Abstract
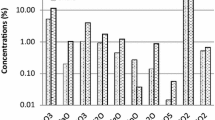
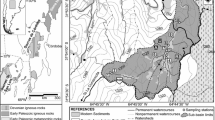
Investigations on springwater acidity were carried out in the Vosges mountains (north-eastern France). Acid or poorly buffered spring and streamwaters were detected in the same area. The proportion of acid springwaters (pH < 5.6) is about 20% among 220 springs. The springwater pH on granite are equally spread between 5.0 and 6.8 whereas on sandstone a majority of springs is in the range 5.6 to 6.2. As a whole, but mainly on sandstone, from the 1960's to 1990's, the shape of the pH distributions shifts toward greater acidity. In the sandstone area, trends in pH, alkalinity, total hardness (corresponding to divalent cations), sulfate and nitrate were considered over the 30 yr period (1963-1996) in relation to the bedrock chemical composition. Kendall seasonal tau coefficients indicate that decreasing trends were significant for the first three parameters. Linear regression on the smoothed mean value revealed 18 and 90% decrease for pH and alkalinity respectively, for springwaters draining poor-base cation sandstone whereas only 8 and 30% decrease respectively, was observed on clay-enriched sandstone. On silica-enriched sandstone, alkalinity began to decrease in the early 70's as well as pH. Loss of alkalinity only occurred in the early 80's for springs draining clay enriched sandstone. This can be interpreted as a titration process by acid atmospheric inputs of the buffering capacity of weathering and exchange processes in the soils and the catchment bedrock. The nitrate presents an increasing step in the early seventies but possibly as a result of change in analytical technics and/or increase in atmospheric inputs mainly resulting from increase in fertiliser inputs in agricultural areas or in car traffic. Surprisingly no change in sulfate was noticed in any groups of springs probably as a result of the adsorption/mobilisation in the soils. These long-term trends in spring waters (1963-1996) confirmed the soil and streamwater acidification trends already mentioned in this region, in relation to acid atmospheric inputs since no climate nor forestry practice changes have been detected over the period. Moreover, in spite of acid atmospheric input reductions, no recovery can presently be detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battarbee, R. W., Allott, T. E. H., Kreiser, A. M. and Juggins, S.: 1993, in Hornung M. and Skeffington R. A. <nt>(eds.)</nt>, Critical loads: Concepts and Applications, ITE Symposium mo 28, HMSO, London, pp. 99–192.
Brömsen (von), U.: 1985, Acidification trends in Swedish groundwaters. Review of the Time Series 1950–85, National Swedish Environmental protection Board. Report 3547, 1–67.
Canh, D. Q.: 1991, A l'occasion du trentième anniversaire du CITEPA, bilan de trente ans de lutte contre la pollution atmosphérique. Etudes documentaires du CITEPA, 100, 19 pp.
Dambrine, E., Ulrich, E., Cenac, P., Durand, P., Gauquelin, T., Mirabel, P., Nys, C., Probst, A., Ranger, J. and Zephoris, M.: 1995, in Landmann G. and Bonneau M. <nt>(eds.)</nt>, Forest Decline and Atmospheric Deposition Effects in the French Mountains, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 461 pp. 177–199.
Driscoll, C. T., P ostek, K. M., Kretser, W. and Raynal, D. J.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 583.
Henriksen, A., Lien, L., Traaen, T. S., Sevaldrud, I. S. and Brakke, D. F.: 1988, Ambio 17, 259.
Etchanchu, D. and Probst, J. L.: 1988, Hydrological Sciences Journal 33(3), 243.
Falkengren-Grerup, U., Linnermark, N. and Tyler, G.: 1987, Chemosphere 16, 2239.
Hirsch, R. M. Slack, J. R. and Smith, R. A.: 1982, Water Resources Research 18(1), 107.
Hirsch, R. M. and Slack, J. R.: 1984, Water Resources Research 20(6), 727.
Jeffries, D. S., Clair, T. A., Dillon, P. J., Painneau, M. and Stainton, M. P.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 577.
