Abstract
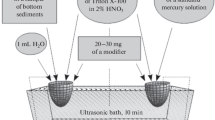
In this present work the distribution of heavy metals in sea water and sediments of the Salerno Gulf is measured. The elements determined were Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn and Hg, employing, as instrumental techniques, either differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) or graphite furnace atomic absorption spectroscopy (GFAAS). A comparison of the results of the two analytical techniques is also made. Mercury determination was carried out employing the cold vapour atomic absorption spectroscopy (CVAAS) technique, with SnCl2 as the reducing agent. The sample digestion was performed by a new procedure using concentrated suprapure H2SO4–K2Cr2O7 mixture. The accuracy and precision of the analytical procedure were evaluated employing Sea Water BCR-CRM 403 and Estuarine Sediment BCR-CRM 277 as reference materials. Accuracy, expressed as relative error e and precision, expressed as relative standard deviation sr, were in order of 2 to 5%. For both matrices, the detection limits, for all the elements, were in the range μg g-1 to ng g-1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino, O., Aceto, M., Sacchero, G., Sarzanini, C. and Mentasti, E.: 1995, ‘Determination of Copper, Iron, Manganese, Nickel and Zinc in Antarctic Sea Water. Comparison of Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Procedures', Anal. Chim. Acta 305, 200–206.
Abollino, O., Aceto, M., Sacchero, G., Sarzanini, C. and Mentasti, E.: 1996,’ Distribution of minor and trace metals in lake and sea environments (Antarctica)', Ann. Chim. (Rome) 86, 229–243.
Achterberg, E. P. and Van den Berg C. M. G.: 1994a, ‘Automated voltammetric system for shipboard determination of metal speciation in sea water', Anal. Chim. Acta 284, 463–471.
Achterberg, E. P. and Van den Berg C. M. G.: 1994b, ‘In-line ultraviolet-digestion of natural water samples for trace metal determination using an automated voltammetric system', Anal. Chim. Acta 291, 213–232.
Boniforti, R., Ferraroli, R., Frigieri, P., Heltai, D. and Queirazza, G.: 1984, ‘Intercomparison of five methods for the determination of trace metals in sea water', Anal. Chim. Acta 162, 33–46.
Cahill, F. P. J. and Van Loon, G. W.: 1976, ‘Trace analysis by atomic absorption spectroscopy and anodic stripping voltammetry', Am. Lab. 8, 11–15.
Clement, R. E., Eiceman, G. A. and Koester, C. J.: 1995, ‘Environmental Analysis', Anal. Chem. 67, 221R–255R.
Copeland, T. R. and Skogerboe, R. K.: 1974, ‘Anodic stripping voltammetry', Anal. Chem. 46, 1257A–1268A.
Das, A. K., Chakraborty, R., Cervera, M. L. and de la Guardia, M: 1995, ‘Metal speciation in solid matrices', Talanta 42, 1007–1030.
De Simone, R.: 1994, ‘Elementi in tracce e microinquinanti organici nei sedimenti marini costieri (da Gaeta a Punta Campanella)', Acqua-Aria 7, 623–628.
Ellis, W. D. J.: 1973, ‘Anodic Stripping Voltammetry', J. of Chem. Educ. 50, A131–A147.
Fagioli, F., Locatelli, C., Landi, S., Torsi, G. and Canas De Moreno, F.: 1994, ‘Lead and cadmium determination in dialysis fluids by atomic absorption spectrometry and differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry', Ann. Chim.(Rome), 84, 19–36.
Florence, T. M.: 1982, ‘The speciation of trace elements in waters', Talanta 29, 345–364.
Florence, T. M.: 1992, ‘Trace element speciation by anodic stripping Voltammetry', Analyst 117, 551–553.
Forstner, U.: 1989, Contaminated Sediments, Springer-Verlag Ed., Berlin, Germany.
IUPAC, Analytical Chemistry Division: 1978, ‘Nomenclature, symbols, units and their usage in spectrochemical analysis. II, data interpretation', Spectrochim. Acta 33B, 241–245.
Locatelli, C., Fagioli, F., Bighi, C., Landi, S. and Garai, T.: 1984, ‘Determination of trace elements in plant material by anodic stripping and peak alternating current voltammetry. Critical comparison with atomic absorption spectroscopy', Ann.Chim. (Rome) 74, 521–535.
Locatelli, C. and Fagioli, F.: 1986, ‘Determination of chromium(VI) in dialysis fluids by alternating current and differential pulse voltammetry', Mikrochim. Acta III, 269–276.
Locatelli, C., Vasca, E., Bighi, C., Fagioli, F. and Garai, T.: 1996, ‘Determination of metals in a multicomponent system by differential pulse and alternating current anodic stripping voltammetry', Electroanalysis 8, 165–170.
Locatelli, C., Bighi, C. and Fagioli, F.: 1996, ‘Application of a new analytical method to the mercury determination in the sediments of the Venice Lagoon', Fresenius Environ. Bull. 5, 386–391.
Mazzuccotelli, A., Cosma, B. and Soggia, F.: 1989, ‘Trace metals distribution in Antarctic sediments (Terranova Bay-Ross Sea) by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy', Ann. Chim. (Rome) 79, 617–628.
Mentasti, E., Porta, V., Abollino, O. and Sarzanini, C.: 1991, ‘Metal trace determination in sea water samples from Antarctica.II', Ann. Chim. (Rome) 81, 343–355.
Mitchell, J. W.: 1973, ‘Ultrapurity in trace analysis', Anal. Chem 45, 492A–500A.
Perkin-Elmer: 1982, Analytical Methods for Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry, Perkin-Elmer Corp., Norwalk, U.S.A.
Pruszkowska, E., Carnrich, G. R. and Slavin, W.: 1983, ‘Direct determination of cadmium in coastal seawater by atomic absorption spectrometry with the stabilized temperature platform furnace and Zeeman background correction', Anal. Chem. 55, 182–186.
Schlemmer, G. and Welz, B.: 1986, ‘Palladium and magnesium nitrates, a more universal modifier for graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry', Spectrochim. Acta 41B, 1157–1165.
Vydra, F., Stulik, K. and Julakova, E.: 1976, Electrochemical Stripping Analysis, Ellis Horwood Ltd. Publ., Chichester, England.
Waller, P. A. and Pickering, W. F.: 1990, ‘Evaluation of labile metal in sediments by anodic stripping voltammetry', Talanta 37, 981–993.
Wang, J.: 1985, Stripping Analysis - Principles, Instrumentation and Applications, VCH Publ., Deerfield Beach, FL, U.S.A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Locatelli, C., Astara, A., Vasca, E. et al. Voltammetric and Spectroscopic Determination of Toxic Metals in Sediments and Sea Water of Salerno Gulf. Environ Monit Assess 58, 23–37 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006078927576
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006078927576