Abstract
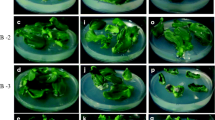
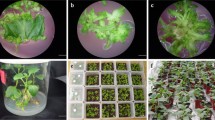
The influence of light incubation during embryo germination on shoot organogenesis from cotyledons of four diploid watermelon [Citrullus lanatus (Thumb.) Matsum. & Nakai cultivars was examined. Germinating embryos in darkness significantly improved the number of explants that produced harvestable shoots during the 6 week incubation period on shoot regeneration medium under a 16-h photoperiod. The percentage of explants with shoots more than doubled for `Crimson Sweet' and was about 1.5-fold greater for `Sweet Gem' and `Yellow Doll' when embryos were germinated in darkness. The percentage of explants with shoots was not significantly improved for `Minilee' by pretreating seedlings in darkness. This study demonstrates that optimal shoot regeneration can be obtained by germinating embryos in darkness before preparing cotyledon explants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng J & Veilleux RE (1991) Genetic analysis of protoplast culturability in Solanum phureja. Plant Sci. 75: 257-265
Choi PS, Soh WY, Kim YS, Yoo OJ & Liu JR (1994) Genetic transformation and plant regeneration of watermelon using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rept. 13: 344-348
Christiansen ML & Warnick DA (1983) Competence and determination in the process of in vitro shoot organogenesis. Dev. Biol. 95: 288-293
Christiansen ML & Warnick DA (1984) Phenocritical times in the process of in vitro shoot organogenesis. Dev. Biol. 101: 382-390
Compton ME & Gray DJ (1993a) Shoot organogenesis and plant regeneration from cotyledons of diploid, triploid, and tetraploid watermelon. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 118: 151-157
Compton ME & Gray DJ (1993b) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature cotyledons of watermelon. Plant Cell Rept. 12: 61-65
Compton ME, Gray DJ & Elmstrom GW (1993) A simple protocol for micropropagating diploid and tetraploid watermelon using shoot-tip explants. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 33: 211-217
Compton ME, Gray DJ & Elmstrom GW (1996) Identification of tetraploid regenerants from cotyledons of diploid watermelon cultured in vitro. Euphytica 87: 165-172
Debeaujon I & Branchard M (1993). Somatic embryogenesis in Cucurbitaceae. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 34: 91-100
Dong JZ & Jia SR (1991) High efficiency plant regeneration from cotyledons of watermelon (Citrullus vulgaris Schrad.). Plant Cell Rept. 9: 559-562
Evans DA, Sharp WR & Flick CE (1981) Plant regeneration from cell cultures. Hort. Rev. 214-314
Gray DJ & Mortensen JA (1987) Initiation and maintenance of long term somatic embryogenesis from anthers and ovaries of Vitis longii 'Microsperma'. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 9: 73-80
Gray DJ, McColley DW & Compton ME (1993) High-frequency somatic embryogenesis from quiescent seed cotyledons of Cucumis melo cultivars. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 118: 425-432
Hartmann HT, Kester DE, Davies FT, Jr & Geneve RL (1997) Plant propagation: principles and practices, 6th edn. Prentice-Hall, Inc. Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Herman DE & Hess CE (1963) The effect of etiolation upon the rooting of cuttings. Proc. Intl. Plant Prop. Soc. 13: 42-62
Leblay C, Chevreau E & Raboin LM (1991) Adventitious shoot regeneration from in vitro leaves of several pear cultivars. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 25: 99-106
Mohammed MF, Read PE & Coyne DP (1992) Dark preconditioning, CPPU, and thidiazuron promote shoot organogenesis on seedling node explants of common and faba beans. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 117: 668-672
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473-497
Punja ZK, Abbas N, Sarmento GG & Tang FA (1990) Regeneration of Cucumis sativus var. sativus and C.sativus var. hardwickii, C.melo, and C.metuliferus from explants through somatic embryogenesis and organogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 21: 93-102
Shahin EA (1984) Isolation and culture of protoplasts: tomato. In: Vasil IK (ed.) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol. 1 (pp 370-380). Academic Press, Orlando
Songstad DD, Armstrong CL & Petersen WL (1991) AgNO3 increases type II callus production from immature embryos of maize inbred B73 and its derivatives. Plant Cell Rep. 9: 699-702
Srivastava DR, Andrianov VM & Piruzian ES (1989) Tissue culture and plant regeneration of watermelon (Citrullus vulgaris Schrad. cv. Melitopolski). Plant Cell Rept. 8: 300-302
Zarr JH (1984) Biostatistical Analysis, 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Compton, M.E. Dark pretreatment improves adventitious shoot organogenesis from cotyledons of diploid watermelon. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 58, 185–188 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006364013126
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006364013126