Abstract
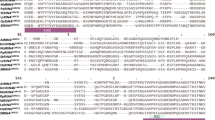
In rice (Oryza sativa L.), local acquired resistance against Pyricularia oryzae (Cav.), the causal agent of rice blast, can be induced by a preinoculation with the non-host pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. We have cloned a cDNA (Rir1a) and a closely related gene (Rir1b) corresponding to transcripts that accumulate in leaf tissue upon inoculation with P. syringae pv. syringae. The cDNA encodes a putative 107 amino acid protein, Rir1a, that exhibits a putative signal peptide cleavage site in its hydrophobic N-terminal part and a C-terminal part that is relatively rich in glycine and proline. The Rir1b gene contains a Tourist and a Wanderer miniature transposable element in its single intron and encodes a nearly identical protein. Rir1a is similar in sequence (ca. 35% identical and ca. 60% conservatively changed amino acids) to the putative Wir1 family of proteins that are encoded by pathogen-induced transcripts in wheat. Using antibodies raised against a Rir1a-fusion protein we show that Rir1a is secreted from rice protoplasts transiently expressing a 35S::Rir1a construct and that the protein accumulates in the cell wall compartment of rice leaves upon inoculation with P. syringae pv. syringae. Possible roles of Rir1a in pathogen defense are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander D, Goodman RM, Gut-Rella M, Glascock D, Weymann K, Friedrich L, Maddox D, Ahl-Goy P, Luntz T, Ward E, Ryals J: Increased tolerance to two oomycete pathogens in transgenic tobacco expressing pathogenesis-related protein 1a. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 7327–7331 (1993).
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Smith JA, Seidman JG, Struhl K: Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York (1987).
Bohlmann H, Clausen S, Behuke S, Giese H, Hiller C, Reimann-Philipp U, Schrader G, Barkholt V, Apel K: Leaf-specific thionins of barley: a novel class of cell wall proteins toxic to plant-pathogenic fungi and possibly involved in the defense mechanism of plants. EMBO J 7: 1559–1565 (1988).
Broglie K, Chet I, Holliday M, Cressman R, Biddle P, Knowlton S, Mauvais CJ, Broglie R: Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Science 254: 1194–1197 (1991).
Bull J, Mauch F, Hertig C, Rebmann G, Dudler R: Sequence of a wheat gene encoding a novel protein associated with pathogen-defense. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 5: 516–519 (1992).
Bureau TE, Ronald PC, Wessler SR: A computer-based systematic survey reveals the predominance of small inverted-repeat elements in wild-type rice genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 8524–8529 (1996).
Cho BH, Smedegaard-Petersen V: Induction of resistance to Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei in near-isogenic barley lines. Phytopathology 76: 301–305 (1986).
Datta SK, Peterhans A, Datta K, Potrykus I: Genetically engineered fertile Indica-rice recovered from protoplasts. Bio/technology 8: 736–740 (1990).
Dudler R, Hertig C: Structure of an mdr-like gene from Arabidopsis thaliana: evolutionary implications. J Biol Chem 267: 5882–5888 (1992).
Epple P, Apel K, Bohlmann H: Overexpression of an endogenous thionin enhances resistance of Arabidopsis against Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell 9: 509–520 (1997).
Franck S, Dudler R: Nucleotide sequence (Gen-Bank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number X87686) of a wheat cDNA encoding a putative pathogen-inducible protein homologous to PWIR1. Plant Physiol 109: 338 (1995).
Görlach J, Volrath S, Knauf Beiter G, Hengy G, Beckhove U, Kogel KH, Oostendorp M, Staub T, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J: Benzothiadiazole, a novel class of inducers of systemic acquired resistance, activates gene expression and disease resistance in wheat. Plant Cell 8: 629–643 (1996).
Gregersen PL, Thordal-Christensen H, Förster H, Collinge DB: Differential gene transcript accumulation in barley leaf epidermis and mesophyll in response to attack by Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei (syn. Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei). Physiol Mol Plant Path 51: 85–97 (1997).
Horino O: Induction of bacterial leaf blight resistance by incompatible strains of Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. In Tomiyama K, Daly J, Uritani I, Oku H, Ouchi S (eds). Biochemistry and Cytology of Plant Parasite Interactions, pp. 43–55. Kodanska, Tokyo (1976).
Jach G, Görnhardt B, Mundy J, Logemann J, Pinsdorf E, Leah R, Schell J, Maas C: Enhanced quantitative resistance against fungal disease by combinatorial expression of different barley antifungal proteins in transgenic tobacco. Plant J 8: 97–109 (1995).
Jose M, Puigdoménech P: Structure and expression of genes coding for structural proteins of the plant cell wall. New Phytol 125: 259–282 (1993).
Kieliszewski MJ, Lamport DTA: Extensin: Repetitive motifs, functional sites, post-translational codes, and phylogeny. Plant J 5: 157–172 (1994).
