Abstract
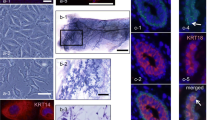
A new murine cell line, named MG1361, was established from mammary adenocarcinomas arising in a MMTV-neu transgenic mouse lineage where breast tumors develop in 100% of females, due to the over-expression of the activated rat neu oncogene in the mammary gland. The MG1361 cell line shows an epithelial-like morphology, has a poor plating efficiency, low clonogenic capacity, and a doubling time of 23.8 hours. Karyotype and flow cytometry analysis revealed a hypotetraploid number of chromosomes, whereas cell cycle analysis showed 31.2% of cells to be in the G1 phase, 21.4% in S and 47.4% in G2 + M. This cell line maintains a high level of neu expression in vitro. The MG1361 cell line was tumorigenic when inoculated in immunodeficient (nude) mice and the derived tumors showed the same histological features as the primary tumors from which they were isolated. MG1361 cells were positive for specific ER and PgR binding which was competed by tamoxifen, making this cell line useful for the evaluation of endocrine therapy. Moreover, they were sensitive to etoposide treatment, suggesting that they could be a model for the study of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. As the tumors arising in MMTV-neu transgenic mice have many features in common with human mammary adenocarcinomas (Sacco et al., Gene Therapy 1995; 2: 493–497), this cell line can be utilized to perform basic studies on the role of the neu oncogene in the maintenance of the transformed phenotype, and to test novel protocols of therapeutic strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Klijn JGM, Berns PMJJ, Bontenbal M, Alexieva-Figusch J, Foekens JA: Clinical breast cancer: New developments in selection and endocrine treatment of patients. J Steroid Biochem Molec Biol 43: 211–221, 1992
Porter-Jordan K, Lippman ME: Overview of the biologic markers of breast cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 8: 73–100, 1994
Maguire HC, Greene MI: Neu (c-erbB-2), a marker in carcinoma of the female breast. Pathobiol 58: 297–303, 1990
Hynes NE, Stern DF: The biology of erbB-2neu/HER-2 and its role in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1198: 165–184, 1994
Dougall WC, Quian X, Peterson NC, Miller MJ, Samanta A, Greene MI: The neu-oncogene: signal transduction pathways, transformation mechanisms and evolving therapies. Oncogene 9: 2109–2123, 1994
Muller WJ, Pattengale PK, Wallace R, Leder P: Single-step induction of mammary adenocarcinoma in transgenic mice bearing the activated c-neu oncogene. Cell 54: 105–115, 1988
Lucchini F, Sacco MG, Hu N, Villa A, Brown J, Cesano L, Mangiarini L, Rindi G, Kindl S, Sessa F, Vezzoni P, Clerici L: Early and multifocal tumors in breast, salivary, harderian and epidermal tissues developed in MMTV-Neu transgenic mice. Cancer Lett 64: 203–209, 1992
Sacco MG, Mangiarini L, Villa A, Macchi P, Barbieri O, Sacchi MC, Monteggia E, Fasolo V, Vezzoni P, Clerici L: Local regression of breast tumor following intramammary ganciclovir administration in double transgenic mice expressing neu oncogene and herpes symplex virus thymidine kinase. Gene Ther 2: 493–497, 1995
Sacco MG, Benedetti S, Duflot-Dancer A, Mesnil M, Bagnasco L, Strina D, Fasolo V, Villa A, Macchi P, Faranda S, Vezzoni P, Finocchiaro G: Partial regression, yet uncomplete eradication of mammary tumors in transgenic mice by retroviral mediated HSV-TK transfer in vivo. Gene Ther, in press
Williams GT: Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell 65: 1097–1098, 1991
Hickman JA: Apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs. Cancer Metas Rev 11: 121–139, 1992
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267: 1456–1462, 1995
Kienzi H: Antiestrogen induced cell death in cultured MCF7 cells, submitted
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning. A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989
Hamburger A, Salmon SE, Kim MB, Trent JM, Soehnlen BJ, Alberts DS, Schmidt HJ: Direct cloning of ovarian carcinoma cells in agar. Cancer Res 38: 3438–3444, 1978
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CPM, Kuijten GAM, Keehnen RMJ, Pals ST, van Oers MHJ: Annexin V for flow cytometrical detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 84: 1415–1420, 1994
Hanahan D: Transgenic mice as probes into complex systems. Science 246: 1265–1275, 1989
Pattengale PK, Stewart TA, Leder A, Sinn E, Muller W, Tepler I, Schmidt E, Leder P: Animal models of human disease. Pathology and molecular biology of spontaneous neoplasms occurring in transgenic mice carrying and expressing activated cellular oncogenes. Am J Pathol 135: 39–61, 1989
Cardiff RD, Sinn E, Muller W, Leder P: Transgenic oncogene mice. Am J Pathol 39: 495–501, 1989
Lowe SW, Bodis S, McClatchey A, Remington L, Ruley HE, Fisher DE, Housman DE, Jacks T: P53 status and the efficacy of cancer therapy in vivo. Science 266: 807–810, 1994
Aas T, Borresen AL, Geisler S, Smith-Sorensen B, Johnsen H, Varhaug JE, Akslen LA, Lonning PE: Specific p53 mutations are associated with de novo resistance to doxorubicin in breast cancer patients. Nature Med 2: 811–814, 1996
Hashimoto H, Chatterjee S, Berger NA: Inhibition of etoposide (V-16)-induced DNA recombination and mutant frequency of Bcl-2 protein overexpression. Cancer Res 55: 4029–4035, 1995
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR: Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68: 251–300, 1980
Bursch W, Liehr JG, Sirbarsku DA, Putz B, Taper H, Schulte-Hermann R: Control of cell death (apoptosis) by diethylstilbestrol in an estrogen dependent kidney tumor. Carcinogenesis 12: 855–860, 1991
Muss HB, Thor AD, Berry DA, Kute T, Liu ET, Koerner F, Cirrincione CT, Budman DR, Wood WC, Barcos M: c-erbB-2 expression and response to adjuvant therapy in women with node-positive early breast cancer. N Engl J Med 330: 1260–1266, 1994
Rasbridge SA, Gillet CE, Seymour AM, Patel K, Richards MA, Rubens RD, Millis RR: The effects of chemotherapy on morphology, cellular proliferation, apoptosis and oncoprotein expression in primary breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer 70: 335–341, 1994
McDonnell TJ, Meyn RE, Robertson LE: Implications of apoptotic cell death regulation in cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol 6: 53–60, 1995
Deshane J, Siegal GP, Alvarez RD, Wang MH, Feng M, Cabrera G, Liu T, Kay M, Curiel DT: Targeted tumor killing via an intracellular antibody erbB-2. J Clin Invest 96: 2980–2989, 1995
Vaughn JP, Iglehart JD, Demirdji S, Davis P, Babiss LE, Caruthers MH, Marks JR: Antisense DNA downregulation of the ERBB2 oncogene measured by a flow cytometric assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 8338–8342, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sacco, M.G., Gribaldo, L., Barbieri, O. et al. Establishment and characterization of a new mammary adenocarcinoma cell line derived from MMTV neu transgenic mice. Breast Cancer Res Treat 47, 171–180 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005988715285
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005988715285