Abstract
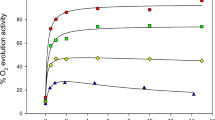
To study the effects of limitations in the Calvin-cycle on Photosystem (PS) II function and on its repair by D1-protein turnover, glycerinaldehyde (DLGA) was applied to 1 h dark-adapted pea leaves via the petiole. The application resulted in a 90% inhibition of photosynthetic oxygen evolution after 90 min illumination at either 120 or 500 µmol m−2 s−1. In the control leaves an increase of light-dependent oxygen production to 147 and 171% was observed after 90 min illumination. According to chlorophyll fluorescence quenching analysis the inhibition of photosynthetic electron transport by DLGA led to a substantial increase in the reduction state of the primary quinone acceptor of PS II, QA, and to a rise in membrane energetisation. However, PS II functionality was hardly affected by DLGA at the low light intensity as indicated by the constant high yield of variable fluorescence, Fv/Fm. Only at 500 µmol m−2 s−1 a 15% loss of Fv/Fm was observed in the presence of DLGA indicating that inactivated PS II centres had accumulated. The control leaves also showed a slight loss of Fv/Fm which did not affect photosynthetic electron transport due to a faster reoxidation of QA. The relative stability of PS II function in the presence of DLGA could not be ascribed to an increased repair by the rapid turnover of the D1-protein. Radioactive pulse-labelling studies with [14C] leucine in combination with immunological determination of the protein content revealed that both synthesis and degradation of the protein were inhibited in DLGA-treated leaves whereas in the control leaves a stimulation of D1-protein turnover was observed. The changes of D1-protein turnover could be explained by differences in the occupancy state of the QB-binding niche. A relation between the phosphorylation status of the PS II polypeptides and the turnover of the D1-protein could not be established. As shown by radioactive labelling with [32P]i, addition of DLGA led to an increase in the phosphorylation level of the PS II polypeptides D1 and D2 at the low light intensity when compared to the non-treated control. At the higher light intensity the phosphorylation level of the PS II polypeptides in control and DLGA-treated leaves were identical in spite of the substantial differences in D1-protein turnover.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adir N, Shochat S and Ohad I (1990) Light-dependent D1 protein synthesis and translocation is regulated by reaction center II. J Biol Chem 265: 2563-2568
Anderson JM and Aro EM (1994) Grana stacking and protection of Photosystem II in thylakoid membranes of higher plant leaves under sustained high irradiance: An hypothesis. Photosynth Res 4: 315-326
Aro EM, Kettunen R and Tyystjärvi E (1992) ATP and light regulated D1 protein modification and degradation. Role of D1 in photoinhibition. FEBS Lett 297: 29-33
Aro EM, Virgin I and Andersson B (1993a) Photoinhibition of Photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta 143: 13-34
Aro EM, McCaffery S and Anderson JM (1993b) Photoinhibition of Photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Plant Physiol 103: 835-843
Berthold DA, Babcock GT and Yocum CF (1981) A highly resolved, oxygen evolving Photosystem II preparation from spinach thylakoid membranes. FEBS Lett 134: 231-234
Dannehl H, Herbik A and Godde D (1995) Stress-induced degradation of the photosynthetic apparatus is accompanied by changes in thylakoid protein turnover and phosphorylation. Physiol Plant 93: 179-186
Dannehl H, Wietoska H, Heckmann H and Godde D (1996) Changes in D1 protein turnover and recovery of PS II activity precede accumulation of chlorophyll in plants after release from mineral stress. Planta 199: 34-42
Danon A and Mayfield SP (1991) Light regulated translational activators: Identification of chloroplast gene specific mRNA binding proteins. EMBO J 10: 3993-4001
Danon A and Mayfield SP (1994a) ADP-dependent phosphorylation regulates RNA-binding in vitro implications in light-modulated translation. EMBO J 13: 2227-2235
Danon A and Mayfield SP (1994b) Light-regulated translation of chloroplast messenger RNAs through redox potential. Science 266: 1717-1719
Demmig-Adams B and Adams WW (1993) The xanthophyll cycle, protein turnover and the high light tolerance of sun-acclimated leaves. Plant Physiol 103: 1413-1420
Ebbert V and Godde D (1994) Regulation of thylakoid protein phosphorylation in intact chloroplasts by the activity of kinases and phosphatases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1187: 290-299
Ebbert V and Godde D (1996) Phosphorylation inhibits 1 protein degradation and increases PS II stability. Photosynth Res 50: 257-269
Elich TD, Edelman M and Mattoo AK (1992) Identification, characterization, and resolution of the in vivo phosphorylated form of the 1 Photosystem II reaction center protein. J Biol Chem 267: 3523-3529
Fromm H, Devic M, Fluhr R and Edelman M (1985) Control of psbA-gene expression: In mature Spirodela chloroplasts light regulation of 32-kd protein synthesis is independent of transcript level. EMBO J 4: 291-295
Godde D and Dannehl H (1994) Stress induced chlorosis and increase in 1 protein turnover precedes photoinhibition in spinach suffering under combined magnesium and sulphur deficiency. Planta 195: 291-300
Godde D, Schmitz H and Weidner M (1991) Turnover of the D-1 reaction center polypeptide from Photosystem 11 in intact spruce needles and spinach leaves. Z Naturforsch 46c: 245-251
