Abstract
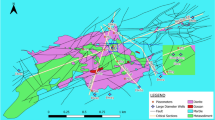
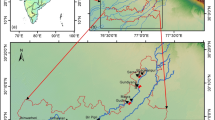
The physico-chemical characteristics of the groundwater of the Temara aquifer were studied by means of piezometric mapping and determination of the ionic composition of the groundwater. In general, the agricultural activity is intense in the area, with water being pumped from numerous wells. Two aquifer formations can be distinguished which, over a wide area, are separated by layers of low permeability. The increased salinity at some points of the coastal zone is probably linked to the combined action of the washing out of Miocene marls, dissolution of carbonate rocks, agricultural pollution and seawater intrusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo, C. A. J and Postma, D.: 1993, Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution, Ed. Balkema, Rotterdam. 536 p.
Arikan, A.: 1988, Ground Water, 26 (2), 222-227.
Custodio, E.: 1983, Hidrogeoquímica. In: Custodio, E. and Llamas, M.R. (Ed), Hidrología Subterránea. Section 10. Omega, Barcelona.
Custodio, E.: 1987, Ground Water problems in coastal areas. In: Studies and Reports in Hydrology (UNESCO).
Gimenez, E.: 1994, Caracterización hidroquímica de los procesos de salinización en el acuífero detrítico costero de la plana de Castellón (España).PhD Thesis, University of Granada, 486 p.
Morell, I., Pulido-Bosch, A. and Fernández Rubio, R.: 1986, 9th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, 61–72, Delft.
Piqué, A.: 1979, Evolution structurale d'un segment de la chaîne hercynienne de la méséta Marocaine Nord-Occidentale. PhD Thesis, University Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, 253 p.
Plummer, L. N., Jones, B. F. and Truesdell, A.H.: 1976, WateqF: A fortran IV version of Wateq. A computer program for calculating chemical equilibrium of natural waters. U.S Geological Survey Water Ressources Investigations Report, 76-31: 61 p.
Pulido-Bosch, A., Morell, I. and Andreu, J. M.: 1995, Environ. Geology 26: 232–239.
Tahiri, A. and Pulido-Bosch, A.: 1995, Boletin Geologico y Minero 106, 429–436.
Truesdell, A. H. and Jones, B. F.: 1974, Wateq: A computer program for calculating chemical equilibrium of natural waters.U.S Geological Survey J. Research 2: 61 p.
Tulipano, L. and Fidelibus, M. D.: 1991, Quaderni del Dipartamento di Geografiano 13. Universitá di Padova, 338–398.
Turekian, K. K.: 1978, Strontium. In: Wedephol. K.H. (Ed), Handbook of Geochemistry. Chap. 38. Springer-Verlag Berlin-Heidelberg.
Wernli, R.: 1977, Ecologae Geol. Helv. 70/1, 143–191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pulido-Bosch, A., Tahiri, A. & Vallejos, A. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Processes in the Temara Aquifer in Northwestern Morocco. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 114, 323–337 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005167223071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005167223071