Abstract
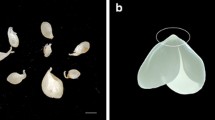
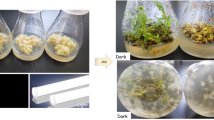
Direct exposure of calluses of Lycium barbarum L. to an auxin-free medium can induce somatic embryogenesis. Somatic
embryogenesis of Lycium barbarum L. is controlled artificially by regulating 2,4-D concentration. The total RNA that was isolated from calluses, embryonic calluses and early somatic embryos was used for analyzing differential genes expression. We obtained three cDNAs from early somatic embryogenesis which were not found in calluses. The results indicate that these cDNAs were early embryogenesis-specific cDNAs and this gene expression was induced in cultured calluses after a transfer to an auxin- free medium. A cDNA library was constructed using poly(A)+-RNA derived from early somatic embryos of Lycium barbarism L. Two full-length cDNAs were isolated from the library by differential screening. Northern blot hybridization analysis indicated that the expression of the full-length cDNA only existed in embryogenic calluses and early somatic embryos of Lycium barbarum L.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng JC, Seeley KA, Goupil P & Sung ZR (1996) Expression of DC8 is associated with, but not dependent on embryogenesis. Plant Molecular Biology 31: 127-l41
Chomczynski P & Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162: 156–160
Corre F, Henry Y, Rode A & Hartmann C (1996) Em gene expression during somatic embryogenesis in the monocot Triticum aestivum L. Plant Science 117: 139–149
Cui KR, Pei XW, Wang JJ & Wang YE (1998) Effects of modulation of abscisic acid during somatic embryogenesis in Lycium barbarum L. Acta Biologiae Experimentalis Sinica 31(2): 195–201
Dudits D, Gyorgyey J, Borgre L & Bako L (1995) Molecular biology of somatic embryogenesis. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In vitro Embryogenesis in Plant (pp. 267–308). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Holk A, Kaldenhoff R & Richter G (1996) Regulation of an embryogenic carrot gene (DC2.15) and identification of its active promoter sites. Plant Molecular Biology 31: 1153–1161
Kiyosue T & Shinozaki K (1995) Cloning of a carrot cDNA for a member of the family of ADP-ribosylation factors (ARFs) and characterization of the binding of nucleotides by its product after expression in E.coli. Plant Cell Physiol. 36: 849–856
Latham KE, Solter D & Schultz RM (l992) Acquisition of a transcriptionally permissive state during the 1-Cell stage of mouse embryogenesis. Dev. Biol. 149: 457–462
Liang P. Averboukh L & Pardee AB (1993) Distribution and cloning of eukaryotic mRNAs by means of differential display: refinements and optimization. Nucleic Acids Research 21: 3269–3275
Liang P & Pardee AB (1992) Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction. Science 257: 967–971
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF & Sambrook J (1982) Molecular Cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Ram PT & Schultz RM (1993) Reporter gene expression in G2 of the 1-Cell mouse embryo. Dev. Biol. 156: 552–556
Sanger F, Nicklen S & Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Sokolov BP & Prockop DJ (1994) A rapid and simple PCR-based method for isolation of cDNAs from differentially expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Research 22: 4009–40l5
Temeles GT, Ram PT, Rothstein JL & Schultz RM (1994) Expression patterns of novel genes during mouse preimplantation embryogenesis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 37: 12l-125
Welsh J, Chada K, Dalal SS, Cheng R, Ralph D & McClelland M (1992) Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA. Nucleic Acids Research 20: 4965–4970
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell 5: 1411–1423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kairong, C., Gengsheng, X., Lin, Q. et al. The analysis of differential gene expression in early somatic embryogenesis on Lycium barbarum. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 59, 169–174 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006311628358
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006311628358