P.: 1993a, ‘La Bioindication Végétale de la Pollution Atmosphérique. Evolution Actuelle et son Utilisation’, in Pollution à l'Échelle Locale et Régionale, Congress, Cachan, France, pp. 199–202.
Garrec, J.-P.: 1993b, ‘Evolution de la pollution atmosphérique en France. De la pollution locale à la pollution globale’, Ann. Géo. 572, 359–365.
Garrec, J.-P.: 1997, ‘L'approche de la Qualité de l'Air dans les Pays en Développement’, in Les Bioindicateurs de la Qualité de l'Air, Congress, Rouen, France, Association Française des Ingénieurs Ecologues, pp. 91–97.
Garrec, J.-P. and Livertoux, M.-H.: 1997, ‘Bioindication végétale de l'ozone dans l'agglomération nancéenne durant l'été 1996’, Pollution Atmosphérique 156, 78–87.
Garrec, J.-P. and Radnai, F.: 1966, ‘Economical study and mapping of air pollution by plant bioindicators’, Technical Report, INRA, Nancy, France, 12 p.
Gaveriaux, J.-P.: 1996, ‘Les lichens et la bioindication de la qualité de l'air’, Bull. Soc. Bot. Nord. Fr. 49, 5–52.
Gery, A.: 1997, Qualité des fumées d'incinération de déchets évaluée par mesure de la cytotoxicité sur cellules de type macrophagique, Doctoral thesis, University of Metz, Metz, France, 108 p.
Giovani, C., Nimis, P. L., Bolognini, G., Padovani, R. and Usco, A.: 1994, ‘Bryophytes as indicators of radiocesium deposition in northeastern Italy’, Sci. Total Environ. 157, 35–43.
Graedel, T. and Crutzen, P.: 1996, ‘L'état de l'atmosphère’, Pour la Science. Hors série 12, 84–90.
Grasso, M. F., Clocchiatti, R., Carrot, F., Deschamps, C. and Vurro, F.: 1999, ‘Lichens as bioindicators in volcanic areas:Mt. Etna and Vulcano Island (Italy)’, Environ. Geol. 37, 207–217.
Guinochet, M.: 1973, Phytosociologie, Paris, Masson & Cie éditeurs, 1st Ed., 227 p.
Hawksworth, D. L. and Rose, F.: 1970, ‘Qualitative scale for estimating sulfur dioxyde air pollution in England and Wales using epiphytic lichens’, Nature 227, 145–148.
Hawksworth, D. L. and Rose, F.: 1976, Lichens as pollution monitors, The institutes of biology's studies in biology, Edward Arnold Publishers, London, England, 60 p.
Hodin, A. and Hertz, P. A.: 1996, ‘Evaluation de la Pollution Atmosphérique Industrielle et Urbaine à Partir des Données Météorologiques de Routine' in L'écotoxicologie du compartiment aérien, Congress, Rouen, France, Société d'Ecotoxicologie Fondamentale et Appliquée, pp. 103–112.
Hoffard, W. H., Marx, D. H. and Brown, H. D.: 1995, The Health of Southern Forests, USDA Forest Service, Pennsylvania State University, U.S.A., 36 p.
Huebert, D. B., L'Hirondelle, S. J. and Addison, P. A.: 1985, ‘The effects of sulfur dioxide on net CO2 assimilation in the lichen Evernia mesomorpha Nyl.’, New Phytol. 100, 643–651.
Hynninen, V.: 1986, ‘Monitoring of airborne metal pollution with moss bags near an industrial source at Harjavalta’, Southwest Finland, Ann. Bot. Fennici. 23, 83–90.
Joumard, R.: 1997, ‘Synthèse sur l'Émission de Véhicule’, in La Pollution Automobile dans les Villes, Congress, Rouen, France, International Society for the Built Environment, 44–52.
Jovanovic, S., Carrot, F., Deschamps, C. Deschamps, N. and Vukotic, P.: 1995, ‘A study of the air pollution in the surroundings of an aluminium smelter, using epiphytic and lithophytic lichens’, J. Trace Microprob. T. 13, 463–471.
Keller, T.: 1974, ‘The use of peroxydase activity for monitoring and mapping air pollution areas’, Eur. J. For Pathol. 4, 11–19.
Kruppa, S. V., Nosal, M. and Manning, W. J.: 1992, ‘Establishing Relationships between Ambient Ozone Exposure Dynamics and Visible Foliar Injury Responses of Tabacco Cultivar’, in Air Pollution Control, 9th World Clean Air Congress, Montréal, Canada, IUAPPA, 12 p.
Landmann, G.: 1995, ‘Impacts de la Pollution Atmosphérique Diffuse sur la Végétation Forestière. Les Enseignements d'une Décennie de Recherches Françaises’, in 'L'écotoxicologie du Compartiment Aérien, Congress, Rouen, France, Société d'Ecotoxicologie Fondamentale et Appliquée, pp. 127–135.
