Abstract
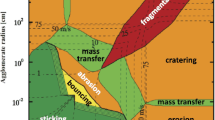
For a better understanding of the processes which lead to the formation of planetesimals in the early solar nebula, we performed an extensive series of laboratory experiments. We find that the capture velocities in collisions between spherical grains are more than one order of magnitude higher than predicted by Chokshi et al (1993). In contrast, irregular grains have no capture threshold and can be better described by a sticking probability which is typically a few 10%, even for velocities exceeding 10 m/s. However, adhesion forces between spherical, micron-sized particles match the theoretical predictions very well, although contact areas and deformations are of the order of inter-atomic distances only. Aggregation experiments in rarefied turbulent gases reveal the fractal nature of dust aggregates. Mass distribution functions are bell-shaped. Similar behaviour can be found in aggregation experiments with sedimenting particles. Experiments on collision-induced aggregate compaction and fragmentation match the numerical simulations by Dominik and Tielens (1997) very well if revised experimental values of the break-up energy (from our impact experiments) and the rolling-friction force (from our AFM measurements on particle chains) are used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum, J., Münch, M.: 1993, 'Experimental Investigations on Aggregate-Aggregate Collisions in the Early Solar Nebula', Icarus 106, 151.
Blum, J., Wurm, G.: 2000, 'Experiments on Sticking, Restructuring and Fragmentation of Preplanetary Dust Aggregates', Icarus in press.
Blum, J., Wurm, G., Kempf, S., Henning, T.: 1996, 'The Brownian Motion of Dust Particles in the Solar Nebula: An Experimental Approach to the Problem of Pre-planetary Dust Aggregation', Icarus 124, 441–451.
Blum, J., Wurm, G., Poppe, T., Heim, L.-O.: 1999, 'Aspects of Laboratory Dust Aggregation with Relevance to the Formation of Planetesimals', in P. Ehrenfreund, K. Krafft, H. Kochan, and V. Pirronello (eds.), Laboratory Astrophysics and Space Research, Astrophysics and Space Science Library, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p. 399.
Chokshi, A., Tielens, A.G.G. M., Hollenbach, D.: 1993, 'Dust Coagulation', Astrophys. J. 407, 806–819.
Derjaguin, B.V., Muller, V. M., Toporov, Y. P.: 1975, 'Effects of Contact Deformations on the Adhesion of Particles', J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 53, 314.
Dominik, C., Tielens, A. G. G. M.: 1995, 'Resistance to Rolling in the Adhesive Contact of Two Spheres', Philosoph. Mag. A 72, 783.
Dominik, C., Tielens, A.G.G. M.: 1997, 'The Physics of Dust Coagulation and the Structure of Dust Aggregates in Space', Astrophys. J. 480, 647–673.
Heim, L., Blum, J., Preuss, M., Butt, H.-J.: 1999, 'Adhesion and Friction Forces Between Spherical Micrometer-Sized Particles', Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 3328–3331.
Johnson, K. L., Kendall, K., Roberts, A.D.: 1971, 'Surface Energy and the Contact of Elastic Solids', Proc. Roy. Soc. London A 324, 301.
Kempf, S., Pfalzner, S., Henning, T.: 1999, 'N-Particle-Simulations of Dust Growth: I. Growth Driven by Brownian Motion', Icarus 141, 388–398.
Kendall, K., Alford, N. M., Birchall, J.D.: 1987, 'A New Method for Measuring the Surface Energy of Solids', Nature 325, 794.
Klahr, H.H., Henning, T.: 1997, 'Particle-Trapping Eddies in Protoplanetary Accretion Disks', Icarus 128, 213–229.
Ossenkopf, V.: 1993, 'Dust Coagulation in Dense Molecular Clouds: The Formation of Fluffy Aggregates', Astron. Astrophys. 280, 617–646.
Poppe, T., Blum, J., Henning, T.: 2000, 'Analogous Experiments on the Stickiness of Micron-Sized Preplanetary Dust', Astrophys. J. accepted.
Weidenschilling, S. J.: 1995, 'Can Gravitation Instability Form Planetesimals?', Icarus 116, 433–435.
Weidenschilling, S. J.: 1997, 'The Origin of Comets in the Solar Nebula: A Unified Model', Icarus 127, 290–306.
Weidenschilling, S. J.: 2000, 'Formation of Planetesimals and Accretion of the Terrestrial Planets', Sp. Sci. Rev., this volume.
Weidenschilling, S. J., Cuzzi, J.N.: 1993, 'Formation of Planetesimals in the Solar Nebula', in Protostars and Planets III, E.H. Levy and J. I. Lunine (eds.), University of Arizona Press, Tucson and London, p. 1031.
Wetherill, G.W., Stewart, G. R.: 1993, 'Formation of Planetary Embryos – Effects of Fragmentation, Low Relative Velocity, and Independent Variation of Eccentricity and Inclination', Icarus 106, 190.
Wurm, G., Blum, J.: 1998, 'Experiments on Preplanetary Dust Aggregation', Icarus 132, 125–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blum, J. Laboratory Experiments on Preplanetary Dust Aggregation. Space Science Reviews 92, 265–278 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005251414391
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005251414391