Abstract
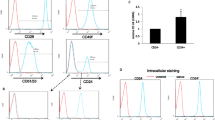
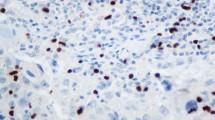
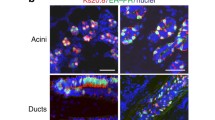
A number of studies have shown that certain variant isoforms of CD44 are overexpressed in human breast cancer, suggesting their use as indicators of the presence of malignant cells. We now show that CD44 isoform mRNA and protein expression is upregulated in normal human breast epithelial cells (HBEC) when these cells are stimulated to proliferate in culture. Reverse transcription-PCR analysis of cultured normal HBEC revealed complex patterns of CD44 mRNA expression that were indistinguishable from patterns previously shown to be characteristic of tissue samples containing malignant HBEC. CD44v6-expressing cells were identified in cultures generated from FACS-purified populations of either normal luminal (CALLA–AMMUC-1+) or myoepithelial (CALLA+MUC-1–AM) cells, even though immunohistochemical analysis of normal breast tissue sections confirmed CD44v6 expression to be limited to the myoepithelium in vivo. Increased expression of both CD44v mRNA and protein in cultured populations of normal HBEC was shown to correlate positively with the proportion of cells that were proliferating (Ki-67+) independent of cell density. These results indicate that activation of CD44 variant isoform expression in HBEC occurs as a normal response to factors that stimulate their proliferation and suggests caution in the use of this marker to identify malignant cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gunthert U: CD44: a multitude of isoforms with diverse functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 184: 47–63, 1993
Picker LJ, Nakache M, Butcher EC: Monoclonal antibodies to human lymphocyte homing receptors define a novel class of adhesion molecules of diverse cell types. J Cell Biol 109: 927–937, 1989
Haynes BF, Telen MJ, Hale LP, Denning SM: CD44-A molecule involved in leukocyte adherence and T-cell activation. Immunol Today 10: 423–428, 1989
Haynes BF, Liao HX, Patton KL: The transmembrane hyaluronate receptor (CD44): multiple functions, multiple forms. Cancer Cells 3: 347–350, 1991
Dall P, Heider K-H, Hekele A, von Mickwitz G, Kaufmann M, Ponta H, Herrlich P: Surface protein expression and messenger RNA-splicing analysis of CD44 in uterine cervical cancer and normal cervical epithelium. Cancer Res 54: 3337–3341, 1994
Finn L, Dougherty G, Finley G, Meisler A, Becich M, Cooper DL: Alternative splicing of CD44 pre-mRNA in human colorectal tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 200: 1015–1022, 1994
Heider K-H, Hofmann M, Hors E, van den Berg F, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST: A human homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44 is expressed in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps. J Cell Biol 120: 227–233, 1993
Heider K-H, Dammrich J, Skroch-Angel P, Muller-Hermelink H-K, Vollmers HP, Herrlich P, Ponta H: Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in intestinal-and diffusetype human gastric carcinomas and normal gastric mucosa. Cancer Res 53: 4197–4203, 1993
Li H, Hamon M-F, de Tribolet N, Janfeerally R, Hofmann M, Diserens A-C, Van Meir EG: Variant CD44 adhesion molecules are expressed in human brain metastases but not in glioblastomas. Cancer Res 53: 5345–5349, 1993
Mulder J-WR, Kruyt PM, Sewnath M, Oosting J, Seldenrijk CA, Weidema WF, Offerhaus GJA, Pals ST: Colorectal cancer prognosis and expression of exon-v6-containing CD44 proteins. Lancet 344: 1470–1472, 1994
Wielenga VIM, Heider K-H, Offerhaus GJA, Adolf GR, van den Berg FM, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST: Expression of CD44 variant proteins in human colorectal cancer is related to tumor progression. Cancer Res 53: 4754–4756, 1993
Dall P, Heider K-H, Sinn H-P, Skroch-Angel P, Adolf G, Kaufmann M, Herrlich P, Ponta H: Comparison of immunohistochcmistry and RT-PCR for detection of CD44v-expression, a new prognostic factor in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 60: 471–477, 1995
Iida N, Bourguignan LYW: New CD44 splice variants associated with human breast cancers. J Cell Physiol 162: 127–133, 1995
Matsumura Y, Tarin D: Significance of CD44 gene products for cancer diagnosis and disease evaluation. Lancet 340: 1053–1058, 1992
