Abstract
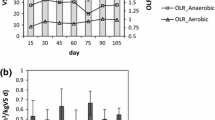
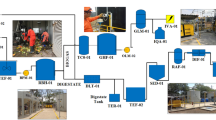
The starch manufacturing industrial units, such as sago mills,both in medium and large scale, suffer from inadequate treatment and disposal problems due to high concentration of suspended solids present in the sludge. A laboratory scale study was conducted to investigate the viability of anaerobic treatment of sago waste sludge, enriched in particulate organicmatter, using a fluidized bed reactor. The start-up of the reactor was carried out using a mixture of digested supernatantsewage sludge and cow dung slurry in different proportions. The effect of operating variables such as COD of the effluent, bed expansion, minimum fluidization velocity on efficiency oftreatment and recovery of biogas was investigated. The maximum efficiency of treatment was found to be 82% and the nitrogen enriched digested sludge was recommended for agricultural use. A kinetic model was developed for the degradation of particulate organic matter using the general kinetic equation [dS/dt = K HC SXC] which allowed for a more accurate mathematical representation of the hydrolysis process. Analysing data from a series of batch tests, the best fit value of C was found to be in the range 0.43 to 0.62.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, S. J., Li, C. T. and Shieh, W. K.: 1988, ‘Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Treatment of an Industrial Wastewater’, J. Water Poll. Contl. Fed. 60, 1826–1832.
Converti, A., Borghi, D. M. and Ferraiolo, G.: 1993, ‘Influence of Organic Loading Rate on the Anaerobic Treatment of High Strength Semisynthetic Wastewater in a Biological Fluidized Bed’, Chem. Eng. J. 52, B21-B28.
Heppner, B., Zellner, G. and Diekmann, H.: 1992, ‘Start-Up Operation of a Propionate-Degrading Fluidized-Bed Reactor’, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 810–816.
Ghosh, S. and Klass, D. L.: 1978, ‘Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion’, Proc. Biochem. 13, 15–24.
Goncalves, R. F., Charlier, A. C. and Sammut, F.: 1994, ‘Primary Fermentation of Soluble and Particulate Organic Metter for Wastewater Treatment’, Wat. Sci. Tech. 30(6), 53–62.
Hawkes, D. L. and Horton, H. R.: 1981, ‘Optimization of Anaerobic Digesters for Maximum Energy Production’, Studies in Env. Sci. 9, 131–142.
Hickey, R. F., Wu, W. M., Veiga, M. C. and Jones, R.: 1991, ‘Start-Up, Operation, Monitoring and Control of High-Rate Anaerobic Treatment Systems’, Water Sci. Technol. 24(8), 207–255.
Hsu, Y. and Shieh, W. K.: 1993, ‘Start-Up of Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Reactors with Acetic Acid as the Substrate’, Biotech. Bioeng. 41, 347–353.
Liang, Y., Yi, Qian, Jicui and Hu: 1993, ‘Research on the Characteristics of Start-Up and Operation of Treating Brewery Wastewater with an AFB Reactor at Ambient Temperatures’, Water Sci. Technol. 28(7), 187–195.
Matsumoto, A. and Noike, T.: 1991, ‘Effects of Substrate Composition and Loading Rate on Methanogenic Process in Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Systems’, Water Sci. Technol. 23, 1311–1317.
Morgan, J. W., Evison, L. M. and Forster, C. F.: 1991, ‘Changes to the Microbial Ecology in Anaerobic Digesters Treating Ice Cream Wastewater During Start-Up’, Water Res. 25(6), 639–653.
Murthy, Y. S. and Patel, M. D.: 1961, ‘Treatment and Disposal of Sago Wastes’, Central Public Health Engineering Research Institute, India, pp. 1–50.
Ozturk, I., Anderson, G. K. and Saw, C. B.: 1989, ‘Anaerobic Fluidized-Bed Treatment of Brewery Wastes and Bioenergy Recovery’, Water Sci. Technol. 21, 1681–1684.
Pescod, M. B. and Thanh, N. C.: 1977, ‘Treatment Alternatives for Wastewaters from the Tapioca Starch Industry’, Progress in Water Technol. 9(3), 563–574.
Pfeffer, J. T.: 1968, ‘Increased Loadings on Digesters with Recycle of Digester Solids’, J. Wat. Pollut. Control Fed. 11, 1920–1933.
Pfeffer, J. T.: 1980, ‘Anaerobic Digestion Processes’, in Stafford, D. A. (ed.), Anaerobic Digestion, Applied Science Publishers, U.K.
Rozzi, A. and Verstraete, W.: 1981, ‘Calculation of Active Biomass and Sludge Production vs Waste Composition in Anaerobic Contact Processes’, Trib. Cebedeau 34, 455, 421–427.
Saroja, K. and Sastry, C. A.: 1972, ‘Report on Treatment of Sago Wastes’, National Environmental Engineering Research Institute, Nagpur, India.
Sastry, C. A. and Mohan Rao, G. J.: 1963, ‘Anaerobic Digestion of Industrial Wastes’, Environmental Health 5(3), 20–25.
Sastry, C. A., Murahari Rao and Saroja, K.: 1964, ‘Studies on the Treatment of Sago Mill Wastewater’, Seminar on Environmental Pollution, Kerala, India.
Shieh, W. K. and Hsu, Y.: 1996, ‘Biomass Loss from an Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Reactor’, Water Res. 30(5), 1253–1257.
Sreekrishnan, T. R., Ramachandran, K. B. and Ghosh, P.: 1991, ‘Effect of Operating Variables on Biofilm Formation and Performance of an Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Reactor’, Biotech. Bioeng. 37, 557–566.
Valentiai, A.: 1995, ‘Degradazione del particolato organico nella fase idrolitice del processo anaerobico: Studio e moxellizzazione’, Tesi di Dottorato, Politecnico di Milano (in Italian).
Valentini, A., Garuti, G. and Rozzi, A.: 1996, Analisi delle cinetiche di degradazione anaerobica del particolato organico e* definizione di un nuovo approccio allo studio', IA Ingegneria Ambientale, XXV, 1/2, 44–52 (in Italian).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saravanane, R., Murthy, D.V.S. & Krishnaiah, K. Anaerobic Fluidized Bed Degradation and the Development of a Kinetic Model for a Particulate Organic Matter Enriched Wastewater Sludge. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 127, 15–30 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005257421504
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005257421504