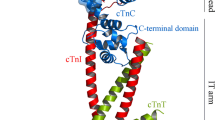
Abstract
Bisphosphorylation of two adjacently located serine residues in the heart-specific N-terminus of the cTnI subunit reduces calcium affinity of the cTnC subunit. An interaction of the phosphorylation region of cTnI with acidic residues of another cTn subunit has been proposed formerly based on 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data. A possible candidate is cTnC. Thus, an interaction model of cTnC with the bisphosphorylated cTnI N-terminus has been built using a homology model of hcTnC based on the crystal structure of tusTnC and the structure of the phosphorylation region of cTnI determined by 2D NMR. By computational search, five clusters of acidic residues on cTnC might interact with the cTnI phosphorylation region. Three sites could be excluded by 31P-NMR experiments. The two remaining sites are located in the N-terminal helix of cTnC and between calcium binding sites III and IV. Reorientation of the arginine and phosphoserine sidechains within the␣phosphorylation region as proposed by refined docking could explain the formerly measured changes in pKa app values. Thus, local pKa changes might lead to the reduction of calcium affinity observed upon cTnI bisphosphorylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AL-HILLAWI, E., BHANDARI, D. G., TRAYER, R. H. & TRAYER, I. P. (1995) The effects of phosphorylation of cardiac troponin I on its interaction with actin and cardiac troponin. Eur. J. Biochem. 228, 962–70.
ARDELT, P., DORKA, D., JAQUET, K., HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR., KÖRTKE, H., KÖRFER, R. & NOTOHAMIPRODJO, G. (1998) Microanalysis and distribution of cardiac troponin I phospho species in heart areas. Biol. Chem. 379, 341–7.
BABU, A., SU, H., RYU, Y. & GULATI, J. (1992) Determination of residue specificity in the EF-hand of troponin C for Ca2+ coordination by genetic engineering. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 15469–74.
BAX, A. & DAVIS, D. G. (1985) MLEV-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 65, 355–60.
BEIER, N., JAQUET, K., SCHNACKERZ, K. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR. (1988) Isolation and characterization of a highly phosphorylated troponin from bovine heart. Eur. J. Biochem. 176, 327–34.
BIDLINGMEYER, B. A., COHEN, S. A. & TARVIN, T. L. (1984) Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J. Chromat. 336, 93–104.
COLLINS, J. H. (1991) Myosin light chains and troponin C: structural and evolutionary relationships revealed by amino acid comparisons. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 12, 3–25.
DAVIS, D. G. & BAX, A. (1985) Assignment of complex 1H spectra via two-dimensional homonuclear Hartmann-Hahn spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 2820–21.
DAYHOFF, M. O., BARKER, W. C. & HUNT, L. T. (1983) Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 91, 524–45.
ENGLAND, P. (1976) Studies on the phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin during modification of contraction in perfused rat heart. Biochem. J. 160, 295–304.
ERNST, R. R., BODENHAUSEN, G. & WOKAUN, A. (1987) Principles of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance in One and Two Dimensions. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
FARAH, C. S. & REINACH, F. C. (1995) The troponin complex and regulation of muscle contraction. FASEB J. 9, 755–67.
FORSEN, S., KORDEL, J., GRUNDSTROM, T. & CHAZIN, W. J. (1993) The molecular anatomy of a calcium binding protein. Acc. Chem. Res. 26, 7–14.
GAHLMANN, R., WADE, R. & GUNNING, P. (1988) Differential expression of slow and fast skeletal muscle troponin C is expressed in human fibroblasts. J. Mol. Biol. 201, 379–91.
GULATI, J., BABU, A. & SU, H. (1992) Functional delineation of the Ca(2+)-deficient EF-hand in cardiac muscle with genetically engineered cardiac-skeletal chimeric troponin C. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 25073–7.
GREASER, M. L. & GERGELY, J. (1971) Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J. Biol. Chem. 246, 4226–33.
HERBERG, F. W., BELL, S. M. & TAYLOR, S. S. (1993) Expression of the catalytic subunit of cAMP dependent protein kinase in Escherichia coli: multiple isoenzymes reflect different phosphorylation states. Protein Eng. 6, 771–7.
HERZBERG, O. & JAMES, M. N. G. (1988) Refined crystal structure of troponin C from turkey skeletal muscle at 2.0 Å resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 203, 761–79.
JAQUET, K., KORTE, K., SCHNACKERZ, K., VYSKA, K. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR. (1993) Characterization of the cardiac troponin I phosphorylation domain by 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 32, 13873–8.
JAQUET, K., THIELECZEK, R. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR. (1995) Pattern formation on cardiac troponin I by consecutive phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Eur. J. Biochem. 231, 468–90.
LAEMMLI, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–85.
MARION, D. & WÜTHRICH, K. (1983) Application of phase sensitive two dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 113, 967–74.
MCKILLOP, D. F. A. & GEEVES M. A. (1991) Regulation of the actomyosin subfragment 1 interaction by troponin/tropomyosin. Evidence for control of a specific isomerization between two actomyosin subfragment 1 states. Biochem. J. 279, 711–18.