Kaufmann M, Heider K-H, Sinn H-P, von Minckwitz G, Ponta H, Herrlich P: CD44 variant exon epitopes in primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet 345: 615–619, 1995
Rodriguez C, Monges G, Rouanet P, Dutrillaux B, Lefrancois D, Theillet C: CD44 expression patterns in breast and colon tumors: a PCR-based study of splice variants. Int J Cancer 64: 347–354, 1995
Friedrichs K, Franke F, Lisboa B-W, Kugler G, Gille I, Terpe H-J, Holzel F, Maass H, Gunthert U: CD44 isoforms correlate with cellular differentiation but not with prognosis in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 55: 5424–5433, 1995
Sher BT, Bargatze R, Holzmann B, Gallatin WM, Matthews D, Wu N, Picker L, Butcher EC, Weissman IL: Homing receptors and metastasis. Adv Cancer Res 51: 361–390, 1988
Gunthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S, Zoller M, Haubmann I, Matzku S, Wenzel A, Ponta H, Herrlich P: A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell 65: 13–24, 1991
Emerman JT, Wilkinson DA: Routine culturing of normal, dysplastic and malignant human mammary epithelial cells from small tissue samples. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 26: 1186–1194, 1990
Emerman JT, Stingl J, Petersen A, Eaves CJ: Selective growth of freshly isolated human breast epithelial cells cultured at low concentrations in the presence or absence of bone marrow cells. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 41: 147–159, 1996
Emerman JT, Eaves CJ: Lack of effect of hematopoietic growth factors on human breast epithelial cell growth in serum-free primary culture. Bone Marrow Transplant 13: 285–291, 1994
Dougherty GJ, Cooper DL, Memory JF, Chiu RK: Ligand binding specificity of alternatively-spliced CD44 isoforms. Recognition of hyaluronan by CD44R1. J Biol Chem 269: 9074–9078, 1994
Burchell J, Durbin H, Taylor-Papadimitriou J: Complexity of expression of antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies HMFG-1 and HMFG-2 in normal and malignant human mammary cpithelial cells. J Immunol 131: 508–513, 1983
Ceriani RL, Thompson K, Peterson JA, Abraham S: Surface determination antigens of human mammary epithelial cells carried on the human milk fat globule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 582–586, 1977
Gusterson BA, Monaghan P, Mahendran R, Ellis J, O'Hare MJ: Identification of myoepithelial cells in human and rat breast by anti-common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen antibody A12. J Natl Cancer Inst 77: 343–349, 1986
Burchell J, Gendler S, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Girling A, Lewis A, Millis R, Lamport D: Development and characterization of breast cancer reactive monoclonal antibodies directed to the core protein of the human milk mucin. Cancer Res 47: 5476–5482, 1987
Foley KP, Leonard MW, Engel JD: Quantitation of RNA using the polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet 9: 380–385, 1993
Reed KC, Mann DA: Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res 13: 7207–7221, 1985
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13, 1983
Screaton GR, Bell MV, Jackson DG, Cornelis FB, Gerth U, Bell JI: Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 12160–12164, 1992
Fox SB, Fawcett J, Jackson DG, Collins I, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Gearing A, Simmons DL: Normal human tissues, in addition to some tumors, express multiple different CD44 isoforms. Cancer Res 54: 4539–4546, 1994
Mackay CR, Terpe H-J, Stauder R, Marston WL, Stark H, Gunthert U: Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol 124: 71–83, 1994
Abbasi AM, Chester KA, Talbot IC, Macpherson AS, Boxer G, Forbes A, Malcolm ADB, Begent RHJ: CD44 is associated with proliferation in normal neoplastic human colorectal epithelial cells. Eur J Cancer 29A: 1995–2002, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, N.L., Bardy, P., Bacani, J. et al. Correlation of CD44 expression with proliferative activity of normal human breast epithelial cells in culture. Breast Cancer Res Treat 50, 143–153 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006006425904
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006006425904