Abstract
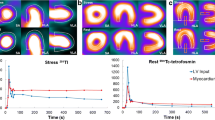
The aim of this study was to evaluate the value of thallium-201 chloride (201Tl) reinjection imaging following dobutamine stress (DRi) to identify viable myocardium in comparison with a rest-redistribution 201Tl protocol (RR). The identification of viable myocardium bears important consequences for adequate selection of patients with poor left ventricular function, often unable to exercise, who are considered for revascularization. Twenty-six patients with chronic coronary artery disease and depressed left ventricular function (ejection fraction 36±10%) were studied by both DRi and RR single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT). Semi-quantitative analysis of regional 201Tl activity (5-point score) and wall motion by echocardiography using a 16-segment model was performed. Regions were classified as viable (normal/reversible/fixed moderate defects) or non-viable (fixed severe defects) and related to regional wall motion. Target heart rate was reached in 25 patients. Myocardial viability was demonstrated in 353/416 (85%) by DRi SPECT and in 346/416 (83%) by RR SPECT. The agreement between the 2 protocols was 98% with a K-value of 0.94; similar results were obtained when the analysis was limited to dyscontractile segments. In conclusion, this study demonstrates the feasibility and diagnostic value of DRi SPECT to identify viable myocardium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dilsizian V, Bonow RO. Current diagnostic techniques of assessing myocardial viability in hibernating and stunned myocardium. Circulation 1993; 87: 1-20.
Tillisch J, Brunken R, Marshall R, Schwaiger M, Mandelkern M, Phelps M, Schelbert H. Reversibility of cardiac wall motion abnormalities predicted by positron tomography. N Eng J Med 1986; 314: 884-888.
Vom Dahl J, Eitzman DT, Al-Aouar ZR, Kanter L, Hicks RJ, Deeb GM, Kirsh MM, Schwaiger M. Relation of regional function, perfusion and metabolism in patients with advanced coronary artery disease undergoing surgical revasculari-zation. Circulation 1994; 90: 2356-2366.
Ragosta M, Beller GA, Watson DD, Kaul S, Gimple LW. Quantitative planar rest-redistribution 201T1 imaging in detection of myocardial viability and prediction of improvement in left ventricular function after coronary bypass surgery in patients with severely depressed left ventricular function. Circulation 1993; 87: 1630-1641.
Kennedy JW, Kaiser GC, Fisher LD, Fritz JK, Myers M, Mudd JG, Ryan TJ. Clinical and angiographic predictors of operative mortality from the collaborative study in coronary artery surgery (CASS). Circulation 1981; 63: 793-802.
Pigott JD, Kouchoukos NT, Oberman A, Cutter GR. Late results of surgical and medical therapy for patients with coronary artery disease and depressed left ventricular function. J Am Coll Cardiol 1985; 5: 1036-1045.
Berger BC, Watson DD, Burwell LR, Crosby IK, Wellons HA, Teates CD, Beller GA. Redistribution of thallium at rest in patients with stable and unstable angina and the effect of coronary artery bypass surgery. Circulation 1979; 60: 1114-1125.
Iskandrian AS, Hakki A, Kane SA, Goel IP, Mundth ED, Hakki A, Segal BL. Rest and redistribution thallium-201 myocardial scintigraphy to predict improvement in left ventricular function after coronary arterial bypass grafting. Am J Cardiol 1983; 51: 1312-1316.
Mori T, Minamiji K, Kurogane H, Ogawa K, Yoshida Y. Rest-injected thallium-201 imaging for assessing viability of severe asynergic regions. J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 1718-1724.
Alfieri O, La Canna G, Giubbini R, Pardini A, Zogno M, Fucci C. Recovery of myocardial function. The ultimate target of coronary revascularization. Eur J Cardio-thorac Surg 1993; 7: 325-330.
Dilsizian V, Rocco TP, Freedman NM, Leon MB, Bonow RO. Enhanced detection of ischemic but viable myocardium by the reinjection of thallium after stress-redistribution imaging. N Eng J Med 1990; 323: 141-146.
Ohtani H, Tamaki N, Yonekura Y, Mohiuddin IH, Hirata K, Ban T, Konishi J. Value of thallium-201 reinjection after delayed SPECT imaging for predicting reversible ischemia ischemia after coronary artery bypass grafting. Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: 394-399.
Tamaki N, Ohtani H, Yamashita K, Magata Y, Yonekura Y, Nohara R, Kambara H, Kawai C, Hirata K, Ban T, Konishi J. Metabolic activity in the areas of new fill-in after thallium-201 reinjection: Comparison with positron emission tomography using fluorine-18-deoxyglucose. J Nucl Med 1991; 32: 673-678.
