Abstract
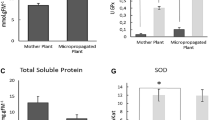
Arnica montana L., like many endangered species, does not give stable yields in commercial plantations. Other Arnica species were investigated for their pharmaceutical activity and A. chamissonis Less., was confirmed as a pharmaceutical substitute for A. montana, extracts having on average 40% higher inhibition of lipoxygenase activity and reduction of superoxide and hydroxyl free radicles on a tissue dry weight basis. A micropropagation protocol was established for A. chammisonis and a plantation of 10,050 plants was established with 0.9% microplant loss at the weaning stage. The plantation is now in commercial production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaraz MJ & Hoult RS (1985) Effects of hypolaetin-8-glucoside and related flavonoids on soybean lipoxygenase and snake venom phospholipase A-2. Arch Pharmacodyn 278:4-12
Anon. (1990) World Plant Conservation Bibliography (pp 645). Royal Botanic Gardens/World Conservation Monitoring Centre, Kew
Barrett C & Cassells AC (1994) An evaluation of antibiotics for the elimination of Xanthomonas campestris pv. pelargonii (Brown) from Pelargonium x domesticum cv. Grand Slam explants in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 36: 169-175
Belin M, Cambornac M, Crepin J, Flavet L, Guellec F, Redziniak G & Robin JR (1998) Arnica chamissonis Less. an alternative to Arnica montana L., plant under threat. Proc. 20th IFSCC Cong. Int. Fed. Soc. Cosmetic Chem. (London) (p 126)
Cassells AC (1998) In vitro production of pathogen-and contaminant-free plants. In: Altman A (ed) Agricultural Biotechnology (pp. 43-56). Marcel Dekker, New York
Cassells AC & Minas JG (1983) Plant and in vitro factors influencing the micropropagation of Pelargonium cultivars by bud-tip culture. Scientia Hortic 21: 53-65
Cassells AC & Tahmatsidou V (1996) The influence of local growth conditions on non-fastidious bacterial contamination of meristem-tips of Hydrangea cultured in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 47: 15-26
Lelliot RA & Stead DE (1987) Methods for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Diseases of Plants. Blackwell, Oxford, UK (p. 216)
Leven W & Willuhn G (1986) Spectrophotometric determination of sesquiterpenelactone (S1) in Arnica flos DAB9 with m-dinitrobenzene. Planta Med. 52: 537-538
Luijten SH, Oostermeijer JGB, Van Leeuwen NC & Den Nijs HCM (1996) Reproductive success and clonal genetic structure of the rare Arnica montana (Compositae) in the Netherlands. Plant System Evol. 201: 15-30
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioasasays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473-497
Nichterlein K (1995) Arnica montana (Mountain Arnica): in vitro culture and the production of sesquiterpene lactones and other metabolites. Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry 33: 47-61
Ponti V, Dianzani MU, Cheeseman K & Slater TF (1978) Studies on the reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium chloride mediated through the action of NADH and phenazine methosulphate. Chem. Biol. Interaction 23: 281-291
Seigler DS (1981) Secondary metabolites and plant systematics. In: Conn EE (ed) The Biochemistry of Plants (pp. 139-176) Academic Press, New York
Willuhn G (1991) Arnica montana L.-Portrat einer Arzneipflanze. Pharm. Ztg. 136: 2453-2468
Willuhn G, Pretzsch G & Wendisch D (1981) Zwei neue pseudoguaianolide aus Bluten von Arnica chammisonis Less. subsp. genuina. Tetrahedron 37: 773-776
Willuhn G, Kresken J & Wendisch D (1983) Sesquiterpenelactone aus Arnica chamissonis III: 4-0-acetyl-6-desoxychamissonolid und 6-0-propionyl-11,13-dihydrohelenalin. Plant Med. 47: 157-160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassells, A.C., Walsh, C., Belin, M. et al. Establishment of a plantation from micropropagated Arnica chamissonis a pharmaceutical substitute for the endangered A. montana. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 56, 139–144 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006224215503
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006224215503