Kuc J: Induced immunity to plant disease. Bioscience 32: 854–860 (1982).
Langcake P, Wickens SGA: Studies on the actions of dichloro-cyclopropanes on the host-parasite relationship in rice blast disease. Physiol Plant Path 7: 113–126 (1975).
Liu D, Raghothama KG, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA: Osmotin overexpression in potato delays development of disease symptoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 1888–1892 (1994).
Logemann J, Melchers LS, Tigelaar H, Sela-Buurlage MB, Ponstein AS, van Roekel JSC, Bres-Vloemans SA, Dekker I, Cornelissen BJC, van den Elzen PJM, Jongedijk E: Synergistic activity of chitinase and β-1,3-glucanase enhances Fusarium resistance in transgenic tomato plants. J Cell Biochem 18A: 88 (1994).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1982).
Mauch F, Mauch-Mani B, Boller T: Antifungal hydrolases in pea tissue. Plant Physiol 88: 936–942 (1988).
Métraux JP, Ahl-Goy P, Staub T, Speich J, Steinemann A, Ryals J, Ward E: Induced systemic resistance in cucumber in response to 2,6-dichloro-isonicotinic acid and pathogens. In: Hennecke H, Verma DPS (eds) Advances in Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions, vol. 1, pp. 432–439. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands (1991).
Neuhaus JM, Sticher L, Meins F Jr, Boller T: A short C-terminal sequence is necessary and sufficient for the targeting of chitinases to the plant vacuole. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 10362–10366 (1991).
Niderman T, Genetet I, Bruyere T, Gees R, Stintzi A, Legrand M, Fritig B, Mösinger E: Pathogenesis-related PR-1 proteins are antifungal: Isolation and characterization of three 14-kilodalton proteins of tomato and of a basic PR-1 of tobacco with inhibitory activity against Phytophthora infestans. Plant Physiol 108: 17–27 (1995).
Ouchi S, Oku H, Hibino C: Localization of induced resistance and susceptibility in barley leaves inoculated with the powdery mildew fungus. Phytopathology 66: 901–905 (1976).
Ouchi S, Oku H, Hibino C, Aldyama I: Induction of accessibility and resistance in leaves of barley by some races of Erysiphe graminis. Phytopath Z 79: 24–34 (1974).
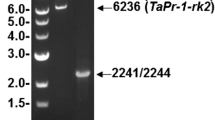
Reimmann C, Hofmann C, Mauch F, Dudler R: Characterization of a rice gene induced by Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae: Requirement for the bacterial lemA gene function. Physiol Mol Plant Path 46: 71–81 (1995).
Ross AF: Systemic acquired resistance induced by localized virus infections in plants. Virology 14: 340–358 (1961).
Ross AF: Systemic effects of local lesion formation. In: Beemster ABR, Dijkstra J (eds) Viruses of Plants, pp. 127–150. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1966).
Ryals JA, Neuenschwander UH, Willits MG, Molina A, Steiner HY, Hunt MD: Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 8: 1809–1819 (1996).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Schweizer P, Hunziker W, Mosinger E: Complementary DNA cloning in vitro transcription, and partial sequence analysis of messenger RNA from winter wheat Triticum aestivum L. with induced resistance to Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici. PlantMol Biol 12: 643–654 (1989).
Showalter AM: Structure and function of cell wall proteins. Plant Cell 5: 9–23 (1993).
Smith JA, Métraux JP: Pseudomonas syringae pathovar syringae induces systemic resistance to Pyricularia oryzae in rice. Physiol Mol Plant Path 39: 451–461 (1991).
Stüber D, Matile H, Garotta G: System for high-level production in Escherichia coli and rapid purification of recombinant proteins: applications to epitpope mapping, preparation of antibodies, and structure-function analysis. In: Levkovits I, Pernis B (eds) Immunological Methods, vol. 4, pp. 121–152. Academic Press, New York (1990).
Vigers AJ, Wiedemann S, Roberts WK, Legrand M, Selitren-nikoff CP, Fritig B: Thaumatin-like pathogenesis-related proteins are antifungal. Plant Sci 83: 155–161 (1992).
von Heijne G: A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucl Acids Res 14: 4683–4690 (1986).
Ward ER, Uknes SJ, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Wiederhold DL, Alexander DC, Ahl Goy P, Metraux JP, Ryals JA: Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3: 1085–1094 (1991).
White RF: Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) induces resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco. Virology 99: 410–412 (1979).
Woloshuk CP, Meulenhoff JS, Sela Buurlage M, van den Elzen PJM, Cornelissen BJC: Pathogen-induced proteins with inhibitory activity toward Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell 3: 619–628 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mauch, F., Reimmann, C., Freydl, E. et al. Characterization of the rice pathogen-related protein Rir1a and regulation of the corresponding gene. Plant Mol Biol 38, 577–586 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006041404436
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006041404436