Leblanc, F. and De Sloover, J.: 1970, ‘Relations between industrialisation and distribution and growth of epiphic lichens in Montreal’, Can. J. Bot. 48, 1485–1496.
Leclerc, B.: 1996, ‘L'état de l'atmosphère’, Pour la Science, Hors série 12, 128–129.
Lee, F. J. and Bennett, J. H.: 1985, ‘Superoxide dismutase. A possible protective enzyme against ozone injury in snap beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)’, Plant Physiol. 69, 1444–1449.
Lippo, H., Poikolainen, J. and Kubin, E.: 1995, ‘The use of moss, lichen and pine bark in the nationwide monitoring of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Finland’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 2241–2246.
Loppi, S., Francalanci, C., Pancini, P., Marchi, G. and Caporali, B.: 1996, ‘Lichens as bioindicators of air quality in Arezzo (Central Italy)’, Ecologia Mediterranea 22, 11–16.
Lorenzini, G. A.: 1994, ‘A miniaturized kit for ozone monitoring’, Applied Biochem. Biotechnol. 48, 1–4.
Lorenzini, G. A.: 1995, ‘An analysis of the distribution of surface ozone in Tuscany (Central Italy) with use of a new miniaturized bioassay with ozone sensitive tabacco seedings’, Environ. Monitor. Assessment 34, 59–72.
Lorenzini, G. A., Nali, C. and Biagioni, M.: 1995, ‘Long range transport of photochemical ozone over the Tyrrehenian sea demonstrated by a new miniaturized bioassay with ozone sensitive tobacco seedlings’, Sci. Total Environ. 166, 193–199.
Manninen, S. and Huttunen, S.: 1995, ‘Scots pine neddles as bioindicators of sulfur deposition’, Can. J. Forest Res. 25, 1559–1569.
Melhorn, H., Seufert, G., Schmidt, A. and Kunert, K. J.: 1986, ‘Effect of SO2 and O3 on production of antioxydants in conifers’, Plant Physiol. 82, 336–338.
Mersch, J. and Claveri, B.: 1997, ‘Biosurveillance des retombées atmosphériques d'hydrocarbures aromatiques polycyliques et de dioxines/furanes par des bryophytes terrestres et des choux à feuilles frisées’, in Les bioindicateurs de la qualité de l'air, Congress, Rouen, France, Association Française des Ingénieurs Ecologues, pp. 37–45.
Morin, P.: 1997, ‘Cartographie de la qualité de l'air de l'agglomération rouannaise à partir de l'observation de lichens’, in Les bioindicateurs de la qualité de l'air', Congress, Rouen, France, Association Française des Ingénieurs Ecologues, pp. 27–35.
Navari-Izzo, F. and Izzo, R.: 1994, ‘Induction of enzyme activities and antioxydant production in barley plants as a result of SO2 fumigation’, Plant Sci. 96, 31–40.
Nylander, W.: 1866, ‘Les lichens du Jardin du Luxembourg’, Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 13, 364–372.
Osswald, W. F., Kraus, R., Hippelli, S., Benz, B., Volpert, R. and Elstner, E. F.: 1992, ‘Comparison of the enzymatic activities of dehydroascorbic acid reductase, gluthation reductase, catalase, peroxydase and superoxide dismutase of healthy and damaged spruce needles (Picea abies (L.) Karst.)’, J. Plant Physiol. 139, 742–748.
Ozenda, P. and Clauzade, G.: 1970, Les lichens-Etude biologique et flore illustrée, Paris, France, Masson Editeur, 801 p.
Penuelas, J., Ribas, A., Gimeno, B. S. and Filellas, I.: 1999, ‘Dependance of ozone biomonitoring on meteorological conditions of different sites in Catalonia (NE Sapain)’, Environ. Monitor. Assess. 56, 221–224.
Poujade, R.: 1971, Précis général des nuisances. Environnement et nuisances, Paris, France, Le Prat éditeur, 255 p.
Quevauviller, P., Herzig, R. and Muntau, H.: 1996, ‘Certified reference material of lichen (CRM 482) for the quality control of trace element biomonitoring’, Sci. Total Environ. 187, 143–152.
Ribas, A., Filella, I., Gimeno, I. and Penuelas, J.: 1998, ‘Evaluation of tabacco cultivars as bioindicators and biomonitors of ozone phytotoxical levels in Catalonia’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 107, 347–365.
Ross, H. B.: 1990, ‘On the use of mosses (Hylocomium splendens and Pleurozium schreberi)’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 50, 63–76.
Ruhling, G. A., Rassmussen, L., Pilegaard, K., Makinen, A. and Steinnes, E.: 1987, ‘Survey of atmospheric heavy metal deposition’, Technical Report 21, Nordisk Ministerråd, Finland, 22 p.
Schmidt, S.: 1997, ‘ ‘Biomonitoring actif’, utilisant les lichens en Allemagne’, in Les bioindicateurs de la qualité de l'air', Congress, Rouen, France, Association Française des Ingénieurs Ecologues, pp. 47–57.
