Abstract
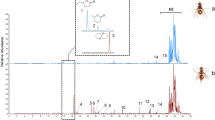
Stereoselectively synthesized enantiomers of ethyl cis-5-iodotrans-2-methylcyclohexane-1-carboxylate (ceralure B1), a potent lure for male Mediterranean fruit flies, were tested in the laboratory and the field against laboratory reared sterile flies. The (−)-ceralure B1 enantiomer was significantly more attractive than the (+)-ceralure B1 antipode. Dose–response studies of the above compounds demonstrated that (−)-ceralure B1 and to a lesser extent, racemic ceralure B1, captured consistently more male flies than trimedlure, the current male attractant used in detection programs. Longevity tests demonstrated that, over a three-week period, both (−)-ceralure B1 and racemic ceralure B1 caught significantly more flies than trimedlure. The synthesis of specific enantiomers of ceralure B1 shows great promise as a male attractant that could replace trimedlure for detection and delimitation in action programs aimed at this exotic pest.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
BEROZA, M., GREEN, N., GERTLER, S. I., STEINER, L. F., and MIYASHITA, D. 1961. New attractants for the Mediterranean fruit fly. J. Agric. Food Chem.9:361-365.
CDFA. 1994. Final programmatic environmental impact report. The exotic fruit fly eradicaton program using aerial application of Malathion and bait. California Department of Food and Agriculture. Clearinghouse number 91043018.
DEMILO, A. B., CUNNINGHAM, R. T., and MCGOVERN, T. P. 1994a. Trimedlure: Effects of structural modifications on its attractiveness to Mediterranean fruit fly males (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol.87:1494-1501.
DOOLITTLE, R. E., CUNNINGHAM, R. T., MCGOVERN, T. P., and SONNET, P. E. 1991. Trimedlure enantiomers: Differences in attraction for Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata(Weid.) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Chem. Ecol.17:475-484.
GILBERT, J., and BINGHAM, R. R. (eds.). 1999. Insect Trapping Guide. California Department of Food and Agriculture. MF 1-9.
HARRIS, E. J., NAKAGAWA, S., and URAGO, T. 1971. Sticky traps for detection and survey of three tephritids. J. Econ. Entomol.64:62-65.
HEATH, R. R., CHAMBERS, D. L., TUMLINSON, J. H., and LANDOLT, P. J. 1990. Controlled release of trimedlure isomer C from a compressed disk and the evaluation of its attractiveness to the Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol.83(3):819-822.
JANG, E. B., CARVALHO, L., and STARK, J. 1997. Attraction of female Oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis, to volatile semiochemicals from leaves and extracts of a nonhost plant, Panax (Polyscias guilfoylei) in laboratory and olfactometer assays. J. Chem. Ecol.23:1389-1401.
LEONHARDT, B. A., CUNNINGHAM, R. T., RICE, R. E., HARTE, E. M., and MCGOVERN, T. P. 1987. Performance of controlled-release formulations of trimedlure to attract the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata. Entomol. Exp. Appl.44:45-51.
LEONHARDT, B. A., CUNNINGHAM, R. T., RICE, R. E., HARTE, E. M., and HENDRICHS, J. 1989. Design, effectiveness, and performance criteria of dispenser formulations of trimedlure, and attractant of the Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol.82:860-867.
MCGOVERN, T. P., and CUNNINGHAM, R. T. 1988. U.S. Patent No. 4,764,366.
MCGOVERN, T. P., CUNNINGHAM, R. T., and LEONHARDT, B. A. 1987. Attractiveness of trans-trimedlure and its four isomers in field tests with the Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol.80:617-620.
RAW, A. S., and JANG, E. B. 2000. Enantioselective synthesis of ceralure B1, ethyl cis-5-iodo-trans-2-methylcyclohexane-1-carboxylate. Tetrahedron56:3285-3290.
SIEBERT, J. B., and COOPER, T. 1995. Embargo on California produce would cause revenue, job loss. Calif. Agric.49(4):7-12.
TANKA, N., STEINER, L. F., OHINATA, K., and OKAMOTO, R. 1969. Low cost larval rearing medium for mass production of Oriental and Mediterranean fruit flies. J. Econ. Entomol.62:967-968.
WARTHEN, JR., J. D., CUNNINGHAM, R. T., DEMILO, A. B., and SPENCER, S. 1994. Trans-ceralure isomers: Differences in attraction for Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata(Weid.) (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Chem. Ecol.20:569-578.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, E.B., Raw, A.S. & Carvalho, L.A. Field Attraction of Mediterranean Fruit Fly, Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) to Synthetic Stereoselective Enantiomers of the Ceralure B1 Isomer. J Chem Ecol 27, 235–242 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005620203504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005620203504