Abstract
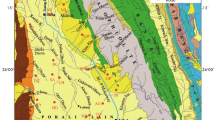
Critical loads of acid deposition havebeen mapped for Chinese soils using a modifiedsemi-quantitative method, which is based on theminerals controlling weathering and soil development,and corrected by introducing an Arrhenius relationshipto describe the effect of temperature and a weightedaveraging approach to evaluate the effect of soiltexture, land use and precipitation. As a consequenceof these modifications, the method has been quantifiedand can be more widely used. Results from this studyshow that the lowest critical loads of acid depositionin China, i.e., those areas most sensitive to aciddeposition, occur in the Podzolic soils in theNortheast, followed by Latosol, Dark brown forest soiland Black soil areas. The Ferralsol areas in SouthChina are intermediate, tolerating about 0.8–1.6 g m-2 yr-1 sulfur deposition. The highestcritical loads of acid deposition are mainly locatedin the Alpine soil areas on the Plateau of Tibet andareas of Xerosol and Podocal soil in Northwest China.The reason for lower critical loads in the Northeastrelative to South China can be attributed to thedifference of temperature, soil moisture and soiltexture. Comparison of critical loads with the sulfurdeposition in 1995 identifies almost one fourth of theland area in southeast China to be subject to risk of acidification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chadwick, M. J. and Kuylenstierna, J. C. I.: 1991, 'Critical Loads and Critical Levels for the Effects of Sulfur and Nitrogen Compounds', in W. James and S. Longhurst (eds.), Acid Deposition: Origins, Impacts and Abatement Strategies, Springer Verlag, New York, 1991, pp. 279–315.
Cosby, B. J., Wright, R. F., Hornberger, G. M. and Galloway, J. N.: 1985, Water Resources Research 21, 51.
De Vries, W.: 1993, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 68, 399.
De Vries, W., Reinds, G. J. and Posch, M.: 1994, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 72, 357.
Hao, J. M., Xie, S. D. and He, K. B.: 1996a, Journal of Environmental Sciences (China) 17(3), 77 (in Chinese).
Hao, J. M., Zhou, X. L., Fu, L. X. and Li, Q. L.: 1996b, China Environmental Science 16(5), 345 (in Chinese).
Hettelingh, J. P., Sverdrup, H., and Zhao, D. W.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 2565.
Kuylenstierna, J. C. I. and Chadwick, M. J.: 1989, 'The Relative Sensitivity of Ecosystems in Europe to the Indirect Effects of Acidic Depositions', in J. Kamari, D. F. Brakke, A. Jenkins, S. A. Norton and R. F. Wight (eds.), Regional Acidification Models, Springer Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Langan, S. J. and Wilson, M. J.: 1994, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 75, 177.
Nilsson, J. and Grennfelt, P. (eds.): 1988, Critical Loads for Sulphur and Nitrogen, Report from a workshop head at Skokloster, Sweden March 1988, published by Nordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen.
Sverdrup, H.: 1990, The Kinetics of Chemical Weathering, Lund University Press.
Sverdrup, H., De Vries, W. and Henriksen, A.: 1990, Mapping Critical Loads: Guidance to the Criteria, Calculations Data Collection and Mapping of Critical Loads, Nordic Council of Ministers Report, 1990, 14.
Sverdrup, H. and de Vries, W.: 1994, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 72, 145.
Sverdrup, H. and Warfvinge, P. G.: 1988, 'Assessment of Critical Load of Acid Deposition on Forest Soil', in J. Nilsson and P. Grennfelt (eds.), Critical Loads for Sulphur and Nitrogen, Report from a workshop head at Skokloster, Sweden March 1988, published by Nordic Council of Ministers, Copenhagen.
Sverdrup, H. and Warfvinge, P. G.: 1993, Soil Acidification Effect on Growth of Trees, Grasses and Herbs, Expressed by the (Ca+Mg+K)/Al Ratio, Technical report of Chemical Engineering II, Lund University.
Warfvinge, P. and Sverdrup, H.: 1992, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 63, 119.
Xie, S. D., Hao, J. M., Zhou, Z. P., Qi, L. and Yin, H. H.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 2401.
Xiong, Y. and Li, Q. K.: 1987, Chinese Soils, the 2nd ed., Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Zhao, D. W., Zhang, X. S., Yang, J. X., Mao, J. T. and Xiong, J. L.: 1995, Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 7(3), 325 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, L., Xie, S., Zhou, Z. et al. Critical Loads of Acid Deposition on Soil in China. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 118, 35–51 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005197414074
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005197414074