Abstract
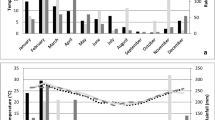
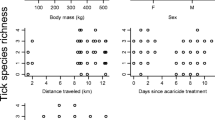
The simulation model LSTSIM was revised and adapted to estimate the effects of different management strategies on populations of the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum (Linnaeus), in non-agricultural areas. The control technologies evaluated were area-wide acaricide application, acaricide self-treatment of white-tailed deer, vegetation reduction and reductions in the density of white-tailed deer. Estimated changes in tick populations using these technologies compared favorably with results from actual integrated tick management studies at five different geographic locations. Area-wide acaricide application and vegetation reduction, as well as combinations of the two technologies proved to be useful for short-term, seasonal management of ticks in small non-agricultural areas and residential sites. Self-treatment of deer with acaricide, applied topically or as a systemic, appears to be the most cost-effective technology for use in area-wide, long-term programs for tick control. The results of simulations suggest that reductions in deer density should be considered as a component of any tick management program.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, B.E., Sims, K.G., Olson, J.G., Childs, J.E., Piesman, J.F., Happ, C.M., Maupin, G.O. and Johnson, B.J.B. 1993. Amblyomma americanum: a potential vector of human ehrichiosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 49, 239–244.
Barnard, D.R., Mount, G.A., Koch, H.G., Haile, D.G. and Garris, G.I. 1989. Management of the lone star tick in recreational areas. USDA Agricultural Handbook 682.
Bloemer, S.R., Snoddy, E.L., Cooney, J.C. and Fairbanks, K. 1986. Influence of deer exclusion on populations of lone star ticks and American dog ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 79, 679–683.
Bloemer, S.R., Mount, G.A., Morris, T. Arnold, Zimmerman, R.H., Barnard, D.R. and Snoddy, E.L. 1990. Management of lone star ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in recreational areas with acaricide applications, vegetative management, and exclusion of white-tailed deer. J. Med. Entomol. 27, 543–550.
Cooksey, L.M., Haile, D.G. and Mount, G.A. 1990. Computer simulation of Rocky Mountain spotted fever transmission by the American dog tick (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 27, 671–680.
Cooney, J.C. and Pickard, E. 1972. Comparative tick control field tests — Land Between The Lakes. Down Earth 28, 9–11.
Clymer, B.C., Howell, D.E. and Hair, J.A. 1970. Environmental alteration in recreational areas by mechanical and chemical treatment as a means of lone star tick control. J. Econ. Entomol. 63, 504–509.
Davidson, W.R., Siefken, D.A. and Creekmore, L.H. 1994. Influence of annual and biennial prescribed burning during March on the adundance of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae in central Georgia. J. Med. Entomol. 31, 72–81.
Dawson, J.E., Childs, J.E., Biggie, K.L., Moore, C., Stallknecht, D.E., Shaddock, J., Bouseman, J. and Olson, J.G. 1994a. White-tailed deer as a potential reservoir of Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis. J. Wildl. Dis. 30, 162–168.
Dawson, J. E., Stallknecht, D.E., Howerth, E.W., Biggie, K.L., Davidson, W.R., Lockhart, J.M., Nettles, V.F., Olson, J.G. and Childs, J.E. 1994b. Susceptibility of white-tailed deer to infection with Ehrlichia chaffeensis, the etiologic agent of human ehrlichiosis. J. Clin. Microb. 32, 2725–2728.
Eng, T.R., Harkess, J.R., Fishbein, D.B., Dawson, J.E., Greene, C.N., Redus, M.A. and Satalowich, F.T. 1990. Epidemiologic, clinical and laboratory findings of human ehrlichiosis in the United States, 1988. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 264, 2251–2258.
Ewing, S.A., Dawson, J.E., Kocan, A.A., Barker, R.W., Warner, C.K., Panciera, R.J., Fox, J.C., Kocan, K.M. and Blouin, E.F. 1995. Experimental transmission of Ehrlichia chaffeensis (Rickettsiales: Ehrlichieae) among white-tailed deer by Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 32, 368–374.
Goddard, J. 1987. A review of the disease agents harbored and transmitted by the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum (L.). Southwestern Entomologist 12, 158–171.
Haile, D.G. and Mount, G.A. 1987. Computer simulation of population dynamics of the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 24, 356–369.
Haile, D.G., Mount, G.A., Cooksey, L.M. 1990. Computer simulation of management strategies for American dog ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) 2nd Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. J. Med. Entomol. 27, 686–696.
Hair, J.A. and Howell, D.E. 1970. Lone star ticks: their biology and control in Ozark recreational areas. Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin B-679.