MEYER, H. E., HOFFMANN-POSORSKE, E. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR. (1991) Determination and location of phosphoserine in proteins and peptides by conversion to S-ethylcysteine. Meth. Enzymol. 201, 169–85.
MITTMANN, K., JAQUET, K. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR (1990) A common motif of two adjacent phosphoserines in bovine, rabbit and human cardiac troponin. FEBS Lett. 273, 41–5.
MITTMANN, K., JAQUET, K. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR (1992) Ordered phosphorylation of a duplicated minimal recognition motif for cAMP-dependent protein kinase present in cardiac troponin I. FEBS Lett. 302, 133–7.
OLAH, G. A. & TREWHELLA, J. (1994) A model structure of the muscle protein complex 4Ca2+ troponin C. troponin I derived from small-angle scattering data: implications for regulation. Biochemistry 33, 12800–806.
OVASKA, M. & TASKINEN, J. (1991) A model for human cardiac troponin C and for modulation of its Ca2+ affinity by drugs. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Genetics 11, 79–94.
PLATEAU, P. & GUERON, M. (1982) Exchangeable proton-NMR without baseline distortion using new strong-pulse sequences. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104, 7310–11.
POTTER, J. D. (1982) Preparation of troponin and its subunits. Methods Enzymol. 84, 241–63.
QUIRK, P. G., PATCHELL, V. B., GAO, Y., LEVINE, B. A. & PERRY, S. V. (1995) Sequential phosphorylation of adjacent serine residues on the N-terminal region of cardiac troponin I. Structure-activity implications of ordered phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 370, 175–8.
RAREY, M., KRAMER, B., LANGAUER, T. & KLEBE, G. (1996) A fast flexible docking method using an incremental construction algorithm. J. Mol. Biol. 26, 470–89.
REIFFERT, S. U., JAQUET, K., HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR., RITCHIE, M. D. & GEEVES, M. A. (1996) Bisphosphorylation of cardiac troponin I modulates the Ca(2+)-dependent binding of myosin subfragment 1 to reconstituted thin filaments. FEBS Lett. 384, 43–7.
REIFFERT, S. U., JAQUET, K., HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR & HERBERG, F. W. (1998) Stepwise subunit interaction changes by mono and bisphosphorylation of cardiac troponin I. Biochemistry, in press.
ROSENFELD, R., VAJDA, S. & DELISA, C. (1995) Flexible docking and design. Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struc. 24, 677–700.
ROSKOSKI, R., JR. (1983) Assay of protein kinase. Meth. Enzymol. 99, 3–7.
SAMBROOK, J., FRITSCH, E. F. & MANIATIS, T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (2nd edn) Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Laboratory Press.
SIA, S. K., LI, M. X., SPYRACOPOULOS, L., GAGNE, S. M., LIU, W., PUTKEY, J. A. & SYKES, B. D. (1997) Structure of cardiac muscle troponin C unexpectedly reveals a closed regulatory domain J. Biol. Chem. 272, 18216–21.
SMITH, L., GREENFIELD, N. J. & HITCHCOCKDEGREGORI, S. E. (1994) The effects of deletion of the amino-terminal helix on troponin C function and stability. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 9857–63.
STULL, J. T. & BUSS, J. E. (1977) Phosphorylation of cardiac troponin I by cyclic adenosine 3':5' monophosphate dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 252, 851–7.
SWEENEY, H. L., BRITO, R. M. M., ROSEVEAR, P. R. & PUTKEY, J. A. (1990) Myosin light chain phosphorylation in vertebrate striated muscle: regulation and function. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 87, 9538–42.
SWIDEREK, K., JAQUET, K., MEYER, H. E. & HEILMEYER, L. M. G., JR. (1988) Cardiac troponin I, isolated from bovine heart, contains two adjacent phosphoserines. Eur. J. Biochem. 176, 335–42.
VALLINS, W. J., BRAND, N. J., DABHADE, N., BUTLERBROWNE, G., YACOUG, M. H. & BARTON, P. J (1990) Molecular cloning of human cardiac troponin I using polymerase chain reaction. FEBS Lett. 270, 57–61.
VILLAR-PALASI, C. & KUMON, A. (1981) Purification and properties of dog cardiac troponin T kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 7409–15.
WÜTHRICH, K. (1986) Polypeptide secondary structures in proteins by NMR. In NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids, pp. 162–75. Chichester: John Wiley.
XU, G. Q. & HITCHCOCK-DEGREGORI, S. E. H. (1988) Synthesis of a troponin C cDNA and expression of wild-type and mutant proteins in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 13962–7.
ZHANG, R., ZHAO, J. & POTTER, J. D. (1995a) Phosphorylation of both serine residues in cardiac troponin I is required to decrease the Ca2+ affinity of cardiac troponin C. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 30773–80.
ZHANG, R., ZHAO, J., MANDVENO, A. & POTTER, J. D. (1995b) Cardiac troponin I phosphorylation increases the rate of cardiac muscle relaxation. Circ. Res. 76, 1028–35.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaquet, K., Lohmann, K., Holak, T. et al. A model for the function of the bisphosphorylated heart-specific troponin-I N-terminus. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19, 647–659 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005381131102
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005381131102