Abstract
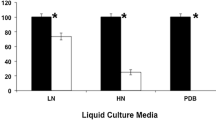
Cladosporium sp. strain AJR318,501 was isolated from DDT-contaminated soil by its ability to decolourise the polymeric dye, Poly R-478. When inoculated into potato/dextrose broth containing 100 mg of DDT l−1, a 21% decrease in DDT concentration was observed 12 days after its addition, however, no transformation products were detected by gas chromatography. TLC of culture medium and mycelia extracts revealed 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane and five unknown transformation products associated with the mycelia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aislabie JM, Richards NK, Boul HL (1997) Microbial degradation of DDT and its residues: a review. New Zealand J. Ag. Res. 40: 269–282.
Aislabie JM, Davison AD, Franzmann PD, Jardine DR, Karuso P (1998) Cometabolism of DDE by an aerobic bacterium. 14th Australasian Biotechnology Conference, Adelaide, Australia.
Barbosa AM, Dekker RFH, St Hardy GE (1996) Veratryl alcohol as an inducer of laccase by an ascomycete, Botryosphaeria sp., when screened on the polymeric dye Poly R-478. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 23: 93–96.
Beunink J, Rehm H-J (1988) Synchronous anaerobic and aerobic degradation of DDT by an immobilised mixed culture system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29: 72–80.
Bumpus JA, Aust SD (1987) Biodegradation of DDT (1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(4-chlorophenyl)ethane) by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 2001–2008.
Fiechter A (1993) Function and synthesis of enzymes involved in lignin degradation. J. Biotechnol. 30: 49–55.
Field JA, de Jong E, Feijoo-Costa G, de Bont JAM (1993) Screening for ligninolytic fungi applicable to the biodegradation of xenobiotics. Trends Biotechnol. 11: 44–49.
Gold MH, Glenn JK, Alic M (1988) Use of polymer dyes in lignin biodegradation assays. In: Wood WA, Kellog ST, eds. Methods in Enzymology, 161 Part B, pp. 74–78.
Guenzi WD, Beard WE (1968) Anaerobic conversion of DDT to DDD and aerobic stability of DDT in soil. Am. Soil Sci. Soc. Proc. 32: 522–524.
Juhasz AL, Britz ML, Stanley GA (1997) Degradation of fluoranthene, pyrene, benz[a]anthracene and dibenz[a,h]anthracene by Burkholderia cepacia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 83: 189–198.
Pfaender FK, Alexander A (1973) Effect of nutrient additions on the apparent cometabolism of DDT. J. Agric. Food Chem. 21: 397–399.
Plimmer JR, Kearney PC, von Endt DW (1968) Mechanism of conversion of DDT to DDD by Aerobacter aerogenes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 4: 594–597.
Walter M (1992) Biodegradation of DDT and DDE. MSc Thesis, Lincoln University, New Zealand.
Wedemeyer G (1967) Dechlorination of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane by Aerobacter aerogenes. Appl. Microbiol. 15: 569–574.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Juhasz, A.L., Naidu, R. Apparent degradation of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT) by a Cladosporium sp.. Biotechnology Letters 21, 991–995 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005694416926
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005694416926