Abstract
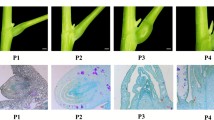
β-1,3-glucanases are usually associated with plant defense responses, although some are also developmentally or hormonally regulated. We characterized two Arabidopsis genes linked in a tandem array, BG4 and BG5, encoding putative novel isoforms of β-1,3-glucanase. The deduced polypeptides, BG4 and BG5, were highly similar to each other (89% amino acid identity) but only moderately related (32 to 41% amino acid identity) to the different categories of previously characterized β-1,3-glucanases, suggesting that BG4 and BG5 may represent a novel class of β-1,3-glucanases in plants. Neither of the genes was responsive to pathogen or SA induction in contrast to the previously identified Arabidopsis β-1,3-glucanases, nor could we detect any developmental or hormonally induced expression in the vegetative parts of the plants. Both RNA blot and in situ hybridization data demonstrated that the BG4 gene was specifically expressed in the style and septum of the ovary, suggesting that the corresponding protein is involved in the reproductive process of the plant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bednarek SY, Raikhel NV: Intracellular trafficking of secretory proteins. Plant Mol Biol 20: 133–150(1992).
Beerhus L, Kombrink E: Primary structure and expression of mRNAs encoding basic chitinase and 1,3-β-glucanase in potato. Plant Mol Biol 24: 353–367(1994).
Bowman JL: Pollination. In: Bowman, J (ed) Arabidopsis; An Atlas of Morphology and Development, pp. 333–347. Springer-Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg/New York (1994).
Bucciaglia PA, Smith AG: Cloning and characterization of Tag 1, a tobacco anther β-1,3-glucanase expressed during tetrad dissolution. Plant Mol Biol 24: 903–914(1994).
Castresana C, de Carvalho F, Gheysen G, Habets M, Inzé D, Van Montague M: Tissue-specific and pathogen-induced regulation of a Nicotiana plumbaginifolia β-1,3-glucanase gene. Plant Cell 2: 1131–1143(1990).
Chen L, Fincher GB, Hø j PB: Evolution of polysaccharide hydrolase substrate specificity. J Biol Chem 268: 13318–13326 (1993).
Cox KH, Goldberg RB: Analysis of plant gene expression. In: Shaw CH (ed) Plant Molecular Biology: A Practical Approach, pp. 1–34. IRL Press, Oxford (1988).
Davis KR, Schott E, Aisubel FM: Virulence of selected phytopathogenic pseudomonads in Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 4: 477–488(1991).
de Jong AJ, Cordewener J, Lo Schiavo F, Terzi M, Vandekerckhove J, van Kamen A, de Vries S: A carrot somatic embryo mutant is rescued by chitinase. Plant Cell 4: 425–433(1992).
De Loose M, Alliotte T, Gheysen G, Genetello C, Gielen J, Soetaert P, Van Montagu M, Inzé D: Primary structure of a hormonally regulated β-glucanase of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Gene 70: 13–23(1988).
Delp G, Saindrenan P, Palva TK, Palva ET: Biochemical and molecular characterisation of differentially induced 1,3-β-glucanases in Arabidopsis thaliana. In: Fritig B, Legrand, M (eds), Mechanisms of Plant Defense Responses, pp. 297–303. Kluwer Academic Publishers (1993).
Denecke J, Botterman J, Deblaere R: Protein secretion in plant cells can occur via a defailt pathway. Plant Cell 2: 51–59 (1990).
de Oliveira DE, Franco LO, Simoens C, Seurinck J, Coppieters J, Botterman J, Van Montagu M:. Inflorescence-specific genes from Arabidopsis thaliana encoding glycine-rich proteins. Plant J 3: 495–507(1993).
Dong X, Mindrinos M, Davis KR, Aisubel FM: Induction of Arabidopsis defense genes by virulent and avirulent Pseudomonas syringae strains and by a cloned avirulence gene. Plant Cell 3: 61–72(1991).