Hoch, A.L., Barker, R.W. and Hair, J.A. 1971. Further observations on the control of lone star ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae) through integrated control procedures. J. Med. Entomol. 8, 731–734.
Hoch, A.L., Semtner, P.J., Barker, R.W. and Hair, J.A. 1972. Preliminary observations on controlled burning for lone star tick (Acarina: Ixodidae) control in wood lots. J. Med. Entomol. 9, 446–451.
Kardatzke, J.T., Neidhardt, K., Dzuban, D.P., Sanchez, J.L. and Azad, A.F. 1992. Cluster of tick-borne infections at Fort Chaffee, Arkansas: rickettsiae and Borrelia burgdorferi in ixodid ticks. J. Med. Entomol. 29, 669–672.
Lockhart, J.M., Davidson, W.R., Dawson, J.E. and Stallknecht, D.E. 1995. Temporal association of Amblyomma americanum with the presence of Ehrlichia chaffeensis reactive antibodies in white-tailed deer. J. Wildl. Dis. 31, 119–124.
Lockhart, J.M., Davidson, W.R., Stallknecht, D.E. and Dawson, J.E. 1996. Site-specific geographic association between Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) infections and Ehrlichia chaffeensis-reactive (Rickettsiales: Ehrlichieae) antibodies in white-tailed deer. J. Med. Entomol. 33, 153–158.
Meyer, J.A., Lancaster, J.L., Jr. and Simco, J.S. 1982. Comparison of habitat modification, animal control and standard spraying for control of the lone star tick. J. Econ. Entomol. 75, 524–529.
Miller, J.A., Garris, G.I., George, J.E. and Oehler, D.D. 1989. Control of lone star ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) on Spanish goats and white-tailed deer with orally administered ivermectin. J. Econ. Entomol. 82, 1650–1656.
Mount, G.A. 1981a. Amblyomma americanum: area control of overwintered nymphs and adults in Oklahoma with acaricides. J. Econ. Entomol. 74, 24–26.
Mount, G.A. 1981b. Amblyomma americanum: control in Oklahoma parks with air-blast sprayer applications of acaricides. J. Econ. Entomol. 74, 27–29.
Mount, G.A. 1981c. Control of lone star ticks through vegetative management. J. Econ. Entomol. 74, 173–175.
Mount, G.A. 1983. Area control of larvae of the lone star tick (Acari: Ixodidae) with acaricides. J. Econ. Entomol. 74, 113–116.
Mount, G.A. 1984a. Aerial application of diazinon granules for area control of the lone star tick (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 77, 1211–1213.
Mount, G.A. 1984b. Effect of age, application date and life stage on the susceptibility of free-living lone star ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) to acaricides. J. Econ. Entomol. 77, 1214–1218.
Mount, G.A. and Dunn, J.E. 1983. Economic thresholds for lone star ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in recreational areas based on a relationship between CO2 and human subject sampling. J. Econ. Entomol. 76, 327–329.
Mount, G.A. and Whitney, R.W. 1984. Ultralow volume mists of chlorpyrifos from a tractor-mounted blower for area control of the lone star tick (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 77, 1219–1223.
Mount, G.A., Hirst, J.M., McWilliams, J.G., Lofgren, C.S. and White, S.A. 1968. Insecticides for control of the lone star tick tested in the laboratory and as high-and ultra-low-volume sprays in wooded areas. J. Econ. Entomol. 61, 1005–1007.
Mount, G.A. and Haile, D.G. 1987. Computer simulation of area-wide management strategies for the lone star tick, Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 24, 523–531.
Mount, G.A., Haile, D.G., Barnard, D.R. and Daniels, E. 1993. New version of LSTSIM for computer simulation of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) population dynamics. J. Med. Entomol. 30, 843–857.
Mount, G.A., Haile, D.G. and Daniels, E. 1997a. Simulation of management strategies for the blacklegged tick, Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) and the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Med. Entomol. 34, 461–484.
Mount, G.A., Haile, D.G. and Daniels, E. 1997b. Simulation of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) population dynamics and transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Med. Entomol. 34, 461–484.
Pound, J.M., Miller, J.A. and LeMeilleur, C.A. 1994. Device and method for its use as an aid in control of ticks and other ectoparasites on wildlife. U.S. Patent No. 5,367,983, issued November 29, 1994.
Pound, J.M., Miller, J.A., George, J.E., Oehler, D.D. and Harmel, D.E. 1996. Systemic treatment of white-tailed deer with ivermectin-medicated bait to control free-living populations of lone star ticks (Acari: Ixodidae). J. Med. Entomol. 33, 385–394.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mount, G., Haile, D., Barnard, D. et al. Integrated Management Strategies for Amblyomma Americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) in Non-Agricultural Areas. Exp Appl Acarol 23, 827–839 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006262216124
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006262216124