Abstract
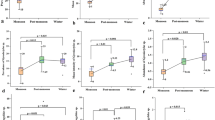
During the 1994/1995 EMAP-Estauries program in the Carolinian Province we investigated the feasibility of using parasites of fish as response indicators. Parasites of fish are an indigenous component of healthy ecosystems. Within the EMAP-E design, the suite of environmental parameters which may affect parasite abundance, richness, prevalence, and diversity can be divided into three categories: 1) the physical and chemical characteristics of the water and sediment (including contaminants) external to the fish; 2) the internal environment defined by the physical condition (physiological) of individual fish; and 3) the presence and relative abundance of benthic macroinvertebrates, many of which serve as intermediate hosts. The biotic response of parasites to environmental stressors is also reflected in the health of fish. Parasite assemblages of silver perch Bairdiella chrysura respond to both natural and anthropogenic stressors. Our results showed that particular environmental stressors and specific parasites that respond include: temperature and monogeneans; contaminants and nematodes; low dissolved oxygen and protists; and salinity, together with a mixture of metal and organic contaminants and crustacea. Parasites of fish are useful biomarkers and appear to be more sensitive to environmental stressors than are the fish themselves. Parasite responses to selected environmental stressors may be used to discriminate polluted and unpolluted sites. The use of parasites of fish as biomarkers has relevant application to fisheries management and coastal monitoring programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S. M., Brown, A. M., Goede, R. W.: 1993. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 122, 63–73.
Boxrucker, J. C.: 1979. Parasitol. 78:195–206.
Boyce, N. P., Yamada, S. B.: 1977. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 34, 706–709.
Carr, W.E.S., Adams, C.A.: 1973. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 102, 511–540.
Esch, G. W., Hazen, T. C., Dimock, R. V. Jr., Gibbons, J. W.: 1976. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 95:687–693.
FDEP 1994. Development of an environmental stress index using parasites of fish. Submitted research proposal.
Goede, R. W., Barton, B. A.: 1990. In: Biological indicators of stress in fish, (ed. S. M. Adams), American Fisheries Society Symposium. 8, 93–108.
Hart, A.W. 1994. Indian River Lagoon National Estuary Program. 85pp.
Harshbarger, J.C., Spero, P.M., Wolcott, N.M.: 1993. In: Pathobiology of marine and estuarine organisms, (eds. Couch, J.A. and Fournie, J.W.), pp. 157–176, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Heath, A.G.: 1987. Water pollution and fish physiology, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 245pp.
Hinton, D.E.: 1993. In: Pathobiology of marine and estuarine organisms, (eds. Couch, J.A. and Fournie, J.W.), pp. 177–215, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Hyland, J.L., Herringer, T.J., Snoots, T.R., Ringwood, A.H., Van Dolah, R.F., Hackney, C.T., Nelson, G.A., Rosen, J.S., Kokkanikis, S.A. 1996. Annual statistical summary: EMAP-Estuaries Demonstration Project in the Carolinian Province — 1994. NOAA Tech. Mem. NOS ORCA 97, pp. 102
Khan, R. A.: 1987. Parasitol. Today 3:99–100.
Khan, R. A.: 1990. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 44:759–763.
Khan, R. A., Thulin, J.: 1991. Adv. Parasitol. 30:201–238.
Landsberg, J. H.: 1989. In: Fish Culture in Warm Water Systems: Problems and Trends. (eds. M. Shilo and S. Sarig), p. 195–252, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Landsberg, J.H., Vermeer, G.K., Richards, S.A., Perry, N.: 1991. J. Aquat. Anim. Health. 3, 206–209.
Leong, T.S., Holmes, J.C.: 1981. J. Fish. Biol. 18, 693–713.
Long, E.R., MacDonald, D.D., Smith, S.L., Calder, F: 1995. Environ. Management 19, 81–97.
Long, E. R., Morgan, L. G.: 1990. NOAA Tech. Mem. NOS OMA 52. 175pp.
Margolis, L., Esch, G.W., Holmes, J.C., Kuris, A.M., Schad, G.A.: 1982. J. Parasitol. 68, 131–133.
McVicar, A. H., Bruno, D. W. and Fraser, C. O.: 1988. Mar. Pollution Bull. 19:169–173.
Moles, A.: 1980. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 109, 293–297.
Möller, H.: 1986. Int. J. Parasitol. 17, 353–361.
Möller, H.: 1986. Int. J. Parasitol. 17:353–361.
Nair, A.G., Nair, N.B.: 1982. J. Anim. Morphol. Physiol. 29, 265–271.
Novotny, J. F., Beeman, J. W.: 1990. Prog. Fish-Cult. 52, 162–170.
Overstreet, R. M. 1988. Aquat. Toxicol. 11:213–239.
Overstreet, R. M. 1993. In: Pathobiology of marine and estuarine organisms, (eds. Couch, J.A., Fournic, J.W.), pp. 111–156, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Overstreet, R.M., Hawkins, W.E., Deardorff, T.L. 1996. In: Environmental Fate and Effects of Pulp and Paper mill effluents.
Pascoe, D., Cram, D.: 1977. J. Fish Biol. 10, 467–472.
Pascoe, D., Mattey, D.: 1977. Z. Parasitenkd. 51, 179–186.
Sakanari, J. A., Moser, M., Reilly, C. A., Yoshino, T. P.: 1984, J. Fish Biol. 24, 553–563.
Sarig, S.: 1971. The prevention and treatment of diseases of warmwater fishes under subtropical conditions, with special emphasis on intensive fish farming. Diseases of fishes, Book 3, Snieszko, S.F. and Axelrod, H.R. (eds.), TFH Publications, Neptune City, New Jersey.
Summers, J.K., Macauley, J.M., Heitmuller, P.T., Engle, V.D., Adams, A.M., Brooks, G.T.: 1992. Annual statistical summary: EMAP-Estuaries Louisianian Province — 1991. U.S. EPA, ORD, Gulf Breeze FL, EPA/600/R-93-001.
Sures, B., Taraschewski, H., Jackwerth, E.: 1994a. Bull. Environ. Contam Toxicol. 52, 269–273.
Sures, B., Taraschewski, H., Jackwerth, E.: 1994b. J. Parasitol. 80, 355–357.
Sures, B., Taraschewski, H., Jackwerth, E.: 1994c. Dis. aquat. org. 19, 105–107.
Thoney, D.A.: 1991. J. Fish Biol. 39:515–534.
Thoney, D.A.: 1993. J. Fish Biol. 43:781–804.
Thoney, D. A., Hargis, W. J., Jr.: 1991. Ann. Rev. Fish Diseases. 1, 133–153.
Zar, I.H.: 1984. Biostatistical analysis. Prentice-Hall, New Jersey. 718pp.
Ziskowski, J.J., Despres-Patanjo, L., Murchelano, R.A., Howe, A.B., Ralph, D., Atran, S. 1987. Mar. Poll. Bull. 18, 496–504.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landsberg, J., Blakesley, B., Reese, R. et al. Parasites of Fish as Indicators of Environmental Stress. Environ Monit Assess 51, 211–232 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005991420265
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005991420265