Ernst D, Schraidner M, Langebartels C, Sandermann Jr H: Ozone-induced changes of mRNA levels of β-1,3-glucanase, chitinase and 'pathogenesis-related' protein 1b in tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 20: 673–682(1992).
Felix G, Meins JF: Ethylene regulation of β-1,3-glucanase in tobacco. Planta 172: 386–392(1987).
Goldsbrough AP, Albrecht H, Stratford R: Salicylic acidinducible binding of a tobacco nuclear protein to a 10 bp sequence which is highly conserved amongst stress-inducible genes. Plant J 3: 563–571(1993).
Goldman MH, Pezzotti M, Seurinck J, and Mariani C:. Developmental expression of tobacco pistil-specific genes encoding novel extensin-like proteins. Plant Cell 4: 1041–1051(1992).
Goodman N, Kiraly Z, Wood KR: The Biochemistry and Physiology of Plant Disease, pp. 352–365. University of Missouri Press, Columbia, Mo (1986).
Gu Q, Kawata EE, Morse M-J, Wu H-M, Cheung AY: A flower-specific cDNA encoding a novel thionin in tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 234: 89–96(1992).
Ham K-S, Kaiffmann S, Albersheim P, Darvill AG: Hostpathogen interactions. XXXIX. A soybean pathogenesisrelated protein with β-1,3-glucanase activity releases phytoalexin elicitor-active heat-stable fragments from fungal walls. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 4: 545–552(1991).
Hennig J, Dewey RE, Cutt JR, Klessig DF: Pathogen, salicylic acid and developmental dependent expression of a β-1,3-glucanase/GUS gene fusion in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J 4: 481–493(1993).
Hird DL, Worrall D, Hodge R, Smart S, Wyatt P, Scott R: The anther-specific protein encoded by Brassica napus and Arabidopsis thaliana A6 gene displays similarity to β-1,3-glucanases. Plant J 4: 1023–1033(1993).
Hon W-C, Griffith M, Mlynarz A, Kwok YC, Yang DSC: Antifreeze proteins in winter rye are similar to pathogenesis related proteins. Plant Physiol 109: 879–889(1995).
Keen NT: The molecular biology of disease resistance. Plant Mol Biol 19: 109–122(1992).
Kiedrowski S, Kawalleck P, Hahlbrock K, Somssich IE, Dangl JL: Rapid activation of a novel plant defense gene is strictly dependent on the Arabidopsis RPM1 disease resistance locus. EMBO J 11: 4677–4684(1992).
Kononowicz AK, Nelson DE, Singh NK Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA: Regulation of the osmotin gene promoter. Plant Cell 4: 513–524(1992).
Leung DWM: Involvement of plant chitinase in sexual reproduction of higher plants. Phytochemistry 311899–1900 (1992).
Linthorst HJM, Melchers LS, Mayer A, Van Roekel JSC, Cornelissen BJC, Bol JF: Analysis of gene families encoding acidic and basic β-1,3-glucanases of tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 8756–8760(1990).
Lotan T, Ori N, Fluhr R: Pathogenesis-related proteins are developmentally regulated in tobacco flowers. Plant Cell 1: 881–887(1989).
Lå ng V, Heino P, Palva ET: Low temperature acclimation and treatment with exogenous abscisic acid induce common polypeptides in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Theor Appl Genet 77: 729–734(1989).
Malamy J, Klessig DF: Salicylic acid and plant disease resistance. Plant J 2: 643–654(1992).
Meins Jr F, Neuhais J-M, Sperisen C, Ryals J: The primary structure of plant pathogenesis-related glucanhydrolases and their genes. In: Boller T, Meins F Jr (eds) Genes Involved in Plant Defense, pp. 245–282. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1992).
Nordin K, Heino P, Palva ET: Separate signal pathways regulate the expression of a low temperature induced gene in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Plant Mol Biol 16: 1061–1071 (1991).
Okada K, Komaki MK, Shimura Y: Mutational analysis of pistil structure and development of Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell Different Dev 28: 27–38(1989).
