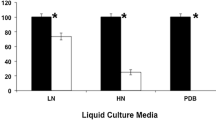
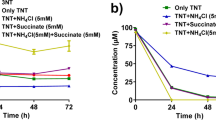
Abstract
Up to 200 mg 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) l−1 was removed within 12 h after adding it to a 5-day old culture of Irpex lacteus. The initial formation of hydroxylamino-dinitrotoluenes (2- and 4-OHAmDNT) from TNT was detected, followed by their successive transformation to aminodinitrotoluenes (2- and 4-AmDNT). Transformation of TNT to AmDNT via OHAmDNT was fast, but the next step was slow and seemed to be a rate-limiting step in TNT degradation. OHAmDNT isomers were also rapidly transformed by an in vitro enzymatic system. Both the mycelium and extracellular enzymes of I. lacteus were required for the TNT degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armenante PM, Pal N, Lewandowski G (1994) Role of mycelium and extracellular protein in the biodegradation of 2,4,6–trichlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 1711–1718.
Boopathy R, Wilson M, Kulpa CF (1993) Anaerobic removal of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene (TNT) under different electron accepting conditions: laboratory study. Water Environ. Res. 65: 271–275.
Drzyzga O, Bruns-Nagel D, Gorontzy T, Blotevogel K, Gemsa D, von Löw E (1998) Mass balance studies with 14C-labeled 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene (TNT) mediated by an anaerobic Desulfovibrio species and an aerobic Serratia species. Curr. Microbiol. 37: 380–386.
Fernando T, Bumpus JH, Aust SD (1990) Biodegradation of TNT (2,4,6–trinitrotoluene) by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 1667–1671.
French CE, Nicklin S, Bruce NC (1998) Aerobic degradation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene by Enterobacter cloacae PB2 and by pentaerythritol tetranitrate reductase.Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 2864–2868.
Haïdour A, Ramos JL (1996) Identification of products resulting of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene, 2,4–dinitrotoluene, and 2,6–dinitrotoluene by Pseudomonas sp. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30: 2365–2370.
Hawari J, Halasz A, Beaudet S, Paquet L, Ampleman G, Thiboutot S (1999) Biotransformation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene with Phanerochaete chrysosporium in agitated cultures at pH 4.5. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 2977–2986.
Honeycutt ME, Jarvis AS, McFarland VA (1996) Cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene and its metabolites. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 35: 282–287.
Lewis TA, Ederer MM, Crawford RL, Crawford DL (1997) Microbial transformation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechol. 18: 89–96.
McFarlan S (1999) 2,4,6–Trinitrotoluene pathway map. http://www.labmed.umn.edu/umbbd/tnt/tnt_map.html
Michels J, Gottschalk G (1994) Inhibition of the lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium by hydroxylaminodinitrotoluene, an early intermediate in the degradation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 60: 187–194.
Michels J, Gottschalk G (1995) Pathway of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene (TNT) degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. In: Spain J, ed. Biodegradation of Nitroaromatic Compounds. New York: Plenum Press, pp. 135–149.
Montpas S, Samson J, Langlois É, Lei J, Piché Y, Chênevert R (1997) Degradation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene by Serratia marcescens. Biotechnol. Lett. 19: 291–294.
Oh KH, Kim YJ (1998) Degradation of explosive 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene by s-triazine degrading bacterium isolated from contaminated soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 61: 702–708.
Pasti-Grigsby MB, Lewis TA, Crawford DL, Crawford RL (1996) Screening for fungi intensively mineralizing 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 47: 452–457.
Shelley MD, Autenrieth RL, Wild JR, Dale BE (1996) Thermodynamic analysis of trinitrotoluene biodegradation and mineralization pathways. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 50: 198–205.
Song HG (1999) Comparison of pyrene biodegradation by white rot fungi. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15: 669–672.
Spain JC (1995) Biodegradation of nitroaromatic compounds. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 49: 523–525.
Spiker JK, Crawford DL, Crawford RL (1992) Influence of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene (TNT) concentration on the degradation of TNT in explosive-contaminated soils by the white rot fungus Phane975 rochaete chrysosporium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 3199–3202.
Stahl JD, Aust SD (1993) Metabolism and detoxification of TNT by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 192: 477–482.
Stahl JD, Aust SD (1995) Biodegradation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. In: Spain J, ed. Biodegradation of Nitroaromatic Compounds. New York: Plenum Press, pp. 117–133.
Tien K, Kirk T (1984) Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization and catalytic properties of a unique H2O2–requiring oxygenase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 81: 2280–2284.
Tien K, Kcheibner K, Hatakka AI, Naveau H, Agathos SN (1999) Transformation and mineralization of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene (TNT) by manganese peroxidase form the whiterot basidiomycete Phlebia radiata. Biodegradation 10: 83–91.
Van Aken B, Skubisz K, Naveau H, Agathos SN (1997) Biodegradation of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene (TNT) by the white-rot basidiomycete Phlebia radiata. Biotechnol. Lett. 19: 813–817.
Vorbeck C, Lenke H, Fischer P, Knackmuss H-J (1994) Identifi-cation of a hydride-Meisenheimer complex as a metabolite of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene by a Mycobacterium strain. J. Bacteriol. 176: 932–934.
Walker JE, Kaplan DL (1992) Biological degradation of explosives and chemical agents. Biodegradation 3: 369–385.
Won WD, DiSalvo LH, Ng J (1976) Toxicity and mutagenicity of 2,4,6–trinitrotoluene and its microbial metabolites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 31: 576–580.
Yinon J (1990) Toxicity and Metabolism of Explosives. Boston: CRC Press, pp. 1–67.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HY., Song, HG. Transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene by white rot fungus Irpex lacteus. Biotechnology Letters 22, 969–975 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005636914121
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005636914121