Abstract
Purpose: A previous cohort study of 759 women with invasive T1‐T2 breast cancer operated on with breast‐conserving surgery in Stockholm between 1976 and 1986 indicated that age <50 years, no postoperative irradiation, and nodal involvement were independent risk factors for ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences (IBTR). The aim of the current study was to analyse if selected biological markers assayed in tumor specimens from these patients could add prognostic information, thereby helping to identify groups of patients at high versus low risk of IBTR.
Methods: The study was designed as a case‐control study ‘nested’ within the cohort. The cohort was stratified according to nodal status and the use of postoperative irradiation. In these four strata, the cases were those 80 women who developed IBTR between 1977 and 1994. In each stratum, women without IBTR were randomly selected as controls (n=159). Median time at risk was 12 (8–18) years. The following factors were analysed: histopathological tumor grade according to Elston–Ellis, DNA ploidy, immunohistochemical staining for apoptosis, angiogenesis, Ki‐67 (MIB‐1), c‐erbB‐2, p‐53, waf‐1, and bcl‐2. The prognostic role of each factor was assessed using linear logistic regression methods.
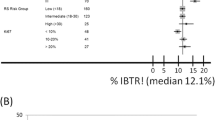
Results: In univariate analyses only age <50 years was identified as a significant risk factor for IBTR, whereas none of the studied biomarkers yielded statistically significant information. However, in a multivariate model, age, MIB-1-index, and tumor grade significantly influenced the risk for IBTR: the odds-ratio (OR) for age ≥50 years was 0.4, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.2–0.9; for medium or high grade tumors it was 0.4 (CI = 09–0.9); and for MIB-1-index >30%, 2.1 (CI = 1.0–4.4). In women ≥50 years, MIB-1-index >30% was associated with an OR of 3.5 (CI = 1.4–8.8) compared to those who were younger. Patients ≥50 years with MIB-1-index ≤30% were thus identified as a low-risk group with an OR of 0.2 (CI = 0.1–0.5). A possible high-risk group was patients <50 years with tumors showing a combination of c-erbB-2 and waf-1 immunoreactivity, with an OR of 6.7 (CI = 1.3–34.7).
Conclusion: Women ≥50 years with MIB-1-index ≤30% constituted a subgroup with a low risk of IBTR. This observation raises the issue whether this group of patients might be spared postoperative irradiation following breast-conserving surgery. However, due to the methodology of the study, including the large number of comparisions, the presented results warrant cautious interpretation and should be regarded as tentative.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blichert-Toft M, Rose C, Andersen JA, et al.: Danish randomised trial comparing breast conservation therapy with mastectomy: six years of life-table analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst Monograph 11: 19–25, 1992
Fisher B, Redmond C, Wolmark N, et al.: Reanalysis and results after 12 years of follow-up in a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. New Engl J Med 333: 1456–1461, 1995
Sarrazin D, Le MG, Arriagada R, et al.: Ten year results of a randomised trial comparing a conservative treatment to mastectomy in early breast cancer. Radiother Oncol 14: 177–184, 1989
van Dongen JA, Bartelink H, Fentiman IS, et al.: Factors influencing local relapse and survival and results of salvage treatment after breast-conserving therapy in operable breast cancer: EORTC trial 10801, breast conservation compared with mastectomy in TNM stage I and II breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 28A(4/5): 801–805, 1992
Veronesi U, Banfi A, Salvadori B, et al.: Breast conservation is the treatment of choice in small breast cancer: Long-term results of a randomized trial. Eur J Cancer 26(6): 668–670, 1990
Fisher B, Redmond C, Poisson R, et al.: Eight year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and lumpectomy with or without irradiation in the treatment of breast cancer. New Engl J Med 320(13): 822–828, 1989
