Abstract
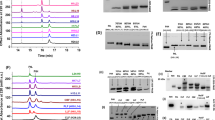
The ferritins were purified from liver homogenates of buffalo, camel, cattle, sheep and shark by thermal denaturation, ammonium sulphate fractionation, Sephacryl S-300 gel filtration and DEAE-blue gel affinity chromatography. The yield and iron content of affinity-purified liver ferritins ranged from 0.008 to 0.052 mg/g and 3.17% to 11.4% respectively. As they are glycoproteins, the ferritins contained variable amounts of neutral carbohydrates. Except for shark ferritin, the ferritins all exhibited immunological cross-reactivity with anti-buffalo liver ferritin and anti-horse spleen ferritin by immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis, gel filtration and ultracentrifugal analysis indicated the presence of a monomeric ferritin in all cases. SDS-gel electrophoresis of shark ferritin gave a protein band of 18 kDa. Ovine, buffalo and bovine ferritin comprised two protein subunits, the H (20 and 21 kDa) and the L types (18 and 19 kDa). Oligomeric ferritin subunits with molecular weights of 27, 37 and 55 kDa were also found for bovine and buffalo ferritin. SDS-PAGE of camel ferritin revealed a complex pattern with four prominent bands of 61, 51, 44 and 39 kDa. Two fast-migrating components of 15 and 16 kDa were also found in the purified liver ferritins, including reference preparations. The PO4 3–/Fe ratios of purified shark (0.10) and bovine ferritin (0.12) were similar to that of standard equine spleen ferritin (0.11). However, the ratio was higher in ovine (0.17), camel (0.22) and bovine (0.26) ferritins. The amino acid compositions, molecular weights and sedimentation coefficients of the different liver ferritins were similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert, E., Coston, R. and Drysdale, J.W., 1973. Carcino-foetal human liver ferritins. Nature, 242, 194–196
Arosio, P., Adelman, T.G. and Drysdale, J.W., 1978. On ferritin heterogeneity. Further evidence for heteropolymers. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 253, 4451–4458
Bartlett, G.R., 1959. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 234, 466–468
Bjork, I. and Fish, W.W., 1971. Native and subunit molecular weight of apoferritin. Biochemistry, 10, 2844–2848
Cetinkaya, N., Lengemann, F.W. and Kogan, P., 1985. Isolation, puri¢cation and characterization of bovine spleen ferritin. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 80, 773–778
Cook, J.D., Lipschitz, D.A., Miles, L.E.M. and Finch, C.A., 1974. Serum ferritin as a measure of iron stores in normal subjects. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 27, 681
Crichton, R.R., 1971. Ferritin: structure, synthesis and function. New England Journal of Medicine, 284, 1413–1422
Crichton, R.R., 1973. Structure and function of ferritin. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 12, 57–65
Davis, B.J., 1964. Disk electrophoresis II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 121, 404–427
Donde, U.M., Maitra, A. and Moodbidri, S.B., 1990. In-house preparation of reagents for immunochem-ical assay of ferritin. Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 5, 85–89
Dubois, M., Gilles, K.A., Hamilton, J.K., Rebers, P.A. and Smith, F., 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356
Farrant, J.L., 1954. An electron microscopic study of ferritin. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 13, 569–576
Fineberg, R.A. and Greenberg, D.M., 1955. Ferritin biosynthesis I. Crystallization of guinea pig ferritin. II. Acceleration of synthesis by the administration of iron. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 214, 91–95, 97–106, 107–113
Friedberg, F., 1962. Some properties of apoferritin isolated from guinea pig liver. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 40, 983–987
Goers, J., 1993. Immunochemical Techniques, A Laboratory Manual, (Academic Press, London)
Gonyea, L.M., Lamb, C.M., Sundberg, R.D. and Deinard, A.S., 1976. Comparison of three procedures for isolating human ferritin, for use as a standard in an immunoradiometric assay. Clinical Chemistry, 24, 513–518
Granick, S., 1946. Ferritin: its properties and signi¢cance for iron metabolism. Chemical Reviews, 38, 379–403
Granick, S., 1951. Structure and physiological functions of ferritin. Physiological Reviews, 31, 489–511
Granick, S. and Hahn, P., 1944. Speed of uptake of iron by the liver and its conversion to ferritin iron. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 155, 661–669
Harrison, P.M., 1977. Ferritin: an iron-storage molecule. Seminars on Haematology, 14, 55–70
