Abstract
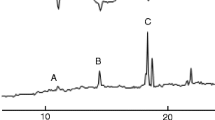
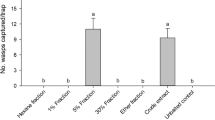
A male-produced aggregation pheromone was demonstrated in Colopterus truncatus Randall (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) by gas chromatographic comparisons of male and female volatile emissions. Male-specific compounds were identified with coupled gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric (GC-MS) analysis and GC and MS comparison of authentic standards. Physiological activity was evaluated by coupled gas chromatographic–electroantennographic (GC-EAG) recordings, and electroantennographic (EAG) assays of standards. The male-produced volatiles eliciting responses from male and female antennae (and relative abundance) were (2E,4E,6E)-3,5-dimethyl2,4,6-octatriene (1) (1.8), (2E,4E,6E)-4,6-dimethyl-2,4,6-nonatriene (2) (100), and (2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,5,7-trimethyl-2,4,6,8-decatetraene (3) (3.3). A fourth male-specific compound, (2E,4E,6E,8E)-4,6,8-trimethyl-2,4,6,8-undecatetraene (4) (0.6) was not EAG-active. EAG dose–response studies showed that the antennae were most sensitive to 2 followed by 3 and 1. Synthetic 2, binary blends of 1 and 3, and tertiary blends of 1, 2, and 3 were highly attractive in the field when synergized with fermenting whole-wheat bread dough. In the field, cross-attraction to the C. truncatus pheromone components was observed for Carpophilus lugubris Murray, C. antiquus Melsheimer, and C. brachypterus Say.
Similar content being viewed by others
cREFERENCES
Appel, D. N., Andersen, K., and Lewis, R., Jr. 1986. Occurrence of nitidulid beetles (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) in Texas oak wilt centers. J. Econ. Entomol. 79:1276–1279.
Bartelt, R. J. 1997. Aggregation pheromones of Carpophilus spp. (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae): Review of chemistry and biology. Recent Res. Dev. Entomol. 1:115–129.
Bartelt, R. J. 1999. Sap beetles, pp. 69–90, in J. Hardie and A. K. Minks (eds.). Pheromones of Non-Lepidopteran Insects Associated with Agricultural Plants. CABI Publishing, New York.
Bartelt, R. J., and Weisleder, D. 1996. Polyketide origin of pheromones of Carpophilus davidsoni and C. mutilatus (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 4:429–438.
Bartelt, R. J., and Zilkowski, B. W. 1999. Nonequilibrium quantitation of volatiles in air streams by solid-phase microextraction. Anal. Chem. 71:92–101.
Bartelt, R. J., Dowd, P. F., Plattner, R. D., and Weisleder, D. 1990a. Aggregation pheromone of dried-fruit beetle, Carpophilus hemipterus: Wind-tunnel bioassay and identification of two novel tetraene hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:1015–1039.
Bartelt, R. J., Dowd, P. F., Shorey, H. H., and Weisleder, D. 1990b. Aggregation pheromone of Carpophilus freemani (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae): A blend of conjugated triene and tetraene hydrocarbons. Chemoecology 1:105–113.
Bartelt, R. J., Dowd, P. F., and Plattner, R. D. 1991. Aggregation pheromone of Carpophilus lugubris: New pest management tools for the nitidulid beetles. ACS Symp. Ser. Am. Chem. Soc. 449:27–40.
Bartelt, R. J., Weisleder, D., Dowd, P. F., and Plattner, R. D. 1992. Male-specific tetraene and triene hydrocarbons of Carpophilus hemipterus: Structure and pheromonal activity. J. Chem. Ecol. 18:379–402.
Bartelt, R. J., Carlson, D. G., Vetter, R. S., and Baker, T. C. 1993a. Male-produced aggregation pheromone of Carpophilus mutilatus (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 19:107–118.
Bartelt, R. J., Seaton, K. L., and Dowd, P. F. 1993b. Aggregation pheromone of Carpophilus antiquus (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) and kairomonal use of C. lugubris pheromone by C. antiquus. J. Chem. Ecol. 19:2203–2216.
Dorsey, C. K., and Leach, J. G. 1956. The bionomics of certain insects associated with oak wilt with particular reference to the Nitidulidae. J. Econ. Entomol. 49:219–230.
Dowd, P. F., Bartelt, R. J., and Wicklow, D. T. 1992. Novel insect trap useful in capturing sap beetles (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae) and other flying insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 85:772–778.
Ephrussi, B., and Beadle, G. W. 1936. A technique of transplantation for Drosophila. Am. Nat. 70:218–225.
Juzwik, J., and French, D. W. 1983. Ceratocystis fagacearum and C. piceae on the surfaces of free-flying and fungus-mat-inhabiting nitidulids. Phytopathology 73:1164–1168.
Williams, R. N., Fickle, D. S., Bartelt, R. J., and Dowd, P. F. 1993. Responses by adult Nitidulidae (Coleoptera) to synthetic aggregation pheromones, a coattractant, and effects of trap design and placement. Eur. J. Entomol. 90:287–294.
Williams, R. N., Ellis, M. S., and Bartelt, R. J. 1995. Efficacy of Carpophilus aggregation pheromones on nine species in northeastern Ohio, and identification of the pheromone of C. brachypterus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 77:141–147.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cossé, A.A., Bartelt, R.J. Male-produced Aggregation Pheromone of Colopterus truncatus: Structure, Electrophysiological, and Behavioral Activity. J Chem Ecol 26, 1735–1748 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005551232335
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005551232335