Abstract
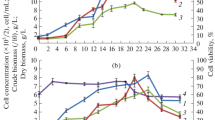
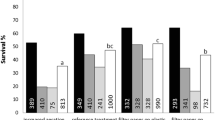
The effect of the relative oxygen partial pressure (pO2) in bioreactors on cell proliferation and subsequent differentiation of somatic embryos from suspension cultures of Cyclamen persicum Mill. was investigated. The growth rate of cell line 3738-VIII in growth-regulator containing medium in bioreactors at 5% pO2 was slightly reduced in comparison to 10% and 20% pO2. Cultures growing at 40% pO2 had a lower growth rate, a markedly reduced cell viability and showed a decrease of the medium pH to 3.5. Because a pH-control with a setpoint of 3.3 caused cell death within 4 days, it was assumed, that the reason for the poor cell proliferation and viability in the cultures at 40% pO2 was an effect of medium acidification rather than of the high O2 partial pressure. A significantly higher number of germinating embryos was obtained from the cultures grown at 40% pO2 than from those grown in flasks or in bioreactors at 5%, 10% and 20% pO2. These results were specific for cell line 3738-VIII. Another cell line, 3736-12, did not show marked differences in cell proliferation, viability, pH or subsequent regeneration of somatic embryos when grown at different O2 partial pressures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butenko RG, Lipsky AK, Chernyak ND & Arya HC (1984) Changes in culture medium pH by cell suspension cultures of Dioscorea deltoidea. Plant Sci. Lett. 35: 207–212
Carman JG (1988) Improved somatic embryogenesis in wheat by partial simulation of the in?ovulo oxygen, growth?regulator and dessication environments. Planta 175:417–424
Chen SJ & Kao CH (1997) Ammonium inhibited growth of suspension?cultured rice cells as affected by medium pH. Plant Growth Regul. 21: 1–6
Chen THH, Thompson BG & Gerson DF (1987) In vitro production of alfalfa somatic embryos in fermentation systems. J. Ferment. Technol. 65: 353–357
Hohe A, Winkelmann T & Schwenkel HG (1999) CO2 accumulation in bioreactor suspension cultures of Cyclamen persicum Mill. and its effect on cell growth and regeneration of somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep. 18: 863–867
Jay V, Genestier S & Courduroux JC (1992) Bioreactor studies on the effect of dissolved oxygen concentrations on growth and differentiation of carrot (Daucus carota L.) cell cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 11: 605–608
Kessell RHJ & Carr AH (1972) The effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on growth and differentiation of carrot (Daucus carota) tissue. J. Exp. Bot. 23: 996–1007
Kiviharju E, Tuominen U & Törmälä T (1992)The effect of explant material on somatic embryogenesis of Cyclamen persicum Mill.. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 28: 178–194
Kovács G, László M, Rajkai G & Barnabás B (1995) Monitoring of haploid maize cell suspension culture conditions in bioreactors. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 43: 123–126
Kreuger M, Postma E, Brouwer Y & van Holst GJ (1995) Somatic embryogenesis of Cyclamen persicum in liquid medium. Physiol. Plant. 94: 605–612
Kvaalen H & von Arnold S (1991) Effects of various partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide on different stages of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 27: 49–57
Merkle SA, Parrott WA & Flinn BS (1995) Morphogenetic aspects of somatic embryogenesis. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In Vitro Embryogenesis in Plants (pp 155–203). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Otani M & Shimada T (1991) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from Cyclamen persicum Mill. leaf cultures. Plant Tiss. Cult. Lett. 8: 121–123
Preil W (1991) Application of bioreactors in plant propagation. In: Debergh PC & Zimmerman RH (eds) Micropropagation, Technology and Application (pp 425–445). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London
Preil W, Florek P, Wix U & Beck A (1988) Towards mass propagation by use of bioreactors. Acta Hort. 226: 99–106
Sakano K, Kiyota S & Yazaki Y (1997) Acidification and alkalinization of culture medium by Catharanthus roseus cells?is anoxic production of lactate a cause of cytoplasmic acidification? Plant Cell Physiol. 38: 1053–1059
Schwenkel HG & Winkelmann T (1998) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from ovules of Cyclamen persicum Mill. Plant Tiss. Cult. Biotechnol. 4: 28–34
Shigeta J, Sato K & Mii M (1996) Effects of initial cell density, pH and dissolved oxygen on bioreactor production of carrot somatic embryos. Plant Sci. 115: 109–114
Snape JB, Thomas NH & Callow JA (1989) How suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus respond to oxygen limitation: Small scale tests with applications to large?scale cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 34: 1058–1062
Stuart DA, Strickland SG & Walker KA (1987) Bioreactor production of alfalfa somatic embryos. HortScience 22:800–803
Takamura T, Miyajima I & Matsuo E (1995) Somatic embryogenesis of Cyclamen persicum Mill. 'Anneke' from aseptic seedlings. Plant Cell Rep. 15: 22–25
Takamura T & Tanaka M (1996) Somatic embryogenesis from the etiolated petiole of Cyclamen (Cyclamen persicum Mill.). Plant Tiss. Cult. Lett. 13: 43–48
Tate JL & Payne GF (1991) Plant cell growth under different levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Plant Cell Rep. 10: 22–25
Wicart G, Mouras A & Lutz A (1984) Histological study of organogenesis and embryogenesis in Cyclamen persicum Mill. tissue cultures: Evidence for a single organogenic pattern. Protoplasma 119: 159–167
Widholm JM (1972) The use of fluorescein diacetat and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol. 47: 189–194
Winkelmann T, Hohe A & Schwenkel HG (1998) Establishing embryogenic suspension cultures in Cyclamen persicum 'Purple Flamed'. Adv. Hort. Sci. 12: 25–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hohe, A., Winkelmann, T. & Schwenkel, HG. The effect of oxygen partial pressure in bioreactors on cell proliferation and subsequent differentiation of somatic embryos of Cyclamen persicum. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 59, 39–45 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006323009860
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006323009860