Skelly, J. M., Davis, D. D., Merrill, W., Cameron, C. A., Brown, H. D., Drummond, D. B. and Dochinger, L. S.: 1987, Diagnosing injury to eastern forest trees: A manual for identifying damage caused by air pollution, pathogens, insects and abiotic stresses, USDA Forest Service, Pennsylvania State University, U.S.A., 122 p.
Steubing, L. and Jager, H. J.: 1982, Monitoring of Air Pollutants by Plants. Methods and Problems, Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hauge, The Netherlands, 163 p.
Tanaka, K., Kondo, N. and Sugahaza, K.: 1982, ‘Accumulation of hydrogenperoxide in chloroplasts of SO2 fumigated spinach leaves’, Plant. Cell. Physiol. 23, 999–1007.
Thomas, W.: 1986, ‘Representativity of mosses as biomonitor organisms for the accumulation of environmental chemicals in plants and soil’, Ecol. and Env. Safety. 11, 339–346.
Toncelli, M. L. and Lorenzini, G.: 1999, ‘Comparative biomonitoring techniques of tropospheric ozone’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 55, 445–458.
Trass, H.: 1973, ‘Lichen sensitivity to air pollution and index of poléotolerance (I.P.)’, Fol. Crypt. Est. 3, 19–22.
Tyler, G.: 1990, ‘Bryophites and heavy metals: A literature review’, Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 104, 231–253.
Vandobben, H. F. and Terbraak, C. J. F.: 1998, ‘Effects of atmospheric NH3 on epiphytic lichens in the Netherlands-The pitfalls of biological monitoring’, Atmos. Environ. 32, 551–557.
Van Haluwyn, C. and Lerond, M.: 1993, Guide des Lichens, Paris, France, Editions Lechevalier, 344 p.
Van Haluwyn, C. and Saison, J.-Y.: 1997, ‘Approche biologique de la qualité de l'air sur l'agglomération lilloise en utilisant des plants de tabac' in Les bioindicateurs de la qualité de l'air, Congress, Rouen, France, Association Française des Ingénieurs Ecologues, pp. 17–25.
Van Loon, L. C.: 1986, ‘The Significance of Changes in Peroxidasein Diseased Plants’, in Greppin, H., Penel, C. and Gaspar, T. (eds.), Molecular and Physiological Aspects of Plant Peroxidases, University of Geneva Genève, Suisse, pp. 405–418.
VDI-RICHTLINIEN: 1995, Measurement of immission effects-Measurement and evaluation of phytotoxic effects of ambient air pollutants (immissions) with lichens mapping of lichens for assessment of air quality, VDI Handbuch Reinhaltung der luft, Band 1, VDI 9799.
Voisin, C., Aerts, C., Jakubczak, E. and Tonnel, A. B.: 1977a, ‘La culture cellulaire en phase gazeuse. Un nouveau modèle expérimental d'étude in vitro des activités macrophagiques alvéolaires’, Bull. Europ. Physiopath. Resp. 13, 69–82.
Voisin, C., Aerts, C., Jakubczack, E., Houdret, J. L., and Tonnel, A. B.: 1977b, ‘Effets du bioxyde d'azote sur les macrophages alvéolaires en survie en phase gazeuse. Un nouveau modèle expérimental pour l'étude in vitro de la cytotoxicité des gaz nocifs’, Bull. Europ. Physiopath. Resp. 13, 137–144.
Voisin, C., Aerts, C., Tonnel, A. B. and Dutriez, N.: 1979a, ‘Action des polluants gazeux de l'atmosphère (NO2, O3) sur la défense phagocytaire de l'appareil respiratoire: évaluation in vitro’, Bull. Union Inter. Tubercul. 54, 416–419.
Voisin, C., Aerts, C., Tonnel, A. B. and Dutriez, N.: 1979b, ‘Aérocontaminants gazeux et défense phagocytaire de l'appareil respiratoire. Cytotoxicité du NO2, de l'ozone et de l'acroléine pour les macrophages alvéolaires en phase gazeuse’, La nouvelle presse médicale 8, 2089–2094.
Waber, M., Werner, H. and Peichl, L.: 1994, ‘Effect related ozone monitoring-comparison of reaction indicator tabbaco Bel-W3 and deposition collector indigo paper’, Chemosphere 28, 1905–1912.
Willekens, H.: 1974, Oxidative Stress Response in Plants: Regulation and Function of H 2 O 2 Scavanging Enzymes, Doctoral thesis, University of Ghent, Belgium.
Wegener, J. W., Van Schaik, M. J. and Aiking, H.: 1992, ‘Active biomonitoring of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by means of mosses’, Environ. Pollut. 76, 15–18.
WWF: 1996, Kit de détection de l'ozone et dossier pédagogique, World Wide Fund for Nature, 40 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falla, J., Laval-Gilly, P., Henryon, M. et al. Biological Air Quality Monitoring: a Review. Environ Monit Assess 64, 627–644 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006385924945
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006385924945