Abstract
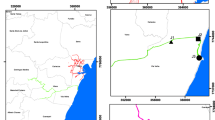
In this paper, we applied the technique of intervention analysis to assess the changes in BOD5 levels in marine water of Victoria Harbour and its vicinity in Hong Kong, after the commissioning of two sewage screening plants located in the central and western part of the Harbour. Data for this analysis were collected from 10 stations along an east-west transect from Junk Bay to Tsing Yi Island during the period from January 1988 to December 1995. Our analysis shows that the BOD5 levels at four of the five stations near the To Kwa Wan Sewage Screening Plant decreased immediately after the commissioning of the Plant in July 1990. The reduction ranged from 6.76% in Station VM5 to 15.44% in Station VM1. For the five stations located near the Stonecutters Island Sewage Screening Plant, their respective BOD5 levels also decreased by amounts ranging from 6.5% in Station WM2 to 21.54% in Station VM8, immediately after the commissioning of the Plant in August 1992. The stations closest to the outfalls of the two respective Plants showed a greater reduction in BOD5 level compared with the stations that are further away from the outfalls. Moreover, the stations near the larger Stonecutters Island Plant outfall also showed a greater decrease in BOD5 level compared with the stations near the smaller To Kwa Wan Plant outfall. These results are consistent with those obtained by a simple descriptive analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, B.: 1987, ‘Application of Intervention Analysis to a Road Fatality Series in Ontario', J. of Forecasting 6, 211–220.
Akaike, H.: 1974, ‘A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification', IEEE Trans. Automatic Control 19(6), 716–723.
Berthouex, P. M., Hunter, W. G., Pallesen, L. C. and Shih, C. Y.: 1975, ‘Modeling Sewage Treatment Plant Input BOD Data', J. Environ. Engineer. Div. 101, 127–138.
Box, G. E. P. and Tiao, G. C.: 1975, ‘Intervention Analysis with Applications to Economic and Environmental Problems', J. American Stat. Assoc. 70(349), 70–79.
Box, G. E. P. and Jenkins, G. M.: 1976, ‘Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control', Second Edition, Holden-Day, San Francisco.
Hipel, K. W., Lennox, W. C., Unny, T. E. and McLeod, A. I.: 1975, ‘Intervention Analysis in Water Resources', Water Resources Res. 11(6), 855–861.
Hong Kong Government Environmental Protection Department: 1996, ‘Marine Water Quality in Hong Kong for 1995', Hong Kong Government Printer, Hong Kong.
Roy, R. and Pellerin, J.: 1982, ‘On Long Term Air Quality Trends and Intervention Analysis', Atmos. Environ. 16(1), 161–169.
SAS: 1993, ‘SAS/ETS User's Guide', SAS Institute Inc., Version 6, Carry, N.C.
Tiao, G. C., Box, G. E. P. and Hamming, W. J.: 1975, ‘Analysis of Los Angeles photochemical Smog Data: A Statistical Overview', J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 25, 260–268.
Yung, Y. K., Wong, C. K., Broom, M. J., Ogden, J. A., Chan, S. C. M. and Leung, Y.: 1996, ‘Longterm Changes in Hydrography, Nutrients and Phytoplankton in Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong', accepted for publication in Hydrobiologia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeung, I., Yung, YK. Intervention Analysis on the Effect of two Sewage Screening Plants on the BOD5 levels in the Hong Kong Victoria Harbour and Vicinity. Environ Monit Assess 58, 79–93 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006043330301
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006043330301