Clark RM, McCullogh PB, Levine MN, et al.: Randomized clinical trial to assess the effectiveness of breast irradiation following lumpectomy and axillary dissection for node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 683–689, 1992
Veronesi U, Luini A, Del Vecchio M, et al.: Radiotherapy after breast-preserving surgery in women with localized cancer of the breast. New Engl J Med 328(22): 1587–1591, 1993
Liljegren G, Holmberg L, Adami HO: Sector resection with or without postoperative radiotherapy for stage I breast cancer: five-year results of a randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 86: 717–722, 1994
Fisher B, Costantino J, Redmond C, et al.: A randomized clinical trial evaluating Tamoxifen in the treatment of patients with node-negative breast cancer who have estrogenreceptor-positive tumors. New Engl J Med 320(8): 479–484, 1989
Fisher B, Redmond C, Dimitrov NV, et al.: A randomized clinical trial evaluating sequential methotrexate and fluorouracil in the treatment of patients with node-negative breast cancer who have estrogen-receptor-negative tumors. New Engl JMed 320(8): 473–478, 1989
Dalberg K, Johansson H, Johansson U, Rutqvist LE: Randomized trial of long-term adjuvant tamoxifen plus postoperative radiation therapy versus radiation therapy alone for patients with early stage breast carcinoma treated with breast-conserving surgery. Cancer 82: 2204–2211, 1998
Borger J, Kemperman H, Hart A, et al.: Risk factors in breastconservation therapy. J Clin Oncol 12(4): 653–660, 1994
Stotter A, Atkinson EN, Fairston BA, McNeese M, Oswald MJ, Balch CM: Survival following locoregional recurrence after breast conservation therapy for cancer. Ann Surg 212(2): 166–172, 1990
de La Rochofordiere A, Asselain B, Campana F, et al.: Age as prognostic factor in premenopausal breast carcinoma. The Lancet 341: 1039–1042, 1993
Boyages J, Recht A, Connolly JL, et al.: Early breast cancer: predictors of breast recurrence for patients treated with conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Radiother Oncol 19: 29–41, 1990
Kurtz JM: Factors influencing the risk of local recurrence in the breast. Eur J Cancer 28(2/3): 660–666, 1992
Kurtz JM, Jacquemier J, Amalric R, et al.: Risk factors for breast recurrence in premenopausal and postmenopausal patients with ductal cancers treated by conservation therapy. Cancer 65: 1867–1878, 1990
Recht A, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ, et al.: The effect of young age on tumor recurrence in the treated breast after conservative surgery and radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14: 3–10, 1988
Haffty BG, Fischer D, Rose M, et al.: Prognostic factors for local recurrence in the conservatively treated breast cancer patient: a cautious interpretation of the data. J Clin Oncol 9(6): 997–1003, 1991
Bartelink H, Borger JH, van Dongen JA, Peterse JL: The impact of tumor size and histology on local control after breast-conserving therapy. Radiother Oncol 11: 297–303, 1988
Vicini PA, Recht A, Abner A, et al.: Recurrence in the breast following conservative surgery and radiation therapy for earlystage breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monographs 11: 33–39, 1992
Pezner RD, Wagman LD, Ben-Ezra J, Odom-Maryon T: Breast conservation therapy: local tumor control in patients with pathologically clear margins who receive 5000 cGy breast irradiation without local boost. Breast Cancer Res Treat 32: 261–267, 1994
Ghossein NA, Alpert S, Barba J, et al.: Breast Cancer. Importance of adequate surgical excision prior to radiotherapy in the local control of breast cancer in patients treated conservatively. Arch Surgery 127: 411–415, 1992
Marx J: How cells cycle toward cancer. Science 263: 319–321, 1994
Hunter T: Braking the Cycle. Cell 75: 839–841, 1993
Stinchomb D: Constaining the cell cycle: Regulation cell division and differentiation by gene therapy. Nature Med 1: 1004–1006, 1995
Sporn M, Roberts A: Peptide growth factors and inflammation, tissue repair, and cancer. J Clin Invest 78: 329–332, 1986
Gullick WJ: Expression of the c-erbB-2 proto-oncogene protein in human breast cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res 113: 51–56, 1989
