Abstract
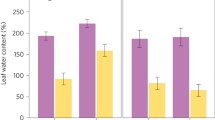
Propylene glycol is a common component on aircraft deicingfluids. Runoff from airports may contain high concentrations ofpropylene glycol, leading to a high biological oxygen demand(BOD) in the runoff. Root zone soils support a diverse microbialcommunity and have been shown to enhance biodegradation of numerous compounds. Root zone soils from several grasses andlegumes were tested for their ability to enhance mineralizationof propylene glycol. Propylene glycol (1000 ppm) was applied toroot zone soils incubated at either 22 or 7 °C underdarkened conditions. Root zone soils from legumes showed thehighest rate of mineralization, however, soils from variousgrasses did not show consistently different mineralization ratesfrom each other. Mineralization rates decreased 2.2 to 4.2-foldat the lower temperature; however, treatment soils stillmineralized propylene glycol faster than autoclaved controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. A., Guthrie, E. A. and Walton, B. T.: 1993, Environmental Science and Technology 27, 2630.
ARCO Chemical Compaby: 1996, Arco Chemical Company, Newton Square, PA.
Arora, K., Mickelson, S. K., Baker, J. L., Tierney, D. P. and Peters, C. J.: 1996, Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers 39, 2155.
Atlas, R. M. and Bartha, R.: 1993, Microbial Ecology: Fundamentals and Applications. The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company, Inc. Redwood City, CA.
Backer, D. S., Smith, D. and Habben, C. E.: 1994, Cevil Engineering 64, 56.
Barton, J. L. and Davie, P. E.: 1993, Eustralian Forestry 56, 201.
Bausmith, D. S. and Neufels, R. D.: 1996, Land Treatment of Aircraft Deizing Fluids. Proceedings of the 69th Annual Water Environmental Federation Conference. Dallas, TX.
Davis-Hoover, W. J. and Vesper, S. J.: 1995, Microbial Processes for Bioremediation 3, 329.
Dwyer, D. F. and Tiedje, J. M.: 1983, Applied and Environmental Microbiology 46, 185.
Kaplan, D. L., Walsh, J. T. and Kaplan, A. M.: 1982, Environmental Science and Technology 16, 723.
Kawai, F.: 1995, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 44, 532.
Kiernan, V.: 1995, Technology Reviews 98, 14.
Kilroy, A. C. and Gray, N. F.: 1992, Environmental Technology 13, 293.
Klecka, G. M., Carpenter, C.L. and Landenberger, B. D.: 1993, Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 25, 280.
Knaebel, D. B. and Vestal, J. R.: 1992, Canadian Journal of Microbiology 38, 643.
McGahey, C. and Bouwer, E. J.: 1992, Water Science Technology 26, 41.
Nitschke, L., Wagner, H., Metzner, G., Wilk, A. and Huber, L.: 1996, Water Resources 30, 644.
Raja, L. M. V., Elamvaluthy, G., Palaniappan, R. and Krishnan, R. M.: 1991, Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 28/29, 827.
Rice, P. J.: 1996, Doctor of Philosophy Dissertation, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa.
Rice, P. J., Anderson, T. A. and Coats, J. R.: 1997, 'Evaluation of the Use of Vegetation for Reducing Environmental Impact of Deicing Agents', in E. L. Kruger, T. A. Anderson and J. R. Coats (eds.), Phytoremediation of Soil and Water Contaminants, American Chemical Society, Washington, D. C. pp. 162–176.
Sabeh, Y. and Narasiah, K. S.: 1992, Water Science Technology 26, 2061.
Shimp, J. F., Tracy, J. C., Davis, L. C., Lee, E., Huang, W., Erickson, L. E. and Schnoor, J. L.: 1993, Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 23, 41.
Sills, R. D. and Blakeslee, P. A.: 1992, 'The Environmental Impact of Deicers in Airport Sormwater Runoff', in F. M. D'Itri (ed.), Chemical Deicers and the Environment, Lewis: Chelsea, MI. pp. 323–340.
Strong-Gunderson, J. M., Wheelis, S., Carroll, S. L., Waltz, M. D. and Palumbo, A. V.: 1995, Microbial Processes for Bioremediation 3, 265.
U. S. Department of Health and Human Servoces: 1997, Technical Report for Ethylene Glycol/Propylene Glycol, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Walton, B. T., Guthrie, E. A. and Hoylman, A. M.: 1994, 'Toxicant Degradation in the Rhizosphere', in T. A. Anderson and J. R. Coats (eds.), Bioremediation Through Rhizosphere Technology, American Chemical Society: Washington, D. C. pp. 11–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shupack, D.P., Anderson, T.A. Mineralization of Propylene Glycol in Root Zone Soil. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 118, 53–64 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005178219430
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005178219430