Gong H and Ohad I (1991) The PQ/PQH2 ratio and occupancy of Photosystem II-QB site by plastoquinone control the degradation of 1 protein during photoinhibition in vivo. J Biol Chem 266: 21293-21299
Johanningmeier U (1987) Expression of psbA gen in E. coli. Z Naturforsch 42c: 755-757
Kim JH, Nemson JA and Melis A (1993) Photosystem II reaction center damage and repair in Dunaliella salina (green alga). Plant Physiol 103: 181-189
Koivuniemi A, Aro EM and Andersson B (1995) Degradation of the 1-and D2-proteins of Photosystem II in higher plants is regulated by reversible phosphorylation. Biochemistry 34: 16022-16029
Komenda J and Barber J (1995) Comparison of psbO and psbH deletion mutants of Synechosystis PCC 6803 indicates that degradation of 1 protein is regulated by the QB Site and dependent on protein synthesis. Biochemistry 34: 9625-9631
Krause GH and Weis E (1991) Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: The basics. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42: 313-349
Mattoo AK, Hoffmann-Falk H, Marder JB and Edelmann M (1984) Regulation of protein metabolism: Coupling of photosynthetic electron transport to in vivo degradation of the rapidly metabolised 32-kilodalton protein of the chloroplast membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 1380-1384
Mayfield SP, Yohn CB, Cohen A and Danon A (1995) Regulation of chloroplast gene expression. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46: 147-166
Ohad I, Keren N, Zer H, Gong H, Mor TS, Gal A, Tal S and Domovich Y (1994) Light-induced degradation of the Photosystem II reaction centre I protein in vivo: An integrative approach. In: Baker NR and Bowyer JR (eds) Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to the Field, pp 161-177. BIOS, Oxford
Osmond CB (1994) What is photoinhibition? Some insights from comparisons of shade and sun plants. In: Baker NR and Bowyer JR (eds) Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to the Field, pp 1-24. BIOS, Oxford
Park YI, Chow WS, Anderson JM and Hurrya Differential susceptibility of Photosystem II to light stress in light acclimated pea leaves depends on the capacity for photochemical and nonradiative dissipation of light. Plant Sci 115: 137-149
Park YI, Anderson JM and Chow WS (1996b) Photoinactivation of functional Photosystem II and 1-protein synthesis in vivo are independent of the modulation of the photosynthetic apparatus by growth irradiance. Planta 198: 300-309
Porra RJ, Tompson WA and Kriedeman PE (1989) Determination of accurate coefficients and simultaneous equations for assaying chlorophyll a and b extracted with four different solvents: Verification of the concentrations of chlorophyll standards by atomic absorptions spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 975: 384-394
Powles SB (1984) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis induced by visible light. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35: 15-44
Rintamäki E, Salo R, Lehtonen R and Aro EM (1995) Regulation of 1 protein degradation during photinhibition of Photosystem II in vivo: Phosphorylation of the 1 protein in various plant groups. Planta 195: 379-386
Rintamäki E, Salo R, Koivuniemi A and Aro EM (1996) Protein phosphorylation and magnesium status regulate the degradation of the 1 reaction centre protein of Photosystem II. Plant Sci 115: 175-182
Schägger H, Borchart U, Aquila H, Link TA and von Jagow G (1985) Isolation and aminoacid sequence of the smallest subunit of beefheart bcl complex. FEBS Lett 190: 89-94
Schreiber U, Schliwa U and Bilger W (1986) Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer. Photosynth Res 10: 51-62
Schuster G, Dewit M, Staehelin LA and Ohad I (1986) Transient inactivation of the thylakoid Photosystem II light-harvesting protein kinase and concomitant changes in intramembrane particle size during photoinhibition of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol 103: 71-80
Styring S and Jegerschöld C (1994) Light-induced reactions impairing electron transfer through Photosystem II. In: Baker NR and Bowyer JR (eds) Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to the Field, pp 51-74. BIOS, Oxford
Telfer A and Barber J (1995) Elucidating the molecular mechanisms of photoinhibition by studying isolated Photosystem II reaction centres. In: Baker NR and Bowyer JR (eds) Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to the Field pp 25-50. BIOS Oxford
van Wijk KJ, Nilsson LO and Styring S (1994) Synthesis of reaction center proteins and reactivation of redox components during repair of Photosystem II after light-induced inactivation. J Biol Chem 269: 28382-28392
van Wijk KJ, Andersson B and Aro EM (1996) Kinetic resolution of the incorporation of the 1 protein into Photosystem II and localization of assembly intermediates in thylakoid membranes of spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem 271: 9627-9636
Walker DA (1987) The Use of the Oxygen Electrode and Fluorescence Probes in Simple Measurements of Photosynthesis. Oxygraphic Limited, Sheffield
Walker DA and Stokes DM (1972) Inhibition of carbon dioxide assimilation by D, L-glycerinaldehyde. Biochem J 128: 1147-1157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollinderbäumer, R., Ebbert, V. & Godde, D. Inhibition of CO2-fixation and its effect on the activity of Photosystem II, on D1-protein synthesis and phosphorylation. Photosynthesis Research 52, 105–116 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005802623823
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005802623823