Harrison, P.M. and Gregory, D.M., 1968. Reassembly of apoferritin molecules from subunits. Nature, 220, 578–580
Harrison, P.M., Banyard, S.H., Hoare, R.J., Russell, S.M. and Tre¡ry, A., 1978. The structure and function of ferritin. CIBA Foundation Symposia, 51, 19–36
Ishitani, K., Niitsu, Y. and Listowsky, I., 1975. Characterization of the di¡erent polypeptide components and analysis of subunit assembly in ferritin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 250, 3142–3148
Laemmli, U.K., 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680–685
Leong, L.M., Tan, B.H. and Ho, K.K., 1992. A speci¢c stain for the detection of non-heme iron proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Analytical Biochemistry, 207, 317–320
Listowsky, I., Betheil, J.J. and Englard, S., 1972. Conformation of ferritin and apoferritin in solution. Optical rotatory dispersion properties. Biochemistry, 6, 1341–1348
Lowe, C.R. and Pearson, J.C., 1984. A¤nity chromatography on immobilized dyes. In: Methods of Enzymology, (Academic Press, London), 77–112
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L. and Randall, R.J., 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275
Matioli, G.T. and Eylar, E.H., 1964. The biosynthesis of apoferritin by reticulocytes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the USA, 52, 508–516
Mazur, A. and Carleton, A., 1963. Relation of ferritin iron to heme synthesis in marrow and reticulocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 238, 1817–1824 180
Mazur, A., Green, S. and Carleton, A., 1950. Mechanism of plasma iron incorporation into hepatic ferritin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 235, 595–603
Niitsu, Y. and Listowsky, I., 1973. The distribution of iron in ferritin. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 158, 276–281
Ouchterlony, O., 1953. Antigen-antibody reactions in coordinated systems of di¡usion. Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Scandinavica, 32, 231–240
Page, M., Lagueux, J. and Gauthier, C., 1980. A three step puri¢cation procedure for human liver ferritin. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry, 58, 494–498
Pape, L., Multani, J.S., Stitt, C. and Saltman, P., 1968. In vivo reconstitution of ferritin. Biochemistry, 7, 606–612
Penders, T.J., De Dooij-Dijk, H.H. and Leijnse, V., 1968. Rapid isolation of ferritin by means of ultracentrifugation. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 168, 588–590
Powell, L.W., Alpert, E., Isselbacher, K.J. and Drysdale, J.W., 1975. Human isoferritins: organ speci¢c iron and apoferritin distribution. British Journal of Haematology, 30, 47–55
Richter, G.W., 1965. Comparison of ferritins from neoplastic and non-neoplastic human cells. Nature, 207, 616–618
Rothen, A., 1944. Ferritin and apoferritin in the ultracentrifuge. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 152, 679–693
Russell, S.M. and Harrison, P.M., 1978. Heterogeneity in horse ferritins. A comparative study of surface charge, iron content, and kinetics of iron uptake. Biochemical Journal, 175, 91–104
Scott, R. and Aughey, E., 1978. Methylcholanthrene and cadmium induced changes in rat prostrate. British Journal of Urology, 50, 25–28
Shinyjo, S., Abe, H. and Masuda,M., 1975. Carbohydrate composition of horse spleen ferritin. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 411, 165–167
Sturgeon, P. and Shoden, A., 1964. Iron Metabolism, (Springer Verlag, Berlin)
Theil, E.C., 1987. Ferritin structure, gene regulation and cellular functions in animals, plants and microorganisms. Annual Reviews of Biochemistry, 56, 289–315
Varma, M.N. and Katz, H.M., 1978. Environmental impact of cadmium. Journal of Environmental Health, 40, 308–314
Vulimiri, L., Linder, M.C., Munro, H.N. and Catsimpoolas, N., 1977. Structural features of rat cardiac ferritins. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta, 491, 67–75
Williams, M.A. and Harrison, P.M., 1968. Electron-microscopic and chemical studies of oligomers in horse spleen ferritin. Biochemical Journal, 110, 265–280
Yamachi, K., Shinichiro, D.A. and Asakava, H., 1989. A procedure for the puri¢cation of ferritin using Matrix Red A. Physiological and Biological Chemistry, 33, 27–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suryakala, S., Deshpande, V. Purification and Characterization of Liver Ferritins from Different Animal Species. Vet Res Commun 23, 165–181 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006225601199
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006225601199