Abstract
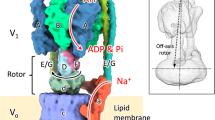
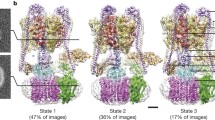
F-type and V-type ATPases couple synthesis or hydrolysis of ATP to the translocation of H+ or Na+ across biological membranes and have similarities in structure and mechanism. In both types of enzymes three main parts can be distinguished: headpiece, membrane-bound piece and stalk region. We report on structural details of the membrane sector and stalk region, including the stator, of V-type ATPase from Clostridium fervidus, as determined by electron microscopy. Besides visualization of the stator structure, one of the main findings is that in certain projections the central stalk connecting V1 and V0 makes an angle of about 70° with the membrane. Implications for the subunit arrangement in V-type and F-type ATPase are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams JP, Leslie AGW, Lutter R and Walker JE (1994) Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of F1-ATPase from bovine heart mitochondria. Nature 370: 621-628
Boekema EJ and Böttcher B (1992) The structure of ATPsynthase from chloroplasts. Conformational changes of CF1 studied by electron microscopy.Biochim Biophys Acta 1098: 131-143
Boekema EJ, Schmidt G, Gräber P and Berden JA (1988a) Structure of the ATPsynthase from chloroplasts and mitochondria by electron microscopy. Z Naturforsch 43C: 219-225
Boekema EJ, Fromme P and Gräber P (1988b) On the structure of the ATP-Synthase from Chloroplasts. Ber Bunsengesel Phys Chem 92: 1031-1036
Boekema EJB, Ubbink-kok, T, Lolkema JS, Brisson A and Konings WN (1997) Visualization of a peripheral stalk in V-type ATPase: Evidence for the stator structure essential to rotational catalysis Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 14291-14293
Birkenhäger R, Hoppert M, Deckers-Hebestreit G, Mayer F and Altendorf K (1995) The F0 complex of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Investigation by electron spectro scopic imaging and immunoelectron microscopy. Eur J Biochem 230: 58-67
Boyer PD (1993) The binding change mechanism for ATP synthase - some probabilities and possibilities. Biochim Biophys Acta 1140: 215-250
Dschida WJ and Bowman BJ (1992) Structure of the vacuolar ATPase from Neurospora crassa as determined by electron microscopy. J Biol Chem 267: 18783-18789
Duncan TM, Bulygin VV, Zhou Y, Hutcheon ML and Cross RL (1995) Rotation of subunits during catalysis by Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92: 10964-10968
Dunn SD (1992) The polar domain of the b subunit of Escherichia coli F1F0-ATPase forms an elongated dimer that interacts with the F1 sector. J Biol Chem 267: 7630-7636
Engelbrecht S and Junge W (1997) ATPsynthase: A tentative structural model. FEBS Lett 414: 485-491
Fillingame RH (1996) Membrane sectors of F-and V-type H+-transporting ATPases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6: 491-498
Finbow ME, Eliopoulos EE, Jackson PJ, Keen JN, Meagher L, Thompson P, Jones P and Findlay JBC (1992) Structure of a 16 kDa integral membrane protein that has identity to the putative proton channel of the vacuolar H+-ATPase. Protein Eng 5: 7-15
Groth G and Wlker JE (1997) Model of the c-subunit oligomer in the membrane domain of F-ATPases. FEBS Lett 410: 117-123
Harauz G, Boekema E and van Heel M. (1988) Statistical image analysis of electronmicrographs of ribosomal subunits. Methods Enzymol 164: 35-49
Höner zu Bentrup K, Ubbink-Kok T, Lolkema JS and Konings WN (1997) An Na+-pumping V1V0-ATPase complex in the thermophilic bacterium Clostridium fervidus. J Bacteriol 179: 1274-1279
Junge W, Sabbert D and Engelbrecht S. (1996) Rotatory catalysis by F-ATPase: Real-time recording of intersubunit recording. Ber Bunseng Phys Chem 100: 2014-2019
Kagawa Y and Hamamoto T (1996) The energy transmission in ATP synthase: from the γ-c rotor to the α3β3 oligomer fixed by OSCP-b stator via the βDELSEED sequence. J Bioenerg Biomembr 28: 421-431
Lill H, Hensel F, Junge W and Engelbrecht S (1996) Cross-linking of engineered subunit γ to (α β)3 in Chloroplast F-ATPase. J Biol Chem 271: 32737-32742
Lücken U Gogol EP and Capaldi RA (1990) Structure of the ATP synthase complex (ECF1F0) of Escherichia coli from cryoelectron microscopy. Biochemistry 29: 5339-5343
Nelson N and Taiz L (1989) The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci 14: 113-116
Noji H, Yasuda R, Yoshida M, Kinosata K (1997) Direct observation of the rotation of F1-ATPase. Nature 386: 299-302
Ogilvie I, Aggeler R and Capaldi RA (1997) Cross-linking of the δ subunit to one of the three α subunits has no effect on functioning, as expected if δ is a part of the stator that links the F1 and F0 parts of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. J Biol Chem 272: 16652-16656
Sabbert D, Engelbrecht S and Junge W (1996) Intersubunit rotation in active F-ATPase. Nature 381: 623-625
Singh S, Turina P, Bustamante CJ, Keller DJ and Capaldi R (1996) Topographical structure of membrane-bound Escherichia coli F1F0 ATP synthase in aqueous buffer. FEBS Lett 397: 30-34
Supekova L, Sbia M, Supek F, Ma Y and Nelson N (1996) A novel subunit of vacuolar H+-ATPase related to the b subunit of FATPase. J Exp Biol 199: 1147-1156
Watts SD and Capaldi RA (1997) Interactions between the F1 and F0 parts in the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. J Biol Chem 272: 15065-15068
Wilkens S, Dahlquist FW, McIntosh LP, Donaldson LW and Capaldi RA (1995) Structural features of the ε subunit of the Escherichia coli ATPsynthase determined by NMR spectroscopy. Nature Struct Biol 2: 961-967
Wilkens S, Dunn SD, Chandler J, Dahlquist FW and Capaldi RA (1997) Solution structure of the N-terminal domains of the δ subunit of the E coli ATPsynthesis Nature Struct Biol 4: 198-201
Uhlin U, Cox GB and Guss JM(1997) Crystal structure of the ε subunit of the proton translocating ATP synthase from Escherichia coli. Structure 5: 1219-1230
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boekema, E., Ubbink-Kok, T., Lolkema, J. et al. Structure of V-type ATPase from Clostridium fervidus by electron microscopy. Photosynthesis Research 57, 267–273 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006044931980
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006044931980