Verani MS, Mahmarian JJ. Myocardial perfusion scintigraphy during maximal coronary artery vasodilation with adenosine. Am J Cardiol 1991; 67: 12D-17D.
Ranhosky A, Kempthorne-Rawson J, and the Intravenous Dipyridamole Thallium Imaging Study Group. The safety of intravenous dipyridamole thallium myocardial perfusion imaging. Circulation 1990; 81: 1205-1209.
Pennell DJ, Underwood SR, Swanton RH, Walker JM, Ell PJ. Dobutamine thallium myocardial perfusion tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1991; 18: 1471-1479.
Cornel JH, Balk AHMM, Boersma E, Maat APWM, Elhendy A, Arnese M, Salustri A, Roelandt JRTC, Fioretti PM. Safety and feasibility of dobutamine-atropine stress echocardiography in patients with ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1996; 9: 27-32.
Arnese M, Cornel JH, Salustri A, Maat APWM, Elhendy A, Reijs AEM, Ten Cate FJ, Keane D, Balk AGMM, Roelandt JRTC, Fioretti PM. Prediction of improvement of regional left ventricular function after surgical revascularization. A comparison of low-dose dobutamine echocardiography with 201Tl single-photon emission computed tomography. Circulation 1995; 91: 2748-2752.
Forster T, McNeill AJ, Salustri A, Reijs AEM, El-Said EM, Roelandt JRTC, Fioretti PM. Simultaneous dobutamine stress echocardiography and technetium-99 isonitrile single-photon emission computed tomography in patients with suspected coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 21: 1591-1596.
Dilsizian V, Freedman NMT, Bacharach SL, Perrone-Filardi P, Bonow RO. Regional thallium uptake in irreversible defects. Magnitude of change in thallium activity after reinjection distinguishes viable from nonviable myocardium. Circulation 1992; 85: 627-634.
Hays JT, Mahmarian JJ, Cochran AJ, Verani MS. Dobutamine thallium-201 tomography for evaluating patients with suspected coronary artery disease unable to undergo exercise or vasodilator pharmacologic stress testing. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 21: 1583-1590.
Wallbridge DR, Tweddel AC, Martin W, Hutton I. A comparison of dobutamine and maximal exercise as stress for thallium scintigraphy. Eur J Nucl Med 1993; 20: 319-323.
Mertes H, Sawada SG, Ryan T, Segar DS, Kovacs R, Foltz J, Feigenbaum H. Symptoms, adverse effects, and complications associated with dobutamine stress echocardiography. Exercise in 1118 patients. Circulation 1993; 88: 15-19.
Meyer SL, Curry GC, Donsky MS, Twieg DB, Parkey RW, Willerson JT. Influence of dobutamine on hemodynamics and coronary blood flow in patients with and without coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1976; 38: 103-108.
Herman SD, LaBresh KA, Santos-Ocampo CD, Garber CE, Barbour MM, Messinger DE, Cloutier DJ, Ahlberg AW, Heller GV. Comparison of dobutamine and exercise using technetium-99m sestamibi imaging for the evaluation of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1994; 73: 164-169.
Marwick TH, D'Hondt AM, Mairesse GH, Baudhuin T, Wijns W, Detry JM, Melin JA. Comparative ability of dobutamine and exercise stress in inducing myocardial ischaemia in active patients. Br Heart J 1994; 72: 31-38.
Galassi AR, Centamore G, Fiscella A, Coppola A, Liberti F, Franco M, Palazzo G, Musumeci S, Gallassi A. Comparison of rest-redistribution thallium-201 imaging and reinjection after stress-redistribution for the assessment of myocardial viability in patients with left ventricular dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1995; 75: 436-442.
Dilsizian V, Perrone-Filardi P, Arrighi JA, Bacharach SL, Quyyumi AA, Freedman NMT, Bonow RO. Concordance and discordance between stress-redistribution-reinjection and rest-redistribution thallium imaging for assessing viable myocardium. Comparison with metabolic activity by positron emission tomography. Circulation 1993; 88: 941-952.
Maddahi J, Schelbert H, Brunken R, Di Carli M. Role of Thallium-201 and PET imaging in evaluation of myocardial viability and management of patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction. J Nucl Med 1994; 35: 707-715.
Dilsizian V, Bonow RO. Differential uptake and apparent 201Tl washout after thallium reinjection. Options regarding early redistribution imaging before reinjection or late redistribution imaging after reinjection. Circulation 1992; 85: 1032-1038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cornel, J.H., Bax, J.J., Elhendy, A. et al. Dobutamine stress-redisstribution-reinjection versus rest-redistribution thallium-201 spect in the assessment of myocardial viability. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 13, 59–64 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005732802777
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005732802777