Abstract
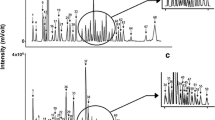
The occurrence of volatile nitrogen-containing compounds in the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae has been studied. Twenty compounds belonging to four groups—amides of carboxylic and fatty acids, heterocyclic compounds and their derivatives, aromatics, and alkoxyamines and amides were identified by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry that used serially coupled capillary columns with different polarity of stationary phases. Distribution of bioactive non-toxic and toxic nitrogen-containing metabolites in cyanobacteria are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bandaranayke, W. M. 1998. Mycosporins: Are they nature's sunscreens? Nat. Prod. Report. 15:159–172.
Banker, R., Carmeli, S., Hadas, O., Teltsch, B., Porat, R., and Sukenik, A. 1997. Identification of cylindrospermopsin in Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Cyanophyceae) isolated from Lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Phycol. 33:613–616.
Bezuglov, V. V., Bobrov, M. Y., and Archakov, A. V. 1998. Bioactive amides of fatty acids. Biochemistry (Moscow) 63:27–37.
Carmichael, W. W. 1986. Algal toxins. Adv. Bot. Res. 12:47–101.
Carmichael, W. W. 1997. The cyanotoxins. Adv. Bot. Res. 27:211–256.
Christoffersen, K. 1996. Ecological implications of cyanobacterial toxins in aquatic food webs. Phycologia 36(Suppl. 6):42–50.
Codd, G. A., and Poon, G. K. 1988. Cyanobacterial toxins, pp. 283–296, in L. J. Rogers and J. R. Gallon (eds.). Biochemistry of the Algae and Cyanobacteria, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Dembitsky, V. M., Shkrob, I., and Dor, I. 1999. Separation and identification of hydrocarbons and other volatile compounds from cultured blue-green alga Nostoc sp. by gas chromatography-mass chromatography using serially coupled capillary columns with consecutive nonpolar and semipolar stationary phases. J. Chromatogr. 682:221–229.
Di Marzo, V. 1998. “Endocannabinoids” and other fatty acid derivatives with cannabimimetic properties: Biochemistry and possible physio-pathological relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1392:153–175.
Falconer, I. R. 1994. Mechanism of toxicity of cyclic peptide toxins from blue-green algae, pp. 177–187, in I. R. Falconer (ed.). Algal Toxins in Seafood and Drinking Water. Academic Press, Cambridge.
Herrmann, V., and JÜttner, F. 1977. Excretion products of algae. Identification of biogenic amines by gas-chromatography and mass spectrometry of their trifluoroacetamides. Anal. Biochem. 78:365–363.
Ikawa, M., Wegener, K., Foxall, T. L., and Sasner, J. J., Jr. 1982. Comparison of the toxins of the blue-green alga Aphanizomenon flos-aquae with the Gonyaulax toxins. Toxicon 20:747–752.
Ikawa, M., Sasner, J. J. Jr., Haney, J. F., and Foxall, T. L. 1995. Pterins of the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Phytochemistry 38:1229–1232.
JÜttner, F., and Wurster, K. 1979. Einfach Anordnung zur Adsorption von Geruchsstoffen aus Algen an Tenax GC und deren Uberfuh rung in Gaschromatographie-System. J. Chromatogr. 175:178–182.
Murata, N., and Nishida, I. 1987. Lipids of blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria), pp. 315–347, in P. K. Stumf (ed.). The Biochemistry of Plants, Vol. 9. Academic Press, New York.
Namikoshi, M., Sivonen, K., Evans, W. R., Sun, F., Carmichael, W. W., and Rinehart, K. L. 1992. Isolation and structures of microcystins from a cyanobacterial water bloom (Finland). Toxicon 30:1473–1479.
Orjala, J., Nagle, D., and Gerwick, W. H. 1995. Malyngamide H, an ichthyotoxic amide possessing a new carbon skeleton from the Caribbean cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 58:764–768.
Paerl, H. W. 1996. A comparison of cyanobacterial bloom dynamics in freshwater, estuarine and marine environments. Phycologia 35(Suppl. 6):25–35.
Patterson, G. M., Larsen, L. K., and Moore, R. E. 1994. Bioactive natural products from bluegreen algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 6:151–157.
Paul, V. J. 1992. Ecological Roles of Marine Products. Comstock Publ., Ithaca, New York.
Pennings, S. C., Weiss, A. M., and Paul, J. J. 1996. Secondary metabolites of the cyanobacterium Microcoleus lyngbyaceus and the sea hare Stylocheilus longicauda: Palatability and toxicity. Mar. Biol. 126:735–743.
Plinski, M., and Codd, G. A. 1997. Cyanobacteria—a factor of animal intoxification: A review. Medyc. Weteryn. 53:8–10.
Sellner, K. G. 1997. Physiology, ecology, and toxic properties of marine cyanobacteria blooms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42:1089–1104.
Shimizu, Y. 1993. Microalgal metabolites. Chem. Rev. 93:1685–1698.
Sivonen, K. 1996. Cyanobacterial toxins and toxin production. Phycologia 35(Suppl 6):12–24.
Slater, G. P., and Block, V. C. 1983. Volatile compounds of the cyanophyceae—a review. Water Sci. Tech. 15:181–190.
Teuscher, E., Lindequist, U., and Mundt, S. 1992. Blue-green algae, sources of natural active agents. Pharm. Ztg. Wiss. 137:57–69.
Thacker, R. W., Nagle, D. G., and Paul, V. J. 1997. Effects of repeated exposures to marine cyanobacterial secondary metabolites on feeding by juvenile rabbitfish and parrotfish. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 147:21–29.
Todd, J. S., and Gerwick, W. H. 1995. Malyngamide I from the tropical marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula and the probable structure revision of stylocheilamide. Tetrahedron Lett. 36:7837–7840.
Tsuchiya, Y., Shudo, K., and Okamoto, T. 1979. Odorous compounds of the blue green algae Oscillatoria sp., and river water. Identification of 2-methyl-isoborneol, geosmin, p-cresol, indole, and 3-methyl-indole. Eisei Kagaki 25:216–220.
Tsuchiya, Y., Matsumoto, A., and Okamoto, T. 1981. Identification of volatile metabolites produced by blue-green algae, Oscillatoria splendida, O. amoena, O. geminata, and Aphanizomenon species. J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. Yakugaku Zasshi 101:852–856.
Underdal, B. 1995. Water pollution-health aspects. Norsk Vet. Tidsskr. 107:377–383.
Weckesser, J., Martin, C., and Jakobi, C. 1996. Cyanopeptolins, depsipeptides from cyanobacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 19:133–138.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dembitsky, V.M., Shkrob, I. & Lev, O. Occurrence of Volatile Nitrogen-containing Compounds in Nitrogen-fixing Cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. J Chem Ecol 26, 1359–1366 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005423406140
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005423406140