Norberg T, Jansson T, Sjögren S, et al.: Overview on human breast cancer with focus on prognostic and predictive factors with special attention on the tumour suppressor gene p53. Acta Oncol 5: 96–102, 1996
Folkman J: What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst 82: 4–6, 1990
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis - correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. New Engl J Med 324: 1–8, 1991
Bouxubar N, Walker KJ, Griffiths K, et al.: Ki67 immunostaining in primary breast cancer: Pathological and clinical assosiations. Br J Cancer 59: 943–947, 1989
Veronesi S, Maisano C, Scibilia J: Comparative prognostic value of Ki-67 and MIB-1 proliferation indices in breast cancer. Anticancer Res 16: 2717–2722, 1996
Auer GU, Caspersson TO, Wallgren AS: DNA content and survival in mammary carcinoma. Analyt Quant Cytol 2: 161–165, 1980
Fallenius A, Auer C, Carstensen J: Prognostic significance of DNA measurements in 409 consecutive breast cancer patients. Cancer 62: 331–341, 1988
Howell A, Barnes D, Harland R, et al.: Steroid-hormone receptors and survival after first relapse in breast cancer. Lancet i: 588–591, 1984
Nomura Y, Miura S, Koyama H, et al.: Relative effect of steroid hormone receptors on the prognosis of patients with operable breast cancer. Cancer 69: 153–164, 1992
Pezzella F, Gatter K: What is the value of bcl-2 protein detection for histopathologists? Histopathology 26: 89–93, 1995
Davidoff AM, Herndon JE, Glover NS, et al.: Relation between p53 overexpression and established prognostic factors in breast cancer. Surgery 110: 259–264, 1991
Elledge RM, Fuqua AW, Clark GM, et al.: The role and prognostic significance of p53 gene alterations in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 27: 95–102, 1993
Isola J, Visakorpi T, Holli K, Kallioniemi O-P: Association of overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p53 with rapid cell proliferation and poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 84(14): 1109–1114, 1992
Levine AJ, Momand J, Finlay CA: The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature 351: 453–456, 1991
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingeber D, Hanahan D: Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 339: 58–61, 1989
Dalberg K, Mattsson A, Rutqvist LE, et al.: Breast conserving surgery for invasive breast cancer: Risk factors for ipsilateral breast tumor recurrences. Breast Cancer Res Treat 43: 73–86, 1997
World Health Organisation: Histological Typing of Breast Tunours. 2nd edition. Geneva, 1981.
Elston CW, Ellis IO: Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19: 403–410, 1991
Bloom HJG, Richardson WW: Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 11: 359–377, 1957
Wrange Ö, Nordenskjöld B, Gustafsson JÅ: Cytosol estradiol receptor in human mammary carcinoma: an assay based on isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem 85(2): 461–475, 1978
Wrange Ö, Humla S, Ramberg I, et al.: Progestin-receptor analysis in human breast cancer cytosol by isoelectric focusing in slabs of polyacrylamide gel. J Ster Biochem 14: 141–148, 1981
Rutqvist LE, Cedermark B, Glas U, et al.: The Stockholm trial on adjuvant tamoxifen in early breast cancer. Correlation between estrogen receptor level and treatment effect. Breast Cancer Res Treat 10: 255–266, 1987
Breslow NE, Day NE: Statistical Methods in Cancer Research. Vol. I. The analysis of case-control studies. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon, 1980
Clayton D, Hills M: Statistical Models in Epidemiology. Oxford Science Publications, Oxford University Press, 1993
Liljegren G, Lindgren A, Bergh J, et al.: Risk factors for local recurrence after conservative treatment in stage I cancer. Definition of a subgroup not requiring radiotherapy. Ann Oncol 8: 235–241, 1997
Tabar L, Fagerberg G, Duffy SW, Day NE, Gad A, Gröntoft O: Update of the Swedish two-county program of mammographic screening for breast cancer. Radiol Clin North Am 30: 187–210, 1992
Nyström L, Rutqvist LE, Wall S, et al.: Breast cancer screening with mammography; overview of Swedish randomised trials. Lancet 341: 973–978, 1993