Knutson, G., Bergström, S., Danielsson, L.-G., Jacks, G., Lundin, I., Maxe, L., Snadén, P., Sverdrup, H. and Warfvinge, P.: 1995, Ecological Bulletins 44, 271.
Kreiser, A., Rose, N. L., Probst, A. and Massabuau, J. C.: 1995, in Landmann G. and Bonneau M. <nt>(eds.)</nt>, Forest Decline and Atmospheric Deposition Effects in the French Mountains, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 461 pp. 363–369.
Landmann, G. and Bonneau, M.: 1995, Forest Decline and Atmospheric deposition Effects in the French Mountains, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 461 p.
Lång, L. O. and Swedberg, S.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 1837.
Massabuau, J. C., Fritz, B. and Burtin, B.: 1987, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 305, 121.
Maxe, L., Jacks, G., Knutsson, G. and Lundin, L.: 1995, Effects of Acidification on Groundwater in Sweden. Hydrological and Hydrochemical Processes, Swedish Environmental protection Agency, Report 4388, pp. 1–166.
Millot, G., Cogne, J., Jeannette, D., Besnus, Y., Bonnet, B., Guri, F. and Scimpf, A.: 1967, Bull. Serv. Carte Geol. Als. et de Lorr. 20, 131.
Party, J. P., Probst, A., Dambrine, E. and Thomas, A. L.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 2407.
Party, J. P., Probst, A., Février, C., Dambrine, E., King, D. and Thomas, A. L.: 1997, Critical Loads in France. Data and References, ADEME Publication, 1997, 44 p.
Perriaux, J.: 1961, Bull. Serv. Carte Geol. Als. et de Lorr. 18, 15.
Peters, N. E. and Driscoll, C. T.: 1987, Biogeochemistry 3, 163.
Probst, A., Probst, J. L., Massabuau, J. C. and Fritz, B.: 1995, in Landmann G. and Bonneau M. <nt>(eds.)</nt>, Forest Decline and Atmospheric Deposition Effects in the French Mountains, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 461. pp. 371–386.
Probst, A., Massabuau, J. C., Probst, J. L. and Fritz, B.: 1990, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 31, 405.
Probst, A., Viville, D., Fritz, B., Ambroise, B. and Dambrine, E.: 1992, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 62, 337.
Skjelkvåle, B. L. and Henriksen, A.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85, 629.
Sverdrup, H., Warfvinge, P., Blake, L. and Goulding, K.: 1995, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 53, 161.
Swedberg, S.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut 85, 1843.
Tamm, C. O. and Hallbäcken, L.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 31, 337.
Tamm, C. O. and Hallbäcken, I.: 1988, Ambio 17(1), 56.
Thimonier, A., Dupouey, J. L. and Timbal, J.: 1992, For. Ecol. Manage. 55, 149.
Thomas, A. L., King, D., Dambrine, E., Party, J. P. and Probst, A.: 1997, Modelling Streamwater Acidity Using GIS, Biogeomon 97, J. of Conference Abstracts 2, (2), 311.
Ulrich, E. and Williot, B.: 1993, Les dépôts atmosphériques en France, ONF-ADEME, Paris, 154 p.
Wright, R. F., Cosby, B. J., Ferrier, R. C., Jenkins, A., Bulger, A. J. and Harriman, R.: 1994, Journal of Hydrology, 161, 257.
Wright, R.: 1977, Historical Changes in the pH of 128 Lakes in Norway and 130 Lakes in Southern Sweden over the period 1923–1976, Tech. Rep. SNSF, NLH, Oslo-As, Norway. TN 34/77.
Zulla, Y. and Billett, M. F.: 1994, European Journal of Soil Science 45, 327.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Probst, A., Party, J.P., Fevrier, C. et al. Evidence of Springwater Acidification in the Vosges Mountains (North-East of France): Influence of Bedrock Buffering Capacity. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 114, 395–411 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005156615921
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005156615921