Ori N, Sessa G, Lotan T, Himmelhoch S, Fluhr R: A major stylar matrix polypeptide (sp41) is a member of the pathogenesisrelated protein superclass. EMBO J 9: 3429–3436(1990).
Palva TK, Holmström K-O, Heino P, Palva ET: Induction of plant defense response by exoenzymes of Erwinia carotovora. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 6: 190–196(1993).
Palva ET: Gene expression under low temperature stress. In: Basra AS (ed) Stress-Induced Gene Expression in Plants, pp. 103–130. Harwood Academic Publishers, Reading, UK (1994).
Payne G, Ward E, Gaffney T, Ahl-Goy P, Moyer M, Harper A, Meins F Jr, Ryals J: Evidence for a third structural class of β-1,3-glucanase in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 15: 797–808 (1990).
Samac D, Shah P: Developmental and pathogen-induced activation of the Arabidopsis acidic chitinase promoter. Plant Cell 3: 1063–1072(1991).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Sela-Buurlage MB, Ponstein AS, Bres-Vloemans SA, Melchers LS, van den Elzen PJM, Cornelissen BJC: Only specific tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) chitinases and β-1,3-glucanases exhibit antifungal activity. Plant Physiol 101: 857–863(1993).
Shinshi H, Wenzler H, Neuhais J-M, Felix G, Hofsteenge J, Meins F Jr: Evidence for N-and C-terminal processing of a plant defense-related enzyme: primary structure of tobacco prepro-β-1,3-glucanase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 5541–5545(1988).
Simmons CR, Litts JC, Huang N, Rodriguez RL: Structure of a rice β-glucanase gene regulated by ethylene, cytokinin, wounding, salicylic acid and fungal elicitors. Plant Mol Biol 18: 33–45d(1992).
Smyth DR, Bowman JL, Meyerowitz EM: Early flower development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2: 755–767(1990).
Stintzi A, Heitz T, Prasad V, Wiedemann-Merdinoglu S, Kaiffmann S, Geoffroy P, Legrand M, Fritig B: Plant pathogenesis-related proteins and their role in defense against pathogens. Biochimie 75: 687–706(1993).
Uknes S, Maich-Mani B, Moyer M, Potter S, Williams S, Dincher S, Chandler D, Slusarenko A, Ward E, Ryals J: Acquired resistance in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell 4: 645–656 (1992).
Verwoerd TC, Dekker BMM, Hockema A: A small-scale procedure for the rapid isolation of plant RNAs. Nucl Acids Res 17: 2362 (1989).
Vidal S, Ponce de Leon I, Denecke J, Palva ET: Salicylic acid and the plant pathogen Erwinia carotovora induce defense genes via antagonistic pathways. Plant J 11: 115–123(1997).
von Heijne G: A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucl Acids Res 14: 4683–4691(1986).
Ward ER, Payne GB, Moyer MB, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Sharkey KC, Beck JJ, Taylor HT, Ahl-Goy P, Meins F Jr, Ryals JA: Differential regulation of β-1,3-glucanase messenger RNAs in response to pathogen infection. Plant Physiol 96: 390–397(1991).
Ward ER, Uknes SJ, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Wiederhold DL, Alexander DC, Ahl-Goy P, Métraix J-P, Ryals JA: Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3: 1085–1094(1991).
Worrall D, Hird DL, Hodge R, Pail W, Draper J, Scott R: Premature dissolution of the microsporocyte callose wall caises male sterility in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell 4: 759–771 (1992).
Xu P, Wang J, Fincher GB: Evolution and differential expression of the (1!3)-β-glucan endohydrolase-encoding gene family in barley, Hordeum vulgare. Gene 120: 157–165 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delp, G., Palva, E.T. A novel flower-specific Arabidopsis gene related to both pathogen-induced and developmentally regulated plant β-1,3- glucanase genes. Plant Mol Biol 39, 565–575 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006194822666
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006194822666