Gyenes G, Gagliardi G, Lax I, et at.: Evaluation of irradiated heart volumes in Stage I breast cancer patients treated with postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 15: 1348–1353, 1997
Cuzick J, Stewart H, Rutqvist LE, et al.: Cause-specific mortality in long-term survivors of breast cancer who participated in trials of radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 12: 447–453, 1994
Rutqvist LE, Lax I, Fornander T, Johansson H: Cardiovascular mortality in a randomized trial of adjuvant radiation therapy versus surgery alone in primary breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 22: 887–896, 1992
Rutqvist LE, Liedberg A, Hammar N, Dalberg K: Myocardial infarction among women with early-stage breast cancer treated with conservative surgery and breastirradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1998 (in press)
Kattlove H, Liberati A, Keeler E, et al.: Benefits and costs of screening and treatment for early breast cancer. JAMA 11(2): 142–154, 1995
Liljegren G, Karlsson G, Bergh J, Holmberg L: The costeffectiveness of routine postoperative radiotherapy after sector resection and axillary dissection for breast cancer stage I. Results from a randomized trial. Ann Oncol 8(8): 757–763, 1997
Forrest P, Stewart H, Everington D, et al.: Randomised controlled trial of conservation therapy for breast cancer: 6-year analysis of the Scottish trial. Lancet 348: 708–713, 1996
Silvestrini R, Daidone M, Di Fronzo G: Relationship between proliferative activity and estrogen receptors in breast cancer. Cancer 44: 665–670, 1979
Meyer J: Cell kinetics in selection and stratification of patients for adjuvant therapy of breast carcinoma. Monogr Natl Cancer Inst 1: 25–28, 1986
Hutson S, Cowen P, Bird C: Morphometric studies of age related changes in normal human breasts and their significance for evolution of mammary cancer. J Clin Pathol 38: 281–286, 1985
Lippman M, Dickson R: Mechanisms of growth control in normal and malignant breast epithelium. Recent Prog Horm Res 45: 383–440, 1989
Veronesi U, Luini A, Mariani L, et al.: Effect of menstrual phase on surgical treatment of breast cancer. Lancet 342: 1545–1547, 1994
Stål O, Sullivan S, Wingren S, et al.: c-erbB-2 expression and benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy of breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 31A: 2185–2190, 1995
Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Benini E, et al.: Expression of p53, Glutathione S-transferas-II and Bcl-2 proteins and benefit from adjuvant radiotherapy in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 89: 639–645, 1997
Holland R, Leling SHJ, Mravunac M, Hendriks JHCL: Histologic multifocality of Tis, T1-2 breast carcinomas. Implications for clinical trials of breast-conserving surgery. Cancer 56: 979–990, 1985
Fisher E, Anderson S, Redmond C, Fisher B: Ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence and survival following lumpectomy and irradiation: Pathological findings from NSABP protocol B-06. Semin Surg Oncol 8: 161–166, 1992
Holland R, Connolly JL, Gelman R, et al.: The presence of an extensive intraductal component following a limited excision correlates with prominent residual disease in the remainder of the breast. J Clin Oncol 8(1): 113–118, 1990
Schnitt SJ, Abner A, Gelman R, et al.: The relationship between microscopic margins of resection and the risk of local recurrence in patients with breast cancer treated with breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy. Cancer 74: 1746–1751, 1994
Jacobs T, Prioleau J, Stillman I, Schnitt S: Loss of tumor marker-immunostaining intensity on stored paraffin slides of breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88: 1054–1059, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalberg, K., Eriksson, E., Kanter, L. et al. Biomarkers for local recurrence after breast‐conservation — a nested case‐control study. Breast Cancer Res Treat 57, 245–259 